|
Couple (mechanics)
In mechanics, a couple is a system of forces with a resultant (a.k.a. net or sum) moment of force but no resultant force.''Dynamics, Theory and Applications'' by T.R. Kane and D.A. Levinson, 1985, pp. 90-99Free download/ref> A better term is force couple or pure moment. Its effect is to impart angular momentum but no linear momentum. In rigid body dynamics, force couples are ''free vectors'', meaning their effects on a body are independent of the point of application. The resultant moment of a couple is a ''special case'' of moment. A couple has the property that it is independent of reference point. Simple couple ;Definition A couple is a pair of forces, equal in magnitude, oppositely directed, and displaced by perpendicular distance or moment. The simplest kind of couple consists of two equal and opposite forces whose lines of action do not coincide. This is called a "simple couple".''Dynamics, Theory and Applications'' by T.R. Kane and D.A. Levinson, 1985, pp. 90-99Free dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Theoretical expositions of this branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece, for instance, in the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes (see History of classical mechanics and Timeline of classical mechanics). During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, Huygens, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. As a branch of classical physics, mechanics deals with bodies that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of light. It can also be defined as the physical science that deals with the motion of and forces on bodies not in the quantum r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Varignon
Pierre Varignon (1654 – 23 December 1722) was a French mathematician. He was educated at the Jesuit College and the University of Caen, where he received his M.A. in 1682. He took Holy Orders the following year. Varignon gained his first exposure to mathematics by reading Euclid and then Descartes' ''La Géométrie''. He became professor of mathematics at the Collège Mazarin in Paris in 1688 and was elected to the Académie Royale des Sciences in the same year. In 1704 he held the departmental chair at Collège Mazarin and also became professor of mathematics at the Collège Royal. He was elected to the Berlin Academy in 1713 and to the Royal Society in 1718. Many of his works were published in Paris in 1725, three years after his death. His lectures at Mazarin were published in Elements de mathematique' in 1731. Varignon was a friend of Newton, Leibniz, and the Bernoulli family. Varignon's principal contributions were to graphic statics and mechanics. Except for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Force is represented by the symbol (formerly ). The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal to the rate at which its momentum changes with time. If the mass of the object is constant, this law implies that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. Concepts related to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which decreases the velocity of an object; and torque, which pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
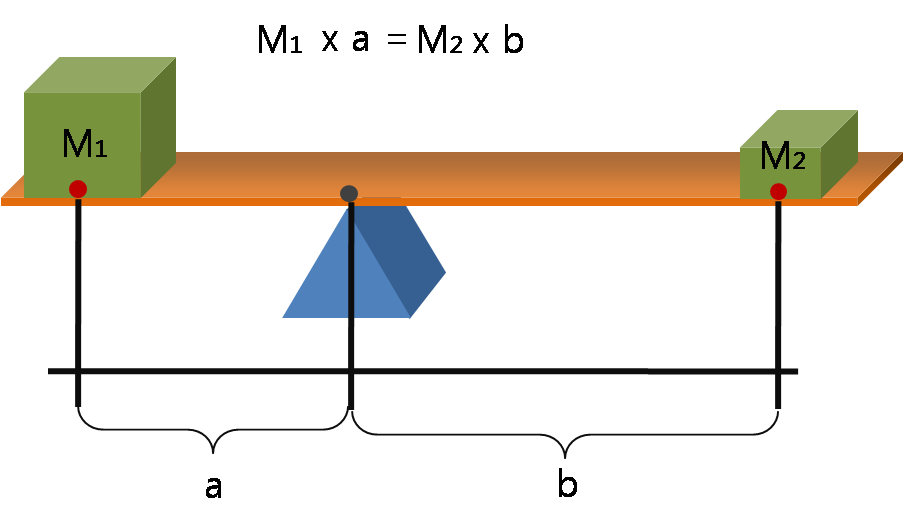
Moment (physics)
In physics, a moment is a mathematical expression involving the product of a distance and physical quantity. Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point and refer to physical quantities located some distance from the reference point. In this way, the moment accounts for the quantity's location or arrangement. For example, the moment of force, often called torque, is the product of a force on an object and the distance from the reference point to the object. In principle, any physical quantity can be multiplied by a distance to produce a moment. Commonly used quantities include forces, masses, and electric charge distributions. Elaboration In its most basic form, a moment is the product of the distance to a point, raised to a power, and a physical quantity (such as force or electrical charge) at that point: : \mu_n = r^n\,Q, where Q is the physical quantity such as a force applied at a point, or a point charge, or a point mass, etc. If the quantity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traction (engineering)
Traction, or tractive force, is the force used to generate motion between a body and a tangential surface, through the use of dry friction, though the use of shear force of the surface is also commonly used. Traction can also refer to the ''maximum'' tractive force between a body and a surface, as limited by available friction; when this is the case, traction is often expressed as the ratio of the maximum tractive force to the normal force and is termed the ''coefficient of traction'' (similar to coefficient of friction). It is the force which makes an object move over the surface by overcoming all the resisting forces like friction, normal loads(load acting on the tiers in negative 'Z' axis), air resistance, rolling resistance, etc. Definitions Traction can be defined as: In vehicle dynamics, tractive force is closely related to the terms tractive effort and drawbar pull, though all three terms have different definitions. Coefficient of traction The ''coefficient of tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steering Wheel
A steering wheel (also called a driving wheel (UK), a hand wheel, or simply wheel) is a type of steering control in vehicles. Steering wheels are used in most modern land vehicles, including all mass-production automobiles, buses, light and heavy trucks, as well as tractors. The steering wheel is the part of the steering system that is manipulated by the driver; the rest of the steering system responds to such driver inputs. This can be through direct mechanical contact as in recirculating ball or rack and pinion steering gears, without or with the assistance of hydraulic power steering, HPS, or as in some modern production cars with the assistance of computer-controlled motors, known as electric power steering. History Near the start of the 18th century, a large number of sea vessels appeared using the ship's wheel design, but historians are unclear when that approach to steering was first used. The first automobiles were steered with a tiller, but in 1894, Alfred Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses thrusters to provide attitude control and translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels are used for attitude control. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation ( roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small ( vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecraft reaction control systems are used for: * attitude control during different stages of a mission; * station keeping in orbit; * close maneuvering during docking procedures; * con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Dipole
The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system, that is, a measure of the system's overall polarity. The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb- meter (C⋅m). The debye (D) is another unit of measurement used in atomic physics and chemistry. Theoretically, an electric dipole is defined by the first-order term of the multipole expansion; it consists of two equal and opposite charges that are infinitesimally close together, although real dipoles have separated charge.Many theorists predict elementary particles can have very tiny electric dipole moments, possibly without separated charge. Such large dipoles make no difference to everyday physics, and have not yet been observed. (See electron electric dipole moment). However, when making measurements at a distance much larger than the charge separation, the dipole gives a good approximation of the actual electric field. The dipole is represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft (ship), propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Acceleration
In physics, angular acceleration refers to the time rate of change of angular velocity. As there are two types of angular velocity, namely spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity, there are naturally also two types of angular acceleration, called spin angular acceleration and orbital angular acceleration respectively. Spin angular acceleration refers to the angular acceleration of a rigid body about its centre of rotation, and orbital angular acceleration refers to the angular acceleration of a point particle about a fixed origin. Angular acceleration is measured in units of angle per unit time squared (which in SI units is radians per second squared), and is usually represented by the symbol alpha (α). In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |