|
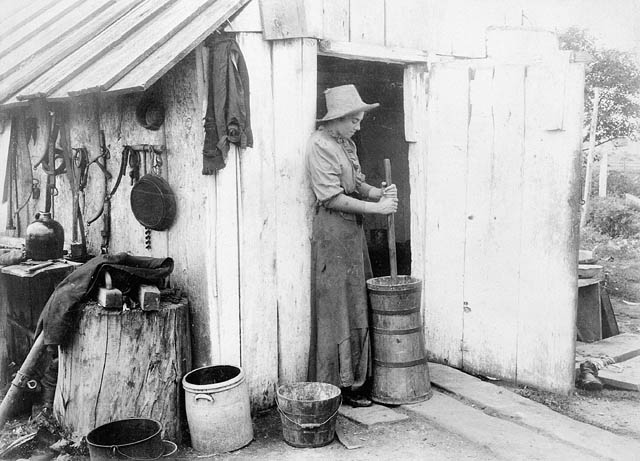
Churning (butter)
Churning is the process of shaking up cream or whole milk to make butter, usually using a butter churn. In Europe from the Middle Ages until the Industrial Revolution, a churn was usually as simple as a barrel with a plunger in it, moved by hand. These have mostly been replaced by mechanical churns. Butter is essentially the fat of milk. It is usually made from sweet cream (that is, cream skimmed from milk rather than whey). In the USA, Ireland, the UK and the Nordic countries, salt is usually added to it. Unsalted (sweet) butters are most commonly used in the rest of Europe. However, it can also be made from acidulated or bacteriologically soured cream. Well into the 19th century butter was still made from cream that had been allowed to stand and sour naturally. The cream was then skimmed from the top of the milk and poured into a wooden tub. Buttermaking was done by hand in butter churns. The natural souring process is, however, a very sensitive one and infection by fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femme Inconnue Avec Une Baratte Près De Long Branch, Ont
''Femme'' (; , literally meaning "woman") is a term traditionally used to describe a lesbian who exhibits a feminine identity or gender presentation. Alternate meanings of the word also exist with some non-lesbian individuals using the word, notably some gay men, bisexuals, nonbinary and transgender individuals. Heavily associated with lesbian history and culture, ''femme'' has been used among lesbians to distinguish traditionally feminine lesbians from their butch (i.e. masculine) lesbian counterparts and partners. Derived from American lesbian communities following World War II when women joined the work force, the identity became a characteristic of the working class lesbian bar culture of the 1940s–1950s. By the 1990s, the term ''femme'' had additionally been adopted by bisexual women. It has however also been argued by bi+ and other queer activists that since the term bisexual is relatively newer than lesbian, bisexual women historically formed part of the lesbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20140709 Radkersburg Majolika A8972
Fourteen or 14 may refer to: * 14 (number), the natural number following 13 and preceding 15 * one of the years 14 BC, AD 14, 1914, 2014 Music * 14th (band), a British electronic music duo * ''14'' (David Garrett album), 2013 *''14'', an unreleased album by Charli XCX * "14" (song), 2007, from ''Courage'' by Paula Cole Other uses * ''Fourteen'' (film), a 2019 American film directed by Dan Sallitt * ''Fourteen'' (play), a 1919 play by Alice Gerstenberg * ''Fourteen'' (manga), a 1990 manga series by Kazuo Umezu * ''14'' (novel), a 2013 science fiction novel by Peter Clines * ''The 14'', a 1973 British drama film directed by David Hemmings * Fourteen, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Lot Fourteen, redevelopment site in Adelaide, South Australia, previously occupied by the Royal Adelaide Hospital * "The Fourteen", a nickname for NASA Astronaut Group 3 * Fourteen Words, a phrase used by white supremacists and Nazis See also * 1/4 (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Cyclopedia
The ''Household Cyclopedia'' was an American guide to housekeeping Housekeeping is the management and routine support activities of running an organised physical institution occupied or used by people, like a house, ship, hospital or factory, such as tidying, cleaning, cooking, routine maintenance, shopping, ... published in 1881. External links ''Household Cyclopedia'' of 1881 1881 non-fiction books Home economics American encyclopedias {{encyclopedia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason Jar
A Mason jar, also known as a canning jar or fruit jar, is a glass jar used in home canning to preserve food. It was named after American tinsmith John Landis Mason, who patented it in 1858. The jar's mouth has a screw thread on its outer perimeter to accept a metal ring or "band". The band, when screwed down, presses a separate stamped steel disc-shaped lid against the jar's rim. Mason lost his patent for the jars and numerous other companies started manufacturing similar jars. Over the years, the brand name ''Mason'' became the genericized trademark for that style of glass home canning jar, and the word "Mason" can be seen on many Ball and Kerr brand jars. The style of jar is occasionally referred to by common brand names such as Ball jar (in the eastern US) or Kerr jar (in the western US) even if the individual jar isn't that brand. In early 20th century America, Mason jars became useful to those who lived in areas with short growing seasons. The jars became an essential pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervo091
Cervo may refer to: Places Italy * Cervo, Liguria, a comune in the province of Imperia in the region of Liguria * Cervo (river), a tributary of the River Sesia in the Piedmont region Portugal * Cervo (Ribeira de Pena), a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira de Pena Spain *Cervo, Lugo, a municipality of the Province of Lugo Automobiles * Suzuki Cervo is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal co ..., a small Kei car made by Japanese carmaker Suzuki. {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttermilk
Buttermilk is a fermented dairy drink. Traditionally, it was the liquid left behind after churning butter out of cultured cream. As most modern butter in western countries is not made with cultured cream but uncultured sweet cream, most modern buttermilk in western countries is cultured separately. It is common in warm climates where unrefrigerated milk sours quickly. Buttermilk can be drunk straight, and it can also be used in cooking. In making soda bread, the acid in buttermilk reacts with the raising agent, sodium bicarbonate, to produce carbon dioxide which acts as the leavening agent. Buttermilk is also used in marination, especially of chicken and pork. Traditional buttermilk Originally, buttermilk referred to the liquid left over from churning butter from cultured or fermented cream. Traditionally, before the advent of homogenization, the milk was left to sit for a period of time to allow the cream and milk to separate. During this time, naturally occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
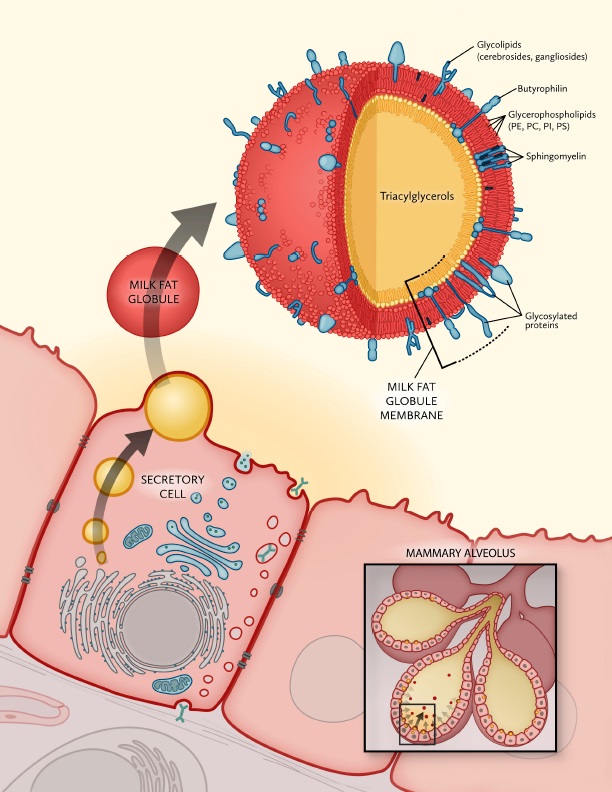
Milk Fat Globule Membrane
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) is a complex and unique structure composed primarily of lipids and proteins that surrounds milk fat globule secreted from the milk producing cells of humans and other mammals. It is a source of multiple bioactive compounds, including phospholipids, glycolipids, glycoproteins, and carbohydrates that have important functional roles within the brain and gut. Preclinical studies have demonstrated effects of MFGM-derived bioactive components on brain structure and function, intestinal development, and immune defense. Similarly, pediatric clinical trials have reported beneficial effects on cognitive and immune outcomes. In populations ranging from premature infants to preschool-age children, dietary supplementation with MFGM or its components has been associated with improvements in cognition and behavior, gut and oral bacterial composition, fever incidence, and infectious outcomes including diarrhea and otitis media. MFGM may also play a role in suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward toward the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid center. A special kind of protein, called apolipoprotein, is embedded in the outer shell, both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role. Many enzymes, transporters, structural proteins, antigens, adhesins, and toxins are lipoproteins. Examples include plasma lipoprotein particles ( HDL, LDL, IDL, VLDL and chylomicrons). Subgroups of these plasma particles are primary drivers or modulators of atherosclerosis. Scope Transmembrane lipoproteins Some transmembrane proteolipids, especially those found in bacteria, are referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early- lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system, and thus reduces the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose. As an agricultural product, dairy milk is collected from farm animals. In 2011, dairy farms produced around of milk from 260 million dairy cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand for dairy products within India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New Zealand, Germany and the Netherlands are the largest expor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms ''colloid'' and ''emulsion'' are sometimes used interchangeably, ''emulsion'' should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the dispersed phase) is dispersed in the other (the continuous phase). Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions. As an example, oil and water can form, first, an oil-in-water emulsion, in which the oil is the dispersed phase, and water is the continuous phase. Second, they can form a water-in-oil emulsion, in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the continuous phase. Multiple emulsions are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds Butter Churn
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by population) in England, after London and Birmingham. The city was a small manorial borough in the 13th century and a market town in the 16th century. It expanded by becoming a major production centre, including of carbonated water where it was invented in the 1760s, and trading centre (mainly with wool) for the 17th and 18th centuries. It was a major mill town during the Industrial Revolution. It was also known for its flax industry, iron foundries, engineering and printing, as well as shopping, with several surviving Victorian era arcades, such as Kirkgate Market. City status was awarded in 1893, a populous urban centre formed in the following century which absorbed surrounding villages and overtook the nearby York population. It is located a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)