|
Cowley, Devon
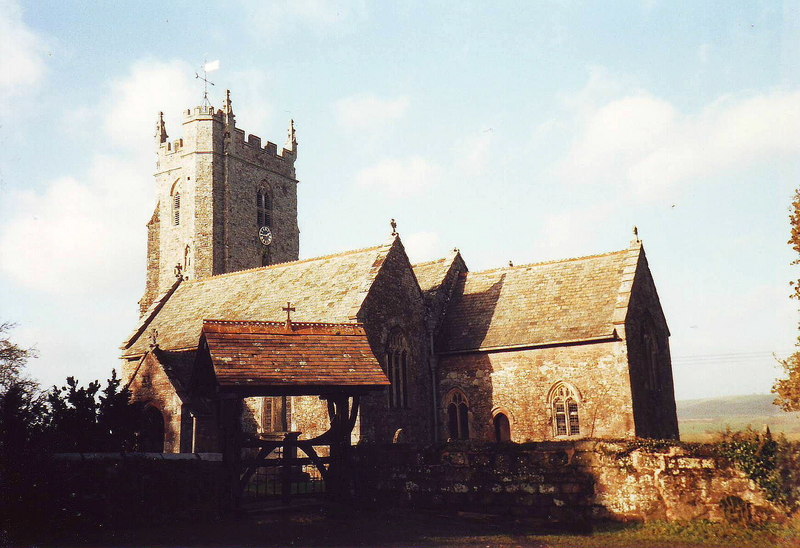
Cowley is a hamlet in the parish of Upton Pyne in Devon, England. Cowley church was built as a chapel of ease to Brampford Speke by Rohde Hawkins in 1867–8. It is chiefly notable for a fine three-arched bridge of classical design, built over the River Creedy in 1813-14 by James Green, pupil of John Rennie and surveyor to the county of Devon. Although so recent in date, the bridge has been scheduled as an ancient monument. Cowley Bridge Junction is a railway junction on the former Bristol and Exeter Railway, that allows access to the former North Devon Railway towards Barnstaple, now renamed the Tarka Line The Tarka Line, also known as the North Devon Line, is a local railway line in Devon, England, linking the city of Exeter with the town of Barnstaple via a number of local villages, operated by Great Western Railway (GWR). The line opened in 18 .... In 1848, the Exeter and Crediton Railway had built a station at Cowley Bridge, but it never opened. References H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowley Bridge Junction Class 220
Cowley may refer to: Places Australia * Cowley County, New South Wales *Cowley, Queensland, a rural locality in the Cassowary Coast Region *Cowley Beach, Queensland *Cowley Creek, Queensland *Lower Cowley, Queensland Canada * Cowley, Alberta England * Cowley, Derbyshire * Cowley, Devon * Cowley, Gloucestershire * Cowley, London * Cowley, Oxfordshire * Cowley Road, Oxford United States * Cowley, Texas * Cowley, Wyoming * Cowley County, Kansas People * Cowley (surname), English-language surname * Cowley Wright (1889–1923), English actor Other uses * Cowley Airport, near Cowley, Alberta, Canada * Cowley Community College, Arkansas City, Kansas * Earl Cowley, a British title See also * Cowley High School (other) * * Crowley (other) {{disambiguation, geo, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of ecclesiastical parishes, which historically played a role in both secular and religious administration. Civil and religious parishes were formally differentiated in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894, which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry. A civil parish can range in size from a sparsely populated rural area with fewer than a hundred inhabitants, to a large town with a population in the tens of thousands. This scope is similar to that of municipalities in Continental Europe, such as the communes of France. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upton Pyne
Upton Pyne is a parish and village in Devon, England. The parish lies just north west of Exeter, mainly between the River Exe and River Creedy. The village is located north of Cowley and west of Brampford Speke and Stoke Canon. It has a population of 539. History The manor came into the possession of the Pyne family during the reign of Henry I (1100–1135) when Herbert de Pins (or de pyn) took over the land. The Pyne family held it for ten successive generations, until Constance Pyne married William Larder about the end of the 15th century. The Larders held the manor for five generations. In the early 18th century the heiress of Stafford of Pynes married her neighbour Sir Henry Northcote (5th baronet) and took the manor to him. Sir Henry probably built the present Pynes House, a typical Queen Anne house, enlarged in 1851. The Pyne family also gave their name to the villages of Culm Pyne and Washford Pyne. One branch of the family moved to Ireland in the time of Elizabeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brampford Speke
Brampford Speke ( ) is a small village in Devon, to the north of Exeter. The population is 419. It is located on red sandstone cliffs overlooking the river Exe. Its sister village of Upton Pyne lies to its southwest, and Stoke Canon is across the river, to the east. To the south is the hamlet of Cowley with its chapel of ease, which was formerly part of the ecclesiastical parish of Brampford Speke. Brampford Speke has a Church of England parish church dedicated to St Peter. There is a primary school in the heart of the village near the river Exe, which was built as a national school in 1867. A baptist chapel was built near the school in 1894. The village also has a corner shop/tea room and a local pub, the Agricultural Inn (formerly the Lazy Toad). The village contains a number of fine houses, including the former landowner's Brampford House in the centre of the village and some traditional cob and thatch cottages and farmhouses. History The village's name perhaps means 'br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohde Hawkins
Major Rohde Hawkins (born 4 February 1821 in Nutfield, Surrey; died 19 October 1884, Holmwood, Surrey) was an English architect of the Victorian period. He is known for the schools and churches that he built. ''Note: Both his given names "Major" and "Rohde" frequently cause difficulty; he was not an army major, and Rohde was his mother's maiden name: she was of a German family.'' Family life Hawkins was the third son of numismatist and keeper of antiquities at the British Museum, Edward Hawkins (1780–1867) and Eliza Rohde, who had married on 29 September 1806. Hawkins was educated at Charterhouse School from 1831 to 1837; the school was then still part of the London Charterhouse in Finsbury. He was engaged by John Greenwood, a Yorkshire mill owner and politician at Swarcliffe, to rebuild Swarcliffe Hall in 1848. Hawkins became close enough to the Greenwood family to marry John Greenwood's granddaughter, Mary Littledale Greenwood of Holmwood, Surrey, on 4 August 1853. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Creedy
The River Creedy is a small river in Devon, England. It gives its name to the local town or ''ton'' of Crediton, which is on its west bank, and to several local historic estates, namely ''Creedy Hilion'', ''Creedy Peitevin'' (later called ''Creedy Wiger'') and Creedy Park, in the parish of Sandford, also to the Benefice of North Creedy. Just below the town, the river merges with the River Yeo and it ends where it meets the River Exe at Cowley Bridge. The river is overlooked by Fordy Wood Copse , a woodland owned and managed by the Woodland Trust. The name is believed to be of Celtic Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to: Language and ethnicity *pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia **Celts (modern) *Celtic languages **Proto-Celtic language *Celtic music *Celtic nations Sports Foo ... origin, but views of its precise origin differ. According to one source it derives from a root meaning ''winding''. Another view holds that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Green (engineer)
James Green (1781–1849) was a noted civil engineer and canal engineer, who was particularly active in the South West of England, where he pioneered the building of tub boat canals, and inventive solutions for coping with hilly terrain, which included tub boat lifts and inclined planes. Although dismissed from two schemes within days of each other, as a result of construction problems, his contribution as a civil engineer was great. Early career James Green was born in Birmingham, the son of an engineering family. He learned much from his father, by whom he was employed until the age of 20. He then worked with John Rennie on a number of projects around the country, until 1808, when he moved to Devon, and established a base at Exeter. He submitted plans for the rebuilding of Fenny Bridges, in East Devon, which had collapsed only 18 months after their previous reconstruction. The plans were accepted, and Green became the Bridge Surveyor for the County of Devon. By 1818 he ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Rennie The Elder
John Rennie FRSE FRS (7 June 1761 – 4 October 1821) was a Scottish civil engineer who designed many bridges, canals, docks and warehouses, and a pioneer in the use of structural cast-iron. Early years He was born the younger son of James Rennie, a farmer near Phantassie, near East Linton, East Lothian, Scotland. John showed a taste for mechanics at a very early age, and was allowed to spend much time in the workshop of Andrew Meikle, a millwright and the inventor of the threshing machine, who lived at Houston Mill on the Phantassie estate. After receiving a normal basic education at the parish school of Prestonkirk Parish Church, he was sent to the burgh school at Dunbar, and in November 1780 he matriculated at the University of Edinburgh, where he remained until 1783. His older brother George remained to assist in the family agricultural business. Rennie worked as a millwright to have established a business. His originality was exhibited by the introduction of cast iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with the Great Western Railway (GWR), which built its main line between London and Bristol, and in time formed part of a through route between London and Cornwall. It became involved in the gauge wars, a protracted and expensive attempt to secure territory against rival companies supported by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) which used the narrow gauge, later referred to as ''standard gauge''. At first it contracted with the GWR for that company to work the line, avoiding the expense of acquiring locomotives, but after that arrangement expired in 1849, the B&ER operated its own line. It opened a number of branches within the general area it served: to Clevedon, Cheddar, Wells, Weston-super-Mare, Chard, Yeovil and Tiverton. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Devon Railway
The North Devon Railway was a railway company which operated a line from Cowley Bridge Junction, near Exeter, to Bideford in Devon, England, later becoming part of the London and South Western Railway's system. Originally planned as a broad gauge (7 ft 0¼ in, 2,140 mm) feeder to the Bristol & Exeter Railway, it became part of a battle between the broad gauge group and the standard gauge railway interests. In this context, standard gauge lines were often described as ''narrow gauge''. The original construction in the middle of the nineteenth century was significant in giving rail connection to the important, but remote towns of North Devon that had hitherto relied on the packhorse and coastal shipping. The Exeter to Barnstaple section followed the rivers Yeo and Taw, passing through pleasing countryside, and meandered with the valleys, but passing only very small settlements. It remains open between Exeter and Barnstaple, and passenger trains on the route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnstaple Railway Station
Barnstaple railway station is the northern terminus of the Tarka Line and serves the town of Barnstaple, Devon. It is from at milepost 211.25 from . It is managed by Great Western Railway, which also operates the train service. It opened in 1854 but from 1874 until 1970 it was known as Barnstaple Junction railway station as it was the junction between lines to , , and Exeter. History The Taw Vale Railway & Dock opened a railway to carry goods traffic between a quay at Fremington Pill and Barnstaple in August 1848. William Thorne, who worked the horse-drawn trains, built a warehouse at the terminus in Barnstaple which was by the Sticklepath turnpike gate and the bridge across the River Taw. On 1 August 1854 the North Devon Railway (as the Taw Vale was now known) opened a gauge line from where it linked with the Exeter and Crediton Railway. The traffic on the original line between Barnstaple and Fremington had ceased in 1851 and this line was now rebuilt to the North Dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)