|
Craigellachie Bridge
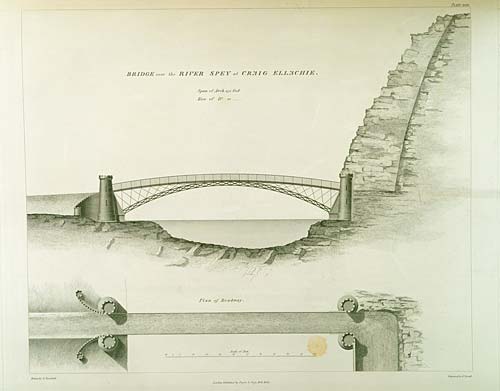
Craigellachie Bridge is a cast iron arch bridge across the River Spey at Craigellachie, near to the village of Aberlour in Moray, Scotland. It was designed by the renowned civil engineer Thomas Telford and built from 1812 to 1814. It is a Category A listed structure. Construction The bridge has a single span of approximately and was revolutionary for its time, in that it used an extremely slender arch which was not possible using traditional masonry construction. The ironwork was cast at the Plas Kynaston iron foundry at Cefn Mawr, near Ruabon in Denbighshire by William Hazledine, who cast a number of Telford bridges. The ironwork was transported from the foundry through the Ellesmere Canal and Pontcysyllte Aqueduct then by sea to Speymouth, where it was loaded onto wagons and taken to the site. Testing in the 1960s revealed that the cast-iron had an unusually high tensile strength. This was probably specified by Telford because, unlike in traditional masonry arch bridges, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossiemouth
Lossiemouth ( gd, Inbhir Losaidh) is a town in Moray, Scotland. Originally the port belonging to Elgin, it became an important fishing town. Although there has been over 1,000 years of settlement in the area, the present day town was formed over the past 250 years and consists of four separate communities that eventually merged into one. From 1890 to 1975, it was a police burgh as Lossiemouth and Branderburgh. Stotfield, the first significant settlement (discounting Kinneddar which has now disappeared), lies to the north west of the town. Next was the Seatown – a small area between the river and the canal inholding of 52 houses, 51 of which are the historic fisher cottages. When the new harbour was built on the River Lossie, the 18th-century planned town of Lossiemouth, built on a grid system, was established on the low ground below the Coulard Hill. Branderburgh formed the final development during the 19th century. This part of the town developed entirely as a result of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moray
Moray () gd, Moireibh or ') is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland. It lies in the north-east of the country, with a coastline on the Moray Firth, and borders the council areas of Aberdeenshire and Highland (council area), Highland. Between 1975 and 1996 Moray, with similar boundaries, was a districts of Scotland, district of the then Grampian Region. History The name, first attested around 970 as ', and in Latinised form by 1124 as ', derives from the earlier Celtic forms *''mori'' 'sea' and *''treb'' 'settlement' (c.f. Welsh language, Welsh ''môr-tref''). During the Middle Ages, the Province of Moray was much larger than the modern council area, also covering much of what is now Highland (council area), Highland and Aberdeenshire. During this period Moray may for a time have been either an independent kingdom or a highly autonomous vassal of Kingdom of Alba, Alba. In the early 12th century, Moray was defeated by David I of Scotland following a conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow Slit
An arrowslit (often also referred to as an arrow loop, loophole or loop hole, and sometimes a balistraria) is a narrow vertical aperture in a fortification through which an archer can launch arrows or a crossbowman can launch bolts. The interior walls behind an arrow loop are often cut away at an oblique angle so that the archer has a wide field of view and field of fire. Arrow slits come in a variety of forms. A common one is the cross, accommodating the use of both the longbow and the crossbow. The narrow vertical aperture permits the archer large degrees of freedom to vary the elevation and direction of their bowshot, but makes it difficult for attackers to harm the archer since there is only a small target at which to aim. Balistraria, plural balistrariae, from balister, crossbowman can often be found in the curtain walls of medieval battlements beneath the crenellations. History The invention of the arrowslit is attributed to Archimedes during the siege of Syracuse in 21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression (physical)
In mechanics, compression is the application of balanced inward ("pushing") forces to different points on a material or structure, that is, forces with no net sum or torque directed so as to reduce its size in one or more directions.Ferdinand Pierre Beer, Elwood Russell Johnston, John T. DeWolf (1992), "Mechanics of Materials". (Book) McGraw-Hill Professional, It is contrasted with tension or traction, the application of balanced outward ("pulling") forces; and with shearing forces, directed so as to displace layers of the material parallel to each other. The compressive strength of materials and structures is an important engineering consideration. In uniaxial compression, the forces are directed along one direction only, so that they act towards decreasing the object's length along that direction. The compressive forces may also be applied in multiple directions; for example inwards along the edges of a plate or all over the side surface of a cylinder, so as to reduce its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontcysyllte Aqueduct
The Pontcysyllte Aqueduct (; cy, Traphont Ddŵr Pontcysyllte) is a navigable aqueduct that carries the Llangollen Canal across the River Dee in the Vale of Llangollen in northeast Wales. The 18-arched stone and cast iron structure is for use by narrowboats and was completed in 1805 having taken ten years to design and build. It is 12 ft (3.7 metres) wide and is the longest aqueduct in Great Britain and the highest canal aqueduct in the world. A footpath runs alongside the watercourse on one side. The aqueduct was to have been a key part of the central section of the proposed Ellesmere Canal, an industrial waterway that would have created a commercial link between the River Severn at Shrewsbury and the Port of Liverpool on the River Mersey. Although a less expensive construction course was surveyed further to the east, the westerly high-ground route across the Vale of Llangollen was preferred because it would have taken the canal through the mineral-rich coalfields of Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellesmere Canal
The Ellesmere Canal was a waterway in England and Wales that was planned to carry boat traffic between the rivers Mersey and Severn. The proposal would create a link between the Port of Liverpool and the mineral industries in north east Wales and the manufacturing centres in the West Midlands. However, the canal was never completed as intended because of its rising costs and failure to generate the expected commercial traffic. The Ellesmere Canal, which was first proposed in 1791, would have created a waterway between Netherpool, Cheshire, and Shrewsbury. However, only certain sections were completed; these were eventually incorporated into the Chester Canal, Montgomery Canal and Shropshire Union Canal. Although several major civil engineering feats were accomplished, major building work ceased following the completion of the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct in 1805. The northern end of the navigation's mainline ended from Chester at Trevor Basin near Ruabon and its southern end wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denbighshire (historic)
, HQ= Denbigh and Ruthin , Arms= , Map= , Code= DEN , CodeName= Chapman code , Government= Denbighshire County Council (1889-1974) , PopulationFirst= 83,629Vision of Britain 1831 Census/ref> , PopulationFirstYear= 1831 , AreaFirst= , AreaFirstYear= 1831 , DensityFirst= 0.2/acre , DensityFirstYear= 1831 , PopulationSecond= 144,783Vision of Britain Denbighshire population an density , PopulationSecondYear= 1911 , AreaSecond= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruabon
Ruabon ( cy, Rhiwabon ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. The name comes from ''Rhiw Fabon'', ''rhiw'' being the Welsh word for "slope" or "hillside" and ''Fabon'' being a mutation from St Mabon, the original church name, of earlier, Celtic origin. An older English spelling, ''Rhuabon'', can sometimes be seen. In 2001, more than 80% of the population of 2,400 were born in Wales, with 13.6% having some ability in Welsh. Early history There is evidence that a settlement existed in Ruabon in the Bronze Age. In 1898, building works in the centre of Ruabon exposed a cist or stone urn containing cremated human remains dating from 2000 years BC. In 1917, the remains of a Bronze Age round barrow were discovered on the playing fields of Ruabon Grammar School; they contained human remains, a flint arrowhead and a bronze axe. Overlooking Ruabon, the Gardden ( cy, Caer Ddin) is an ancient hillfort surrounded by circular ditches, dating back to the Iron Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building stone such as marble, granite, and limestone, cast stone, concrete blocks, glass blocks, and adobe. Masonry is generally a highly durable form of construction. However, the materials used, the quality of the mortar and workmanship, and the pattern in which the units are assembled can substantially affect the durability of the overall masonry construction. A person who constructs masonry is called a mason or bricklayer. These are both classified as construction trades. Applications Masonry is commonly used for walls and buildings. Brick and concrete block are the most common types of masonry in use in industrialized nations and may be either load-bearing or non-load-bearing. Concrete blocks, especially those with hollow cores, offer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Span (architecture)
Span is the distance between two intermediate supports for a structure, e.g. a beam or a bridge. A span can be closed by a solid beam or by a rope. The first kind is used for bridges, the second one for power lines, overhead telecommunication lines, some type of antennas or for aerial tramways. The span is a significant factor in finding the strength and size of a beam as it determines the maximum bending moment and deflection. The maximum bending moment M_ and deflection \delta_in the pictured beam is found using: :M_ = \frac :\delta_ = \frac = \frac where :q = Uniformly distributed load :L = Length of the beam between two supports (span) :E = Modulus of elasticity :I = Area moment of inertia The second moment of area, or second area moment, or quadratic moment of area and also known as the area moment of inertia, is a geometrical property of an area which reflects how its points are distributed with regard to an arbitrary axis. The ... Note that the maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




