|
Cortical Patterning
Cortical patterning is a field of developmental neuroscience which aims to determine how the various functional areas of the cerebral cortex are generated, what size and shape they will be, and how their spatial pattern across the surface of the cortex is specified. Early brain lesion studies indicated that different parts of the cortex served different cognitive functions, such as visual, somatosensory, and motor functions, beautifully assimilated by Brodmann in 1909. Today the field supports the idea of a ' protomap', which is a molecular pre-pattern of the cortical areas during early embryonic stages. The protomap is a feature of the cortical ventricular zone, which contains the primary stem cells of the cortex known as radial glial cells. A system of signaling centers, positioned strategically at the midline and edges of the cortex, produce secreted signaling proteins that establish concentration gradients in the cortical primordium. This provides positional information f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Neuroscience
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the dorsal ectoderm becomes specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
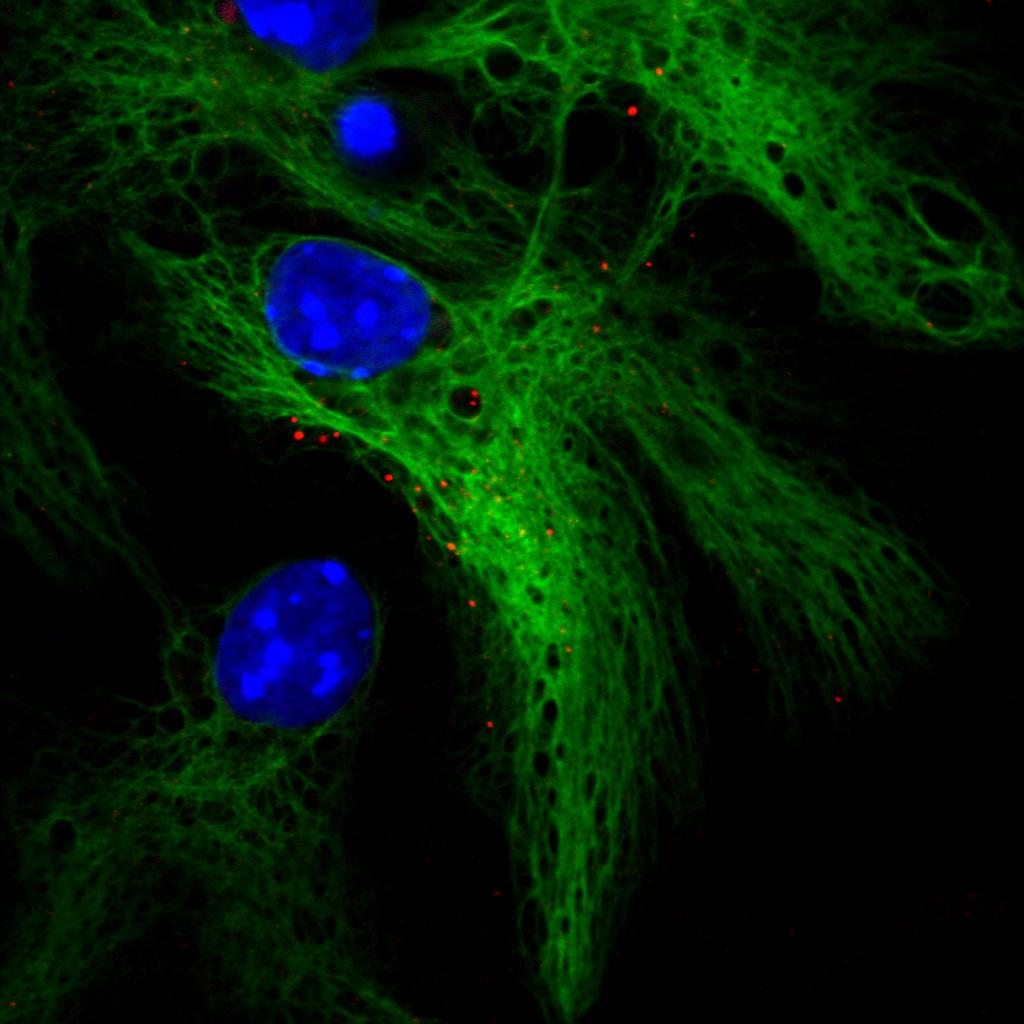
Synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells, and synapses are the means by which they do so. At a synapse, the plasma membrane of the signal-passing neuron (the ''presynaptic'' neuron) comes into close apposition with the membrane of the target (''postsynaptic'') cell. Both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sites contain extensive arrays of molecular machinery that link the two membranes together and carry out the signaling process. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma. Astrocytes also exchange information with the synaptic neurons, responding to synaptic activity and, in turn, regulating neurotransmission. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Neuroscience
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the dorsal ectoderm becomes specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a '' sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the cerebral cortex reside in a thin layer of gray matter, only 2–4 mm thick, at the surface of the brain. Much of the interior volume is occupied by white matter, which consists of long axonal projections to and from the cortical neurons residing near the surface. Gyrification allows a larger cortical surface area and hence greater cognitive functionality to fit inside a smaller cranium. In most mammals, gyrification begins during fetal development. Primates, cetaceans, and ungulates have extensive cortical gyri, with a few species exceptions, while rodents generally have none. Gyrification in some animals, for example the ferret, continues well into postnatal life. Gyrification during human brain development As fetal development proceeds, gy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Stem Cell
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor stem cells persist in highly restricted regions in the adult vertebrate brain and continue to produce neurons throughout life. Differences in the size of the central nervous system are among the most important distinctions between the species and thus mutations in the genes that regulate the size of the neural stem cell compartment are among the most important drivers of vertebrate evolution. Stem cells are characterized by their capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types. They undergo symmetric or asymmetric cell division into two daughter cells. In symmetric cell division, both daughter cells are also stem cells. In asymmetric division, a stem cell produces one stem cell and one specialized cell. NSCs primarily differentiate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Unit Hypothesis
The Radial Unit Hypothesis (RUH) is a conceptual theory of cerebral cortex development, first described by Pasko Rakic. The RUH states that the cerebral cortex develops during embryogenesis as an array of interacting cortical columns, or 'radial units', each of which originates from a transient stem cell layer called the ventricular zone, which contains neural stem cells known as radial glial cells. Cortical evolution The reiterative nature of the cerebral cortex, in the sense that it is a vast array of repeating functional circuits, led to the idea that cortical evolution is governed by mechanisms regulating the addition of cortical columns, enabling additional functional areas to become specialized and incorporated into the brain. The addition of new radial units is thought to depend on control of the cell cycle (proliferation) of cortical stem cells lining the ventricular system in the ventricular zone and subventricular zone. Protomap Intimately related to the RUH is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they manage to find their way so accurately is an area of ongoing research. Axon growth takes place from a region called the growth cone and reaching the axon target is accomplished with relatively few guidance molecules. Growth cone receptors respond to the guidance cues. Mechanisms Growing axons have a highly motile structure at the growing tip called the growth cone, which responds to signals in the extracellular environment that instruct the axon in which direction to grow. These signals, called guidance cues, can be fixed in place or diffusible; they can attract or repel axons. Growth cones contain receptors that recognize these guidance cues and interpret the signal into a chemotropic response. The general theoretical framework is that whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |