|
Chlamyphoridae
Chlamyphoridae is a family of cingulate mammals. While glyptodonts have traditionally been considered stem-group cingulates outside the group that contains modern armadillos, there had been speculation that the extant family Dasypodidae could be paraphyletic based on morphological evidence. In 2016, an analysis of ''Doedicurus'' mtDNA found it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, all extant armadillos but '' Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family. __TOC__ Classification Below is a taxonomy of the extant species of armadillos in this family. Family Chlamyphoridae * Subfamily Chlamyphorinae ** Genus '' Calyptophractus'' *** Greater fairy armadillo, ''Calyptophractus retusus'' ** Genus '' Chlamyphorus'' *** Pink fairy armadillo, ''Chlamyphorus truncatus'' * Subfamily Euphractinae ** Genus '' Euphractus'' ***Six-banded armadillo, ''Euphractus sexcinctus'' ** Genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cingulata
Cingulata, part of the superorder Xenarthra, is an order of armored New World placental mammals. Dasypodids and chlamyphorids, the armadillos, are the only surviving families in the order. Two groups of cingulates much larger than extant armadillos (maximum body mass of 45 kg (100 lb) in the case of the giant armadillo) existed until recently: pampatheriids, which reached weights of up to 200 kg (440 lb) and chlamyphorid glyptodonts, which attained masses of 2,000 kg (4,400 lb) or more. The cingulate order originated in South America during the Paleocene epoch about 66 to 56 million years ago, and due to the continent's former isolation remained confined to it during most of the Cenozoic. However, the formation of a land bridge allowed members of all three families to migrate to southern North America during the Pliocene or early Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. After surviving for tens of millions of years, all of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptodont
Glyptodonts are an extinct subfamily of large, heavily armoured armadillos. They arose in South America around 48 million years ago and spread to southern North America after the continents became connected several million years ago. The best-known genus within the group is '' Glyptodon''. While they were formerly considered to constitute the distinct family Glyptodontidae, in 2016, an analysis of '' Doedicurus'' Mitochondrial DNA (also known as mtDNA / mDNA) found that it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, glyptodonts and all armadillos but '' Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family, Chlamyphoridae, and glyptodonts were demoted from the former family Glyptodontidae to a subfamily. Evolution Glyptodonts first evolved during the Eocene in South America, which remained their center of species diversity. For example, an Early Miocene glyptodont with many primitive feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doedicurus
''Doedicurus'', or ''Dædicurus'', is an extinct genus of glyptodont from South America containing one species, ''D. clavicaudatus''. Glyptodonts are a member of the family Chlamyphoridae, which also includes some modern armadillo species, and they are classified in the superorder Xenarthra alongside sloths and anteaters. Being a glyptodont, it was a rotund animal with heavy armor and a carapace. Averaging at an approximate , it was one of the largest glyptodonts to have ever lived. Though glyptodonts were quadrupeds, large ones like ''Doedicurus'' may have been able to stand on two legs like other xenarthrans. It notably sported a spiked tail club, which may have weighed in life, and it may have swung this in defense against predators or in fights with other ''Doedicurus'' at speeds of perhaps . ''Doedicurus'' was likely a grazer, but its teeth and mouth, like those of other glyptodonts, seem unable to have chewed grass effectively, which may indicate a slow metabolism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamyphorinae
Chlamyphorinae is a subfamily of South American armadillos in the family Chlamyphoridae. Members of this subfamily, the fairy armadillos, are largely fossorial and have reduced eyes and robust forearms with large claws for digging. __TOC__ Taxonomy The subfamily has two monotypic genera: *'' Calyptophractus'', greater fairy armadillo *'' Chlamyphorus'', pink fairy armadillo Phylogeny Chlamyphorinae is the sister group of Tolypeutinae (giant In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''gigas'', cognate giga-) are beings of human-like appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 fr ..., three-banded and naked-tailed armadillos), as shown below. References Armadillos Mammal subfamilies Taxa named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphractinae
Euphractinae is an armadillo subfamily in the family Chlamyphoridae. Euphractinae are known for having a well developed osteoderm that has large cavities filled with adipose tissue, and more hair follicles with well developed sebaceous glands in comparison to the Dasypodidae sub family. These are believed to be evolutionary adaptations in the Euphractinae to support it in the cooler climate that it usually lives in. __TOC__ Taxonomy It contains the following genera: *''Chaetophractus'', hairy armadillos *''Euphractus'', six-banded armadillos *'' Zaedyus'', pichis Extinct genera include: * '' Paleuphractus'' * '' Doellotatus'' * ''Proeuphractus'' * ''Macroeuphractus'' Phylogeny A mitochondrial DNA investigation has concluded that Euphractinae is the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae (fairy armadillos) and Tolypeutinae (giant, three-banded and naked-tailed armadillos) along with extinct glyptodont Glyptodonts are an extinct subfamily of large, heavily a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptodontinae
Glyptodonts are an extinct subfamily of large, heavily armoured armadillos. They arose in South America around 48 million years ago and spread to southern North America after the continents became connected several million years ago. The best-known genus within the group is ''Glyptodon''. While they were formerly considered to constitute the distinct family Glyptodontidae, in 2016, an analysis of ''Doedicurus'' Mitochondrial DNA (also known as mtDNA / mDNA) found that it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, glyptodonts and all armadillos but ''Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family, Chlamyphoridae, and glyptodonts were demoted from the former family Glyptodontidae to a subfamily. Evolution Glyptodonts first evolved during the Eocene in South America, which remained their center of species diversity. For example, an Early Miocene glyptodont with many primitive features, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolypeutinae
Tolypeutinae is a subfamily of armadillos in the family Chlamyphoridae, consisting of the giant, three-banded and naked-tailed armadillos. __TOC__ Taxonomy It contains the following genera: *''Cabassous'' *''Kuntinaru'' *''Priodontes'' *''Tolypeutes'' *'' Vetelia'' Phylogeny Tolypeutinae is the sister group of Chlamyphorinae Chlamyphorinae is a subfamily of South American armadillos in the family Chlamyphoridae. Members of this subfamily, the fairy armadillos, are largely fossorial and have reduced eyes and robust forearms with large claws for digging. __TOC__ Ta ..., the fairy armadillos, as shown below. References Armadillos Extant Chattian first appearances {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasypodidae
Dasypodidae is a family of mostly extinct genera of armadillos. One genus, ''Dasypus'', is extant, with at least seven living species. __TOC__ Classification Below is a taxonomy of armadillos in this family. Family Dasypodidae *† Genus '' Acantharodeia'' *† Genus '' Amblytatus'' *† Genus '' Archaeutatus'' *† Genus '' Astegotherium'' *† Genus '' Barrancatatus'' *† Genus '' Chasicotatus'' *† Genus '' Chorobates'' *† Genus '' Coelutaetus'' *† Genus '' Eocoleophorus'' *† Genus '' Epipeltecoelus'' *† Genus '' Eutatus'' *† Genus '' Hemiutaetus'' *† Genus '' Isutaetus'' *† Genus '' Lumbreratherium'' *† Genus '' Macrochorobates'' *† Genus '' Mazzoniphractus'' *† Genus '' Meteutatus'' *† Genus '' Pedrolypeutes'' *† Genus '' Prodasypus'' *† Genus '' Proeutatus'' *† Genus '' Prostegotherium'' *† Genus '' Pucatherium'' *† Genus '' Punatherium'' *† Genus '' Stegotherium'' *† Genus ''Stenotatus'' *† Genus ''Utaetus'' * Subfamily Dasypod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
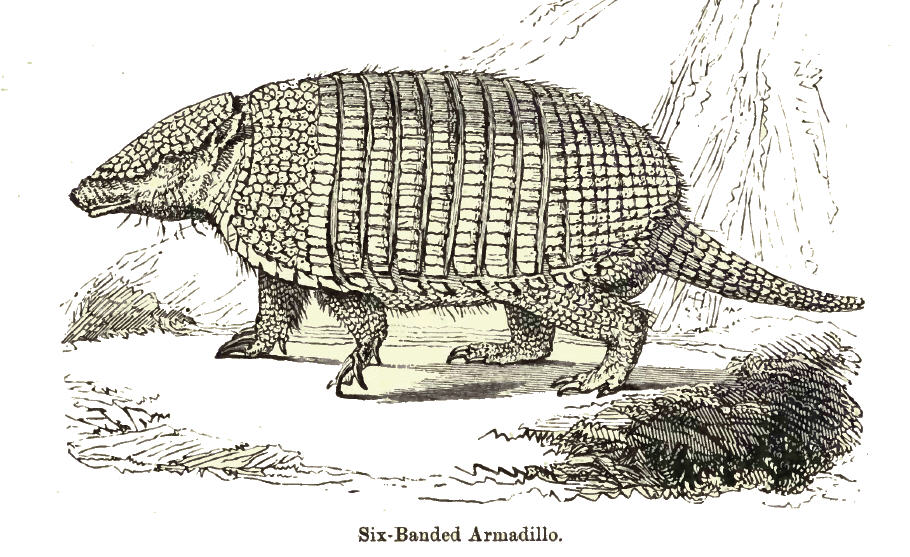
Six-banded Armadillo
The six-banded armadillo (''Euphractus sexcinctus''), also known as the yellow armadillo, is an armadillo found in South America. The sole extant member of its genus, it was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The six-banded armadillo is typically between in head-and-body length, and weighs . The carapace (hard shell on the back) is pale yellow to reddish brown, marked by scales of equal length, and scantily covered by buff to white bristle-like hairs. The forefeet have five distinct toes, each with moderately developed claws. Six-banded armadillos are efficient diggers and form burrows to live in and search for prey. The armadillo is alert and primarily solitary. An omnivore, it feeds on insects, ants, carrion, and plant material. Due to their poor eyesight, armadillos rely on their sense of smell to detect prey and predators. Births take place throughout the year; gestation is 60 to 64 days long, after which a litter of one to three is born. Weaning o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetophractus
''Chaetophractus'' is a small genus of armadillos in the family Chlamyphoridae. It contains the following three species: Members of the genus are endemic to the continent of South America. They are found in the central and southern countries such as Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Paraguay. ''Chaetophractus nationi'' is probably a junior synonym of Chaetophractus nationi, ''Chaetophractus vellerosus'' and the genus ''Chatophractus'' may be paraphyletic. References Armadillos Mammal genera Taxa named by Leopold Fitzinger Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphractus
The six-banded armadillo (''Euphractus sexcinctus''), also known as the yellow armadillo, is an armadillo found in South America. The sole extant member of its genus, it was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The six-banded armadillo is typically between in head-and-body length, and weighs . The carapace (hard shell on the back) is pale yellow to reddish brown, marked by scales of equal length, and scantily covered by buff to white bristle-like hairs. The forefeet have five distinct toes, each with moderately developed claws. Six-banded armadillos are efficient diggers and form burrows to live in and search for prey. The armadillo is alert and primarily solitary. An omnivore, it feeds on insects, ants, carrion, and plant material. Due to their poor eyesight, armadillos rely on their sense of smell to detect prey and predators. Births take place throughout the year; gestation is 60 to 64 days long, after which a litter of one to three is born. Weani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |