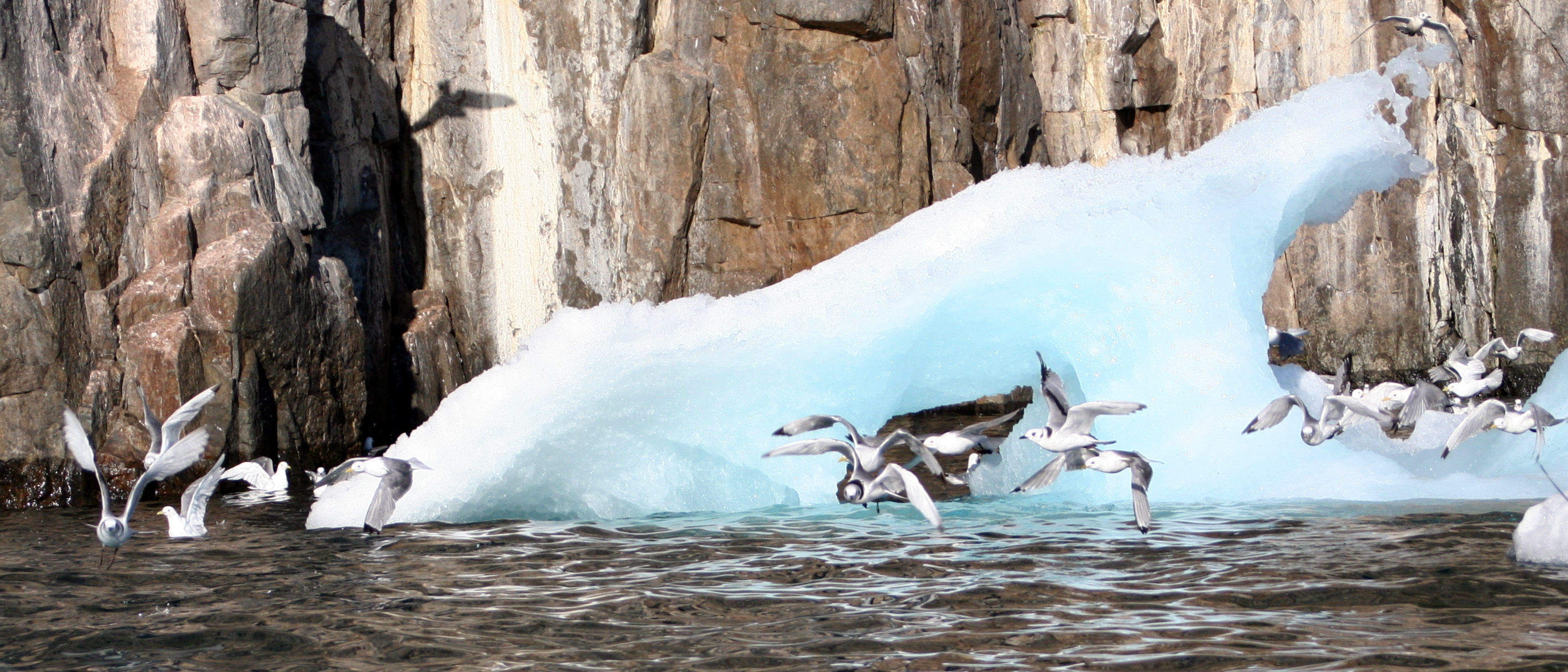|
Coburg Island
Coburg Island ( iu, script=latn, Nirjutiqavvik, italic=no) is an uninhabited island in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the members of Queen Elizabeth Islands located in Baffin Bay's Lady Ann Strait. It is separated from Ellesmere Island by Glacier Strait; Devon Island is to the south. Elsewhere in Nunavut, there is also a tinSaxe-Coburg Island lying in Davis Strait, south of Leopold Island, itself east of Baffin Island's Cape Mercy (Cumberland Peninsula). Geography The island is characterized by cliffs, rocky shores, and tundra. Fauna Bowhead whale, narwhal, polar bear, Pinniped, seal, walrus, and beluga whale, white whale frequent the area. Conservation Coburg Island has several designated conservation classifications including International Biological Program site and Key Habitat Site, Key Migratory Bird Terrestrial Habitat site. Along with the surrounding marine area, the island is a part of the Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area. Cambridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Ann Strait
Lady Ann Strait is a waterway in Jones Sound in the Provinces and Territories of Canada, Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is wide at the point between Cape Fitz Roy on Devon Island to the southwest, and Coburg Island to the northeast. The strait empties into northwestern Baffin Bay. References Lady Ann Strait at the Atlas of Canada External links Straits of Qikiqtaaluk Region Bodies of water of Baffin Bay {{QikiqtaalukNU-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
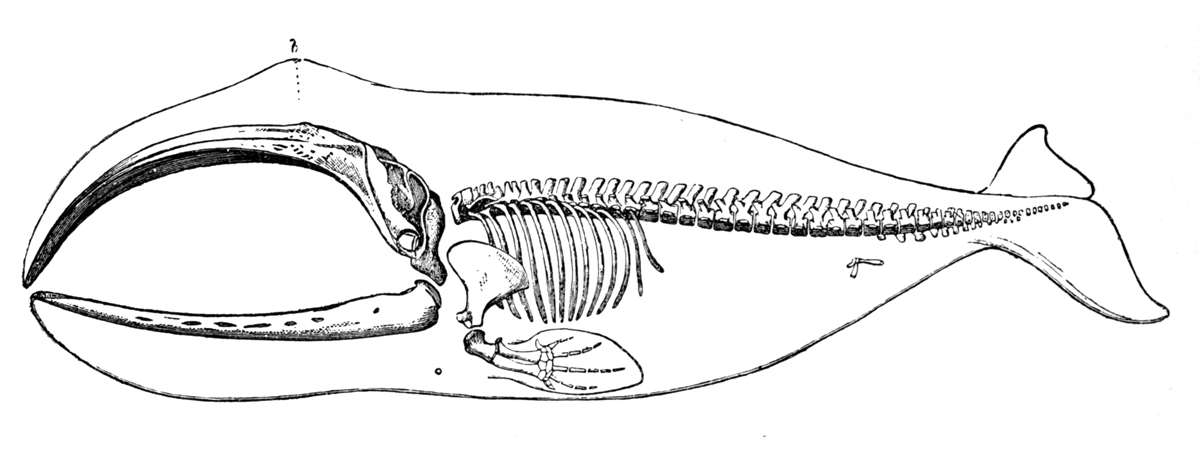
Bowhead Whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and are named after their characteristic massive triangular skull, which they use to break through Arctic ice. Other common names of the species are the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and Arviq in aboriginal languages (Inuktitut). American whalemen called them the steeple-top, polar whale, or Russian whale. Bowheads have the largest mouth of any animal representing almost one-third of the length of the body, the longest baleen plates with a maximum length of and may be the longest-lived mammals, with the ability to reach an age of more than 200 years. The bowhead was an early whaling target. Their population was severely reduced before a 1966 moratorium was passed to protect the species. Of the five stocks of bowhead populations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-legged Kittiwake
The black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') is a seabird species in the gull family Laridae. This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' as ''Larus tridactylus''. The English name is derived from its call, a shrill 'kittee-wa-aaake, kitte-wa-aaake'. The genus name ''Rissa'' is from the Icelandic name ''rita'' for this bird, and the specific ''tridactyla'' is from Ancient Greek ''tridaktulos'', "three-toed", from ''tri-'', "three-" and ''daktulos'', "toe". In North America, this species is known as the black-legged kittiwake to differentiate it from the red-legged kittiwake, but in Europe, where it is the only member of the genus, it is often known just as kittiwake. Range and distribution The black-legged kittiwake is a coastal bird of the arctic to subarctic regions of the world.del Hoyo, J; Elliott, A; Sargatal, J (1996). ''Handbook of the Birds of the World Vol. 3''. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. pp. 622–6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Guillemot
The black guillemot or tystie (''Cepphus grylle'') is a medium-sized seabird of the Alcidae family, native throughout northern Atlantic coasts and eastern North American coasts. It is resident in much of its range, but large populations from the high arctic migrate southwards in winter. The bird can be seen in and around its breeding habitat of rocky shores, cliffs and islands in single or smalls groups of pairs. They feed mainly by diving towards the sea floor feeding on fish, crustaceans or other benthic invertebrates. They are listed on the IUCN red list as a species of least concern. Both sexes have very similar appearances with black plumage and a large white patch on the upper side of their wings in summer. The bill is also black, being rather long and slender, while the feet are coral-red. In winter adult underparts are white and the upperparts are a pale grey with the back and shoulders exhibiting barred light grey and white patterning. The birds breed in solitary pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the Program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Point
Cambridge Point is an uninhabited headland on Coburg Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located off Marina Peninsula. Geography Characterized by prominent coastline cliffs, open sea, rocky shores, and tundra habitats, the point's elevation ranges from above sea level. It is in size. Conservation The point is a Canadian Important Bird Area (#NU010). A portion of Cambridge Point is also contained within the Nirjutiqavvik (Coburg Island) National Wildlife Area. Fauna The area is frequented by bowhead whale, narwhal, polar bear, seal, walrus, and white whale. Notable bird species include: * Black guillemot * Black-legged kittiwake * Glaucous gull * Northern fulmar * Thick-billed murre References Cambridge Pointat the Atlas of Canada The Atlas of Canada (french: L'Atlas du Canada) is an online atlas published by Natural Resources Canada that has information on every city, town, village, and hamlet in Canada. It was originally a print atlas, with its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area
Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area is a National Wildlife Area on Coburg Island within the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Baffin Bay's Lady Ann Strait between Ellesmere Island, to the north, and Devon Island to the south. The NWA includes Coburg Island and its surrounding marine area. Established in 1995, it is in area. Of this, a total of make up a marine area with marine and intertidal components. The NWA is one of the most important seabird nesting areas in the Canadian Arctic for black guillemot, black-legged kittiwake, northern fulmar, and thick-billed murre. It is also an important area for polar bears, walruses, ringed, and bearded seals. Narwhal and beluga whales migrate through the area. The Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area is home to many seabird species and marine animals, providing essential nutrients to nearby Indigenous communities. The wildlife area is managed by Inuit from Grise Fiord, a nearby community, along with othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Habitat Site
A Key Habitat Site is a Canadian Wildlife Service designation for an area that supports at least 1% of the country's population of any migratory bird species, or subspecies, at any time. There may be overlap with areas designated as a migratory bird sanctuary or National Wildlife Area A National Wildlife Area is a conservation designation for a geographical region in Canada that restricts most human activities on that region. However, land use permits may be issued "for activities that are compatible with conservation". Suc .... References External links Key migratory bird terrestrial habitat sites in the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, March 2006 Canadian Wildlife Service Environment and Climate Change Canada Ornithology {{Canada-protected-area-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Biological Program
The International Biological Program (IBP) was an effort between 1964 and 1974 to coordinate large-scale ecological and environmental studies. Organized in the wake of the successful International Geophysical Year (IGY) of 1957-1958, the International Biological Program was an attempt to apply the methods of big science to ecosystem ecology and pressing environmental issues. The IBP was organized under the leadership of C. H. Waddington beginning in 1962 and officially started in 1964, with the goal of exploring "The Biological Basis of Productivity and Human Welfare". In its early years, Canadian and European ecologists were the main participants; by 1968, the United States also became heavily involved. However, unlike other more successful applications of the big science model of scientific research, the IBP lacked a clear, socially and scientifically pressing goal. Many biologists, particularly molecular biologists and evolutionary ecologists, were sharply critical of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabirds And Iceberg At Coburg Island
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations. The first seabirds evolved in the Cretaceous period, and modern seabird families emerged in the Paleogene. In general, seabirds live longer, breed later and have fewer young than other birds do, but they invest a great deal of time in their young. Most species nest in colonies, which can vary in size from a few dozen birds to millions. Many species are famous for undertaking long annual migrations, crossing the equator or circumnavigating the Earth in some cases. They feed both at the ocean's surface and below it, and even feed on each other. Seabirds can be highly pelagic, coastal, or in some cases spend a part of the year away from the sea entirely. Seabirds an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beluga Whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the white whale, as it is the only cetacean to regularly occur with this colour; the sea canary, due to its high-pitched calls; and the melonhead, though that more commonly refers to the melon-headed whale, which is an oceanic dolphin. The beluga is adapted to life in the Arctic, with anatomical and physiological characteristics that differentiate it from other cetaceans. Amongst these are its all-white colour and the absence of a dorsal fin, which allows it to swim under ice with ease. It possesses a distinctive protuberance at the front of its head which houses an echolocation organ called the melon, which in this species is large and deformable. The beluga's body size is between that of a dolphin and a true whale, with males growing up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the family Odobenidae and genus ''Odobenus''. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus (''O. r. rosmarus''), which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus (''O. r. divergens''), which lives in the Pacific Ocean. Adult walrus are characterised by prominent tusks and whiskers, and their considerable bulk: adult males in the Pacific can weigh more than and, among pinnipeds, are exceeded in size only by the two species of elephant seals. Walruses live mostly in shallow waters above the continental shelves, spending significant amounts of their lives on the sea ice looking for benthic bivalve mollusks to eat. Walruses are relatively long-lived, social animals, and they are considered to be a "keystone species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |