|
Crookham, Berkshire
Crookham is a dispersed hamlet in the English county of Berkshire, and part of the civil parish of Thatcham. Geography The settlement lies near the A339 and A4 roads, and is located approximately south-east of Thatcham (where, according to the grid reference, the majority of the 2011 census population was included). Crookham - like the adjoining Crookham Common - is situated at the end of the former runway of RAF Greenham Common. History Immediately before 1066, Crookham was owned by Alwi Ceuresbert, a King's thane. Crookham appears in the Domesday Book under Thatcham Hundred. It was later, about 1125, granted to Reading Abbey. There was only one manor and this was sublet to various families, some of whom hosted Royal visits, including that of Henry III who visited the hamlet in 1229, most probably to engage in hunting in the rural areas. By 1299, Crookham Manor House had a chapel attached to it. On 29 and 30 August 1320, Edward II stayed there. In 1445 the sub-manor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (place)
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. The word and concept of a hamlet has roots in the Anglo-Norman settlement of England, where the old French ' came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic) Franconian languages. Compare with modern French ', Dutch ', Frisian ', German ', Old English ' and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the qala ( Dari: قلعه, Pashto: کلي) meaning "fort" or "hamlet". The Afghan ''qala'' is a fortified group of houses, generally with its own co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, Curonia, the Ukrainian state of the Cossack Hetmanate and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''hérað'' (Icelandic), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), '' satakunta'' or ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), ''kihelkond'' (Estonian), ''kiligunda'' (Livonian), ''cantref'' (Welsh) and ''sotnia'' (Slavic). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnstaple (UK Parliament Constituency)
Barnstaple was a constituency centred on the town of Barnstaple in Devon, in the South West of England. It returned two Members of Parliament to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom until 1885, thereafter, one. It was created in 1295 and abolished for the 1950 general election. Most of the area and the town falls into the North Devon seat. Boundaries 1885–1918: The Municipal Boroughs of Barnstaple and Bideford, and the Sessional Divisions of Bideford and Braunton. 1918–1950: The Municipal Boroughs of Barnstaple and Bideford, the Urban Districts of Ilfracombe, Lynton, and Northam, and the Rural Districts of Barnstaple and Bideford (including Lundy Island). Members of Parliament 1295–1885 1885–1950 Election results Elections in the 1830s Elections in the 1840s Elections in the 1850s The election was declared void on petition, due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Amyand
Sir George Amyand, 1st Baronet (26 September 1720 – 16 August 1766) was a British Whig politician, physician and merchant. Origins He was the second son of Claudius Amyand, Surgeon-in-Ordinary to King George II, by his wife Mary Rabache, and was baptised at the fashionable St James's Church, Piccadilly. Claudius's father was a Huguenot who had quitted France following the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. Career Amyand was an assistant to the Russia Company in March 1756, an army contractor during the Seven Years' War, who collaborated with Nicholas Magens and Henry Fox, 1st Baron Holland. He was a director of the East India Company in 1760 and 1763. In that year, he bought the manor of Frilsham, Berkshire from Willoughby Bertie, 4th Earl of Abingdon. Between 1754 and 1766, Amyand sat as Member of Parliament (MP) for Barnstaple, in North Devon. He lived nearby at Great George Street. On 9 August 1764, he was created a baronet, of Moccas Court, in the County of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Fuller
Nicholas Fuller (c. 1557 – 1626) was an English Hebraist and philologist. Life The son of Robert Fuller by his wife Catharine Cresset, he was a native of Hampshire, and was born about 1557. He was sent to schools at Southampton, kept by John Horlock and Adrian Saravia. He entered, in the capacity of secretary, the household of Robert Horne, bishop of Winchester; and on his death through the influence of William Barlow who was Horne's brother-in-law, continued as secretary to John Watson. On Watson's death in 1584, he determined to live a scholar's life. His means were insufficient for his purpose, but he obtained an appointment as tutor to William and Oliver Wallop, sons of Henry Wallop, and, accompanying them to Oxford, instructed them by day, while he pursued his own studies at night. He was a member of Hart Hall, Oxford and graduated B.A. 30 January 1586, and M.A. 30 March 1590. He found a friend in Robert Abbot, took orders, and was presented to the ill-paid livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne Of Denmark
Anne of Denmark (; 12 December 1574 – 2 March 1619) was the wife of King James VI and I; as such, she was Queen of Scotland from their marriage on 20 August 1589 and Queen of England and Ireland from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until her death in 1619. The second daughter of King Frederick II of Denmark and Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, Anne married James at age 14. They had three children who survived infancy: Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, who predeceased his parents; Princess Elizabeth, who became Queen of Bohemia; and James's future successor, Charles I. Anne demonstrated an independent streak and a willingness to use factional Scottish politics in her conflicts with James over the custody of Prince Henry and his treatment of her friend Beatrix Ruthven. Anne appears to have loved James at first, but the couple gradually drifted and eventually lived apart, though mutual respect and a degree of affection survived. In En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
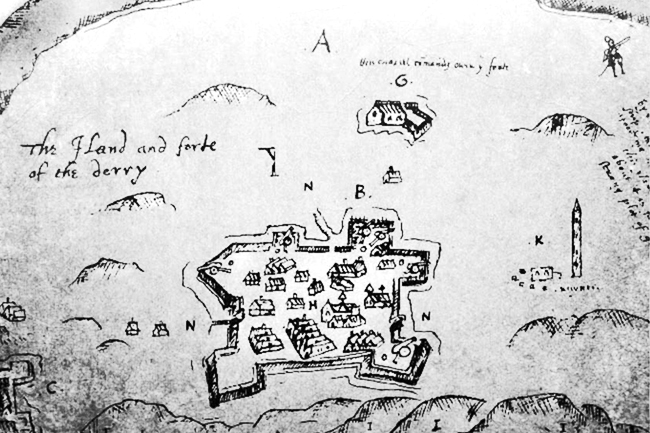
Henry Docwra, 1st Baron Docwra Of Culmore
Henry Docwra, 1st Baron Docwra of Culmore (1564 – 18 April 1631) was a leading English-born soldier and statesman in early seventeenth-century Ireland. He is often called "the founder of Derry", due to his role in establishing the city. Background He was born at Chamberhouse Castle, Crookham, near Thatcham, Berkshire, into a minor gentry family, the Docwras (there are several variant spellings of the name, including Dockwra and Dowkra), who came originally from Yorkshire.McGurk, John ''Sir Henry Docwra 1564–1631 – Derry's Second Founder'' Four Courts Press Dublin 2007, pp.18-26 He was (as far as is known) the only surviving son of Edmund Docwra MP and his wife Dorothy Golding, daughter of John Golding of Halstead, Essex, and sister of the noted translator Arthur Golding. His father was a prominent local politician, who sat in the House of Commons as MP for Aylesbury in the Parliament of 1571, and for New Windsor in that of 1572. He was later obliged by financial diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to the throne following the death of his elder brother Alphonso. Beginning in 1300, Edward accompanied his father on invasions of Scotland. In 1306, he was knighted in a grand ceremony at Westminster Abbey. Following his father's death, Edward succeeded to the throne in 1307. He married Isabella, the daughter of the powerful King Philip IV of France, in 1308, as part of a long-running effort to resolve tensions between the English and French crowns. Edward had a close and controversial relationship with Piers Gaveston, who had joined his household in 1300. The precise nature of their relationship is uncertain; they may have been friends, lovers, or sworn brothers. Edward's relationship with Gaveston inspired Christopher Marlowe's 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist denominations for their places of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III Of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of King John and Isabella of Angoulême, Henry assumed the throne when he was only nine in the middle of the First Barons' War. Cardinal Guala Bicchieri declared the war against the rebel barons to be a religious crusade and Henry's forces, led by William Marshal, defeated the rebels at the battles of Lincoln and Sandwich in 1217. Henry promised to abide by the Great Charter of 1225, a later version of the 1215 '' Magna Carta'', which limited royal power and protected the rights of the major barons. His early rule was dominated first by Hubert de Burgh and then Peter des Roches, who re-established royal authority after the war. In 1230, the King attempted to reconquer the provinces of France that had once belonged to his father, but the invasion was a debacle. A revolt led by William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate (land)
An estate is a large parcel of land under single ownership, which would historically generate income for its owner. British context In the UK, historically an estate comprises the houses, outbuildings, supporting farmland, and woods that surround the gardens and grounds of a very large property, such as a country house, mansion, palace or castle. It is the modern term for a manor, but lacks a manor's now-abolished jurisdiction. The "estate" formed an economic system where the profits from its produce and rents (of housing or agricultural land) sustained the main household, formerly known as the manor house. Thus, "the estate" may refer to all other cottages and villages in the same ownership as the mansion itself, covering more than one former manor. Examples of such great estates are Woburn Abbey in Bedfordshire, England, and Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England, built to replace the former manor house of Woodstock. In a more urban context are the "Great Estates" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Abbey
Reading Abbey is a large, ruined abbey in the centre of the town of Reading, in the English county of Berkshire. It was founded by Henry I in 1121 "for the salvation of my soul, and the souls of King William, my father, and of King William, my brother, and Queen Maud, my wife, and all my ancestors and successors." In its heyday the abbey was one of Europe's largest royal monasteries. The traditions of the Abbey are continued today by the neighbouring St James's Church, which is partly built using stones of the Abbey ruins. Reading Abbey was the focus of a major £3 million project called "Reading Abbey Revealed" which conserved the ruins and Abbey Gateway and resulted in them being re-opened to the public on 16 June 2018. Alongside the conservation, new interpretation of the Reading Abbey Quarter was installed, including a new gallery at Reading Museum, and an extensive activity programme. Abbey Ward of Reading Borough Council takes its name from Reading Abbey, which li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)