|
Consumer Economics
Consumer economics is a branch of economics. It is a broad field, principally concerned with microeconomic analysis behavior in units of consumers, families, or individuals (in contrast to traditional economics, which primarily government or business units). It sometimes also encompasses family financial planning and policy analysis. The term largely describes what was more commonly called "home economics" in the past. History The traditional economists had little interest in analyzing family units. When economic theory was insufficient to explain the phenomenon of women starting to enter the labor force ''en masse'', consumer economics both gained attention and received important contributions from economic theorists. Major theoretical cornerstones include Gary Becker's Household Production Model, time allocation models and Stigler's information search theory. Consumer economics concludes the family-unit economists were strongly influenced by the most recent "consumer era"; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment and with national policies relating to these issues. Microeconomics also d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or uses purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Consumer rights “Consumers, by definition, include us all," said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech : John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." Having a business name does not separate the business entity from the owner, which means that the owner of the business is responsible and liable for debts incurred by the business. If the business acquires debts, the creditors can go after the owner's personal possessions. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. The term is also often used colloquially (but not by lawyers or by public officials) to refer to a company, such as a corporation or cooperative. Corporations, in contrast with sole proprietors and partnerships, are a separate legal entity and provide limited liability for their owners/members, as well as being subject to corporate tax rates. A corporation is more complicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Planning
In general usage, a financial plan is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's current pay and future financial state by using current known variables to predict future income, asset values and withdrawal plans. This often includes a budget which organizes an individual's finances and sometimes includes a series of steps or specific goals for spending and saving in the future. This plan allocates future income to various types of expenses, such as rent or utilities, and also reserves some income for short-term and long-term savings. A financial plan is sometimes referred to as an investment plan, but in personal finance, a financial plan can focus on other specific areas such as risk management, estates, college, or retirement. Context of business In business, a financial plan can refer to the three primary financial statements ( balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement) created within a business plan. Financial forecast or financial plan can also re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Economics
Home economics, also called domestic science or family and consumer sciences, is a subject concerning human development, personal and family finances, consumer issues, housing and interior design, nutrition and food preparation, as well as textiles and apparel. Much less common today, it was and is most commonly taught in high school. Home economics courses are offered around the world and across multiple educational levels. Historically, the purpose of these courses was to professionalize housework, to provide intellectual fulfillment for women, and to emphasize the value of "women's work" in society and to prepare them for the traditional roles of sexes. Family and consumer sciences are taught as an elective or required course in secondary education, as a continuing education course in institutions, and at the primary level. Beginning as home economics in the United States, the course was a key part of the education system for teaching one the art of taking care of a househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Becker
Gary Stanley Becker (; December 2, 1930 – May 3, 2014) was an American economist who received the 1992 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. He was a professor of economics and sociology at the University of Chicago, and was a leader of the third generation of the Chicago school of economics. Becker was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1992 and received the United States Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2007. A 2011 survey of economics professors named Becker their favorite living economist over the age of 60, followed by Kenneth Arrow and Robert Solow. Economist Justin Wolfers called him "the most important social scientist in the past 50 years." Becker was one of the first economists to analyze topics that had been researched in sociology, including racial discrimination, crime, family organization, and rational addiction. He argued that many different types of human behavior can be seen as rational and utility-maximizing, including those that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System. Congress established three key objectives for monetary policy in the Federal Reserve Act: maximizing employment, stabilizing prices, and moderating long-term interest rates. The first two objectives are sometimes referred to as the Federal Reserve's dual mandate. Its duties have expanded over the years, and currently also include supervising and regulating banks, maintaining the stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United States and its various units—states, cities/towns/townships/villages/counties, and metropolitan areas. They also provide information about personal income, corporate profits, and government spending in their National Income and Product Accounts (NIPAs). The BEA is one of the principal agencies of the U.S. Federal Statistical System. Its stated mission is to "promote a better understanding of the U.S. economy by providing the most timely, relevant, and accurate economic data in an objective and cost-effective manner". BEA has about 500 employees and an annual budget of approximately $101 million. National accounts BEA's national economic statistics (National Economic Accounts) provide a comprehensive view of U.S. production, consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
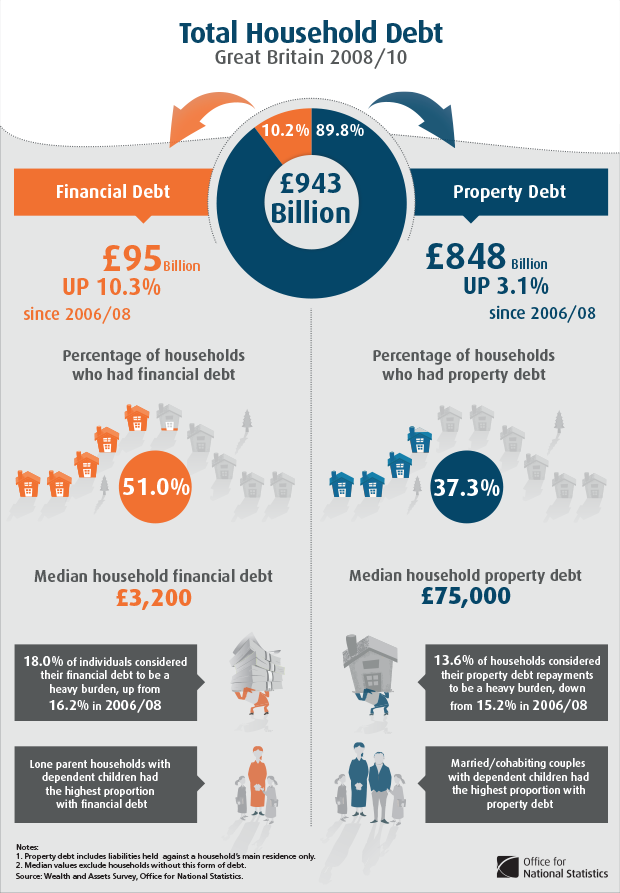
Household Debt
Household debt is the combined debt of all people in a household, including consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent European economic crises of 2007–2012. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries. Overview Household debt can be defined in several ways, based on what types of debt are included. Common debt types include home mortgages, home equity loans, auto loans, student loans, and credit cards. Household debt can also be measured across an economy, to measure how indebted households are relative to various measures of income (e.g., pre-tax and disposable income) or relative to the size of the economy (GDP). The burden of debt can also be measured in terms of the amount of interest it generates relative to the income of the borrower. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14597240757).jpg)