|
Cosmos (Humboldt Book)
''Cosmos: A Sketch of a Physical Description of the Universe'' (in German ''Kosmos – Entwurf einer physischen Weltbeschreibung'') is an influential treatise on science and nature written by the German scientist and explorer Alexander von Humboldt. ''Cosmos'' began as a lecture series delivered by Humboldt at the University of Berlin, and was published in five volumes between 1845 and 1862 (the fifth was posthumous and completed based on Humboldt's notes). In the first volume of ''Cosmos'', Humboldt paints a general "portrait of nature", describing the physical nature of outer space and the Earth. In the second volume he describes the history of science. Widely read by academics and laymen, ''Cosmos'' applies the ancient Greek view of the orderliness of the cosmos (the harmony of the universe) to the Earth, suggesting that universal laws apply as well to the apparent chaos of the terrestrial world and that contemplation of nature can yield an awareness of its wholeness and cohere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatise
A treatise is a formal and systematic written discourse on some subject, generally longer and treating it in greater depth than an essay, and more concerned with investigating or exposing the principles of the subject and its conclusions." Treatise." Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Accessed September 12, 2020. A monograph is a treatise on a specialized topic. Etymology The word 'treatise' first appeared in the fourteenth century as the Medieval English word ''tretis'', which evolved from the Medieval Latin ''tractatus'' and the Latin ''tractare'', meaning to treat or to handle. Historically significant treatises Table The works presented here have been identified as influential by scholars on the development of human civilization. Discussion of select examples Euclid's ''Elements'' Euclid's ''Elements'' has appeared in more editions than any other books except the ''Bible'' and is one of the most important mathematical treatises ever. It has been translated to nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German Natural history, naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopy, microscopist. Ehrenberg was an Evangelicalism, evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin and became a friend of the famous List of explorers, explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile, Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), and has a population of 52 million. Colombia's cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a Spanish colony, fusing cultural elements brought by immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by enslaved Africans, as well as with those of the various Amerindian civilizations that predate colonization. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
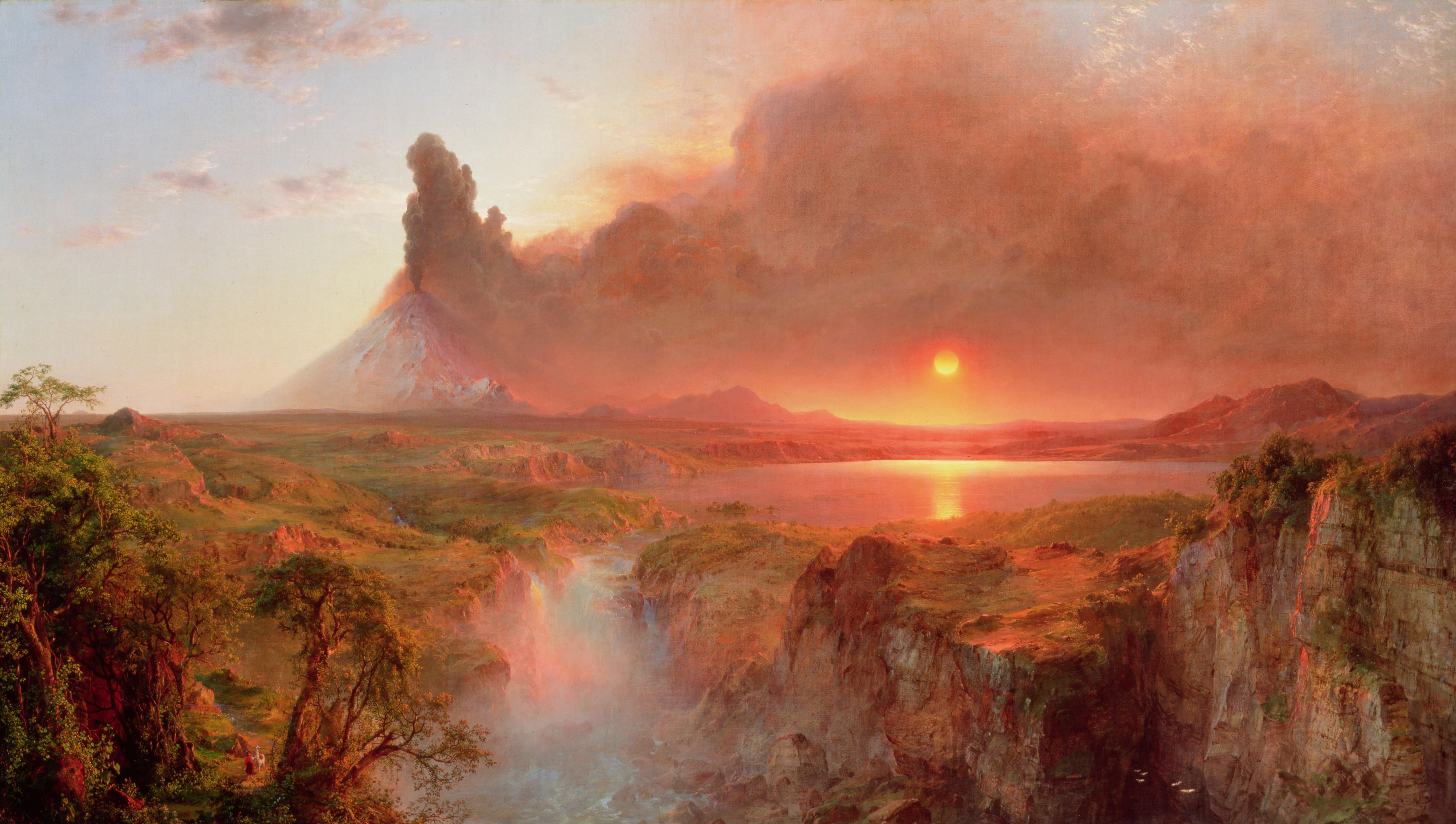
Frederic Edwin Church
Frederic Edwin Church (May 4, 1826 – April 7, 1900) was an American landscape painter born in Hartford, Connecticut. He was a central figure in the Hudson River School of American landscape painters, best known for painting large landscapes, often depicting mountains, waterfalls, and sunsets. Church's paintings put an emphasis on realistic detail, dramatic light, and panoramic views. He debuted some of his major works in single-painting exhibitions to a paying and often enthralled audience in New York City. In his prime, he was one of the most famous painters in the United States. Biography Beginnings Frederic Edwin Church was a direct descendant of Richard Church, a Puritan pioneer from England who accompanied Thomas Hooker on the original journey through the wilderness from Massachusetts to what would become Hartford, Connecticut. Church was the son of Eliza (1796–1883) and Joseph Church (1793–1876). Frederic had two sisters and no surviving brothers. His father was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champion of individualism and a prescient critic of the countervailing pressures of society, and his ideology was disseminated through dozens of published essays and more than 1,500 public lectures across the United States. Emerson gradually moved away from the religious and social beliefs of his contemporaries, formulating and expressing the philosophy of transcendentalism in his 1836 essay "Nature". Following this work, he gave a speech entitled "The American Scholar" in 1837, which Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. considered to be America's "intellectual Declaration of Independence."Richardson, p. 263. Emerson wrote most of his important essays as lectures first and then revised them for print. His first two collections of essays, '' Essays: Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walt Whitman
Walter Whitman (; May 31, 1819 – March 26, 1892) was an American poet, essayist and journalist. A humanist, he was a part of the transition between transcendentalism and realism, incorporating both views in his works. Whitman is among the most influential poets in the American canon, often called the father of free verse. His work was controversial in his time, particularly his 1855 poetry collection ''Leaves of Grass'', which was described as obscene for its overt sensuality. Born in Huntington on Long Island, Whitman resided in Brooklyn as a child and through much of his career. At the age of 11, he left formal schooling to go to work. Later, Whitman worked as a journalist, a teacher, and a government clerk. Whitman's major poetry collection, ''Leaves of Grass'', was first published in 1855 with his own money and became well known. The work was an attempt at reaching out to the common person with an American epic. He continued expanding and revising it until his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely regarded as a central figure of Romanticism in the United States, and of American literature. Poe was one of the country's earliest practitioners of the short story, and considered to be the inventor of the detective fiction genre, as well as a significant contributor to the emerging genre of science fiction. Poe is the first well-known American writer to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career. Poe was born in Boston, the second child of actors David and Elizabeth "Eliza" Poe. His father abandoned the family in 1810, and when his mother died the following year, Poe was taken in by John and Frances Allan of Richmond, Virginia. They never formally adopted him, but he was with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Alexander, Vor Uni Berlin
Humboldt may refer to: People * Alexander von Humboldt, German natural scientist, brother of Wilhelm von Humboldt * Wilhelm von Humboldt, German linguist, philosopher, and diplomat, brother of Alexander von Humboldt Fictional characters * Humboldt Fleisher, character in novel '' Humboldt's Gift'' * Wes Humboldt, character played by Mike O’Brien on ''Corner Gas'' Places Australia * Humboldt, Queensland, a locality in the Central Highlands Region Canada * Humboldt, Saskatchewan * Rural Municipality of Humboldt No. 370, Saskatchewan * Humboldt (electoral district), a former federal electoral district * Humboldt (provincial electoral district), a former Saskatchewan provincial electoral district United States * Settled places: ** Dewey-Humboldt, Arizona ** Humboldt, Illinois ** Humboldt, Iowa ** Humboldt, Kansas ** Humboldt, Minnesota ** Humboldt, Nebraska ** Humboldt, Ohio ** Humboldt, Portland, Oregon ** Humboldt, Pennsylvania ** Humboldt, South Dakota ** Humboldt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
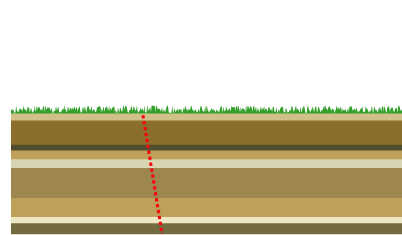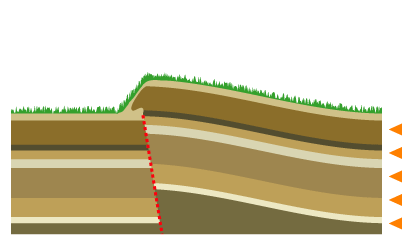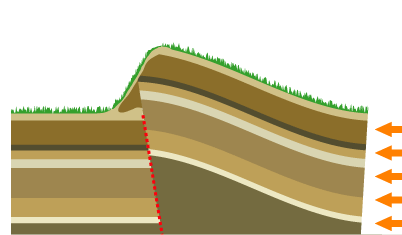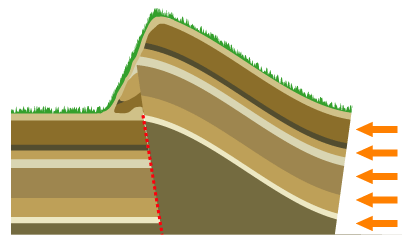
Mountain Formation
Mountain formation refers to the geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains. These processes are associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates). Fold (geology), Folding, Fault (geology), faulting, Volcano, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the Orogeny, orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the structural geology, geological structures found on it. The understanding of specific landscape features in terms of the underlying tectonics, tectonic processes is called ''geomorphology, tectonic geomorphology'', and the study of geologically young or ongoing processes is called ''neotectonics''. From the late 18th century until its replacement by plate tectonics in the 1960s, geosyncline, geosyncline theory was used to explain much mountain-building. Types of mountains There are five main types of mountains: volcani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Von Buch
Christian Leopold von Buch (26 April 1774 – 4 March 1853), usually cited as Leopold von Buch, was a German geologist and paleontologist born in Stolpe an der Oder (now a part of Angermünde, Brandenburg) and is remembered as one of the most important contributors to geology in the first half of the nineteenth century. His scientific interest was devoted to a broad spectrum of geological topics: volcanism, petrology, fossils, stratigraphy and mountain formation. His most remembered accomplishment is the scientific definition of the Jurassic system. Biography Buch studied with Alexander von Humboldt under Abraham Gottlob Werner at the mining school in Freiberg, Saxony. He afterwards completed his education at the universities of Halle and Göttingen. German and Italian explorations He began writing on geological topics early in life. His ''Versuch einer mineralogischen Beschreibung von Landeck'' (Breslau, 1797) was translated into French (Paris, 1805), and into English as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation Crater
The elevation crater theory is a now-discredited geologic theory originating in the 18th and 19th centuries which intended to explain the origin of mountains and orogens, holding that mountains formed by vertical movements associated with volcanism. Şengör (1982), p. 4 The idea that mountains could be formed by magma and volcanic activity was expressed as early as 1777 by Peter Simon Pallas, who claimed the Ural and Altai Mountains had been formed this way. Pallas based his ideas on the granitic central axes that he had observed in both ranges. The theory was revived and elaborated further by Leopold von Buch in the 19th century. Observations supporting this view were also given by Alexander von Humboldt in his book '' Kosmos''. Şengör (1982), p. 5 Humbold and Buch considered basaltic volcanism to be linked to elevation craters and trachyte to be the product of "true volcanoes". Otto Wilhelm Hermann von Abich applied the theory to the Caucasus Mountains and, following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos Kaulbach 215
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term ''kosmos'' ( grc, κόσμος, Latinized ''kósmos'') for the order of the universe. Greek wikt:κόσμος, κόσμος "order, good order, orderly arrangement" is a word with several main senses rooted in those notions. The verb wikt:κοσμέω, κοσμεῖν (''κοσμεῖν'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |