|
Chinaman (ship)
A Chinaman was a ship engaged in the Old China Trade, in the 18th and 19th centuries, by analogy with East Indiaman. See also *Chinaman (term) * ''Empress of China'', an early American full-rigged ship in the Old China Trade *Guineaman, a ship used to transport slaves from the region of Guinea *East Indiaman, a ship used to transport colonial goods from the East Indies and the Indian Subcontinent *West Indiaman, a ship used to transport colonial goods from the West Indies The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ... Sailing ships History of foreign trade in China Tall ships {{ship-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
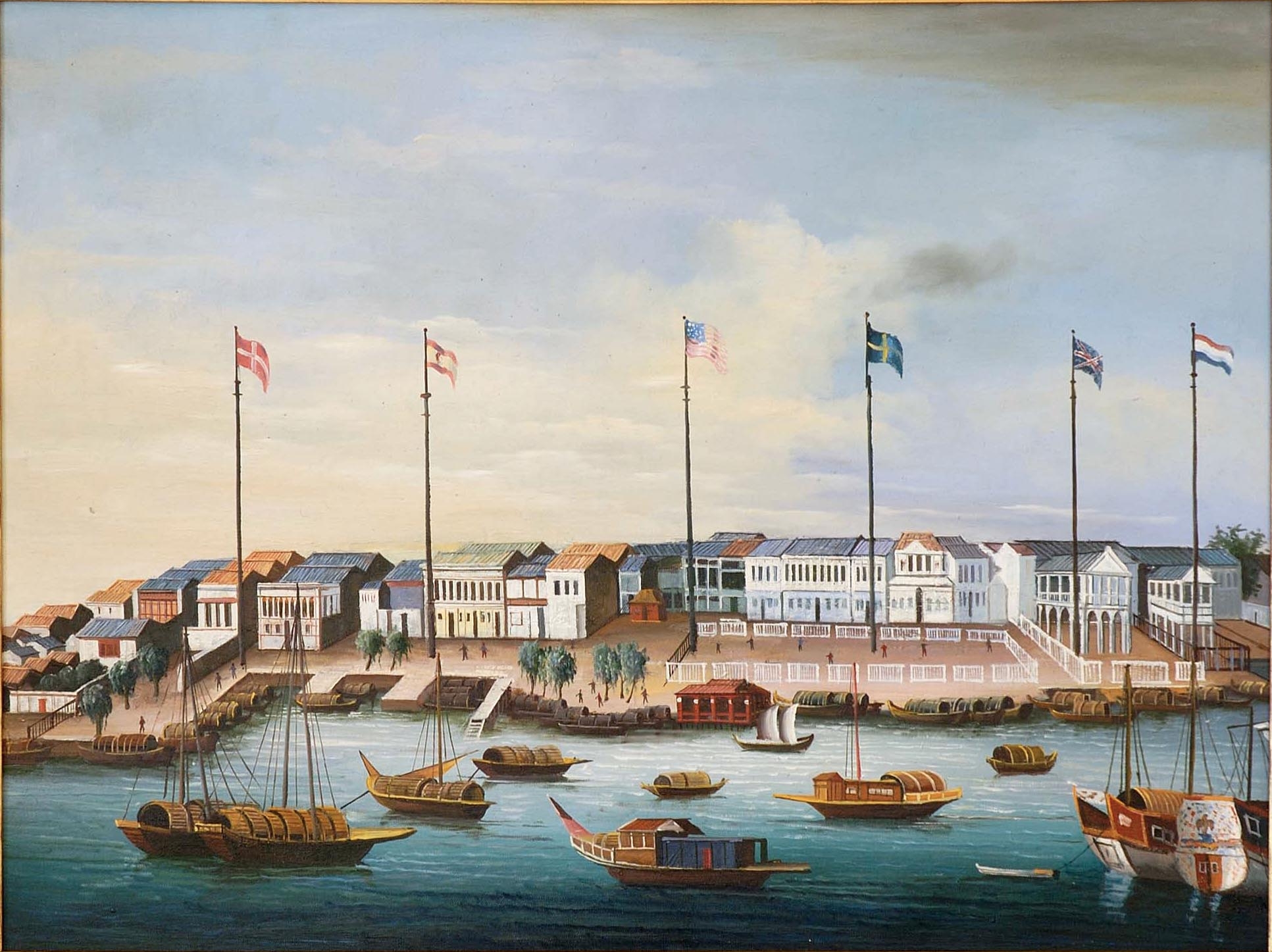
Old China Trade
The Old China Trade () refers to the early commerce between the Qing Empire and the United States under the Canton System, spanning from shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War in 1783 to the Treaty of Wanghia in 1844. The Old China Trade represented the beginning of relations between the United States and East Asia, including eventually U.S.–China relations. The maritime fur trade was a major aspect of the Old China Trade, as was illegal trafficking in opium. The trade era overlapped the First Opium War, which resulted from an attempt by China to enforce its prohibition on opium smuggling by Western traders and blockade-runners between 1839–1842. Origins Anglo-American hostilities ceased in 1783 following the Second Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War and subsequently freed American trade from British control. At the time, increased global demand for tea was one of the primary reasons for a shortage of silver; this was the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indiaman
East Indiaman was a general name for any sailing ship operating under charter or licence to any of the East India trading companies of the major European trading powers of the 17th through the 19th centuries. The term is used to refer to vessels belonging to the Austrian, Danish, Dutch, English, French, Portuguese, or Swedish companies. Some of the East Indiamen chartered by the British East India Company were known as "tea clippers". In Britain, the East India Company held a monopoly granted to it by Queen Elizabeth I of England in 1600 for all English trade between the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Horn. This grant was progressively restricted during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, until the monopoly was lost in 1834. English (later British) East Indiamen usually ran between England, the Cape of Good Hope and India, where their primary destinations were the ports of Bombay, Madras and Calcutta. The Indiamen often continued on to China before returning to England v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinaman (term)
''Chinaman'' () is a term referring to a Chinese man or person, a Mainland Chinese national or, in some cases, a person native to geographical East Asia or of perceived East Asian race. While the term has no negative connotations in older dictionaries and the usage of such compound terms as Englishman, Frenchman, Dutchman, Irishman, and Welshman are sometimes cited as unobjectionable parallels, the term is noted as having pejorative overtones by modern dictionaries. Its derogatory connotations evolved from its use in pejorative contexts regarding Chinese people and other Asians as well as its grammatical incorrectness which resembles stereotypical characterizations of Chinese accents in English-speaking associated with discrimination. While usage of the term ''Chinaman'' is nowadays strongly discouraged by Asian American organizations, it has also been used as a self-referential archetype by authors and artists of Asian descent. It may have come from literal translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Of China (1783)
''Empress of China'', also known as ''Chinese Queen'', was a three-masted, square-rigged sailing ship of 360 tons,Tantillo, Len. (2000) ''The Hudson River in the Age of Sail'' (exhibition). Hudson River Maritime Museum. initially built in 1783 for service as a privateer. After the Treaty of Paris brought a formal end to the American Revolutionary War, the vessel was refitted for commercial purposes. She became the first American ship to sail from the newly independent United States to China, opening what is known today as the Old China Trade and transporting the first official representative of the American government to Canton. First voyage The first American merchant vessel to enter Chinese waters left New York harbor on Washington's birthday, February 22, 1784. The ''Empress'' returned to New York on May 11, 1785 after a round voyage of 14 months and 24 days. The success of the voyage encouraged others to invest in further trading with China. President Washington bought a set o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
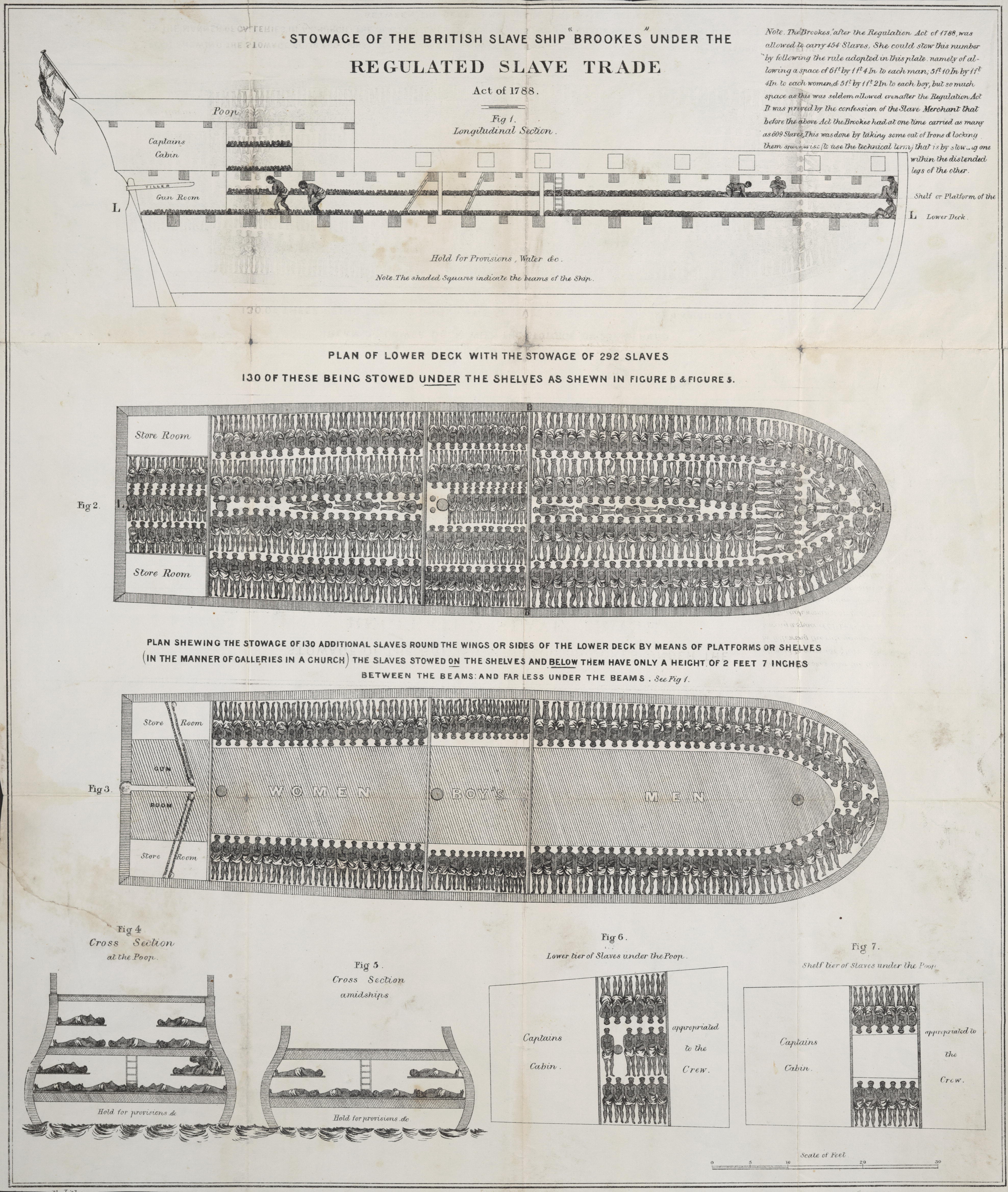
Guineaman
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea (region)
Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the African coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north. Etymology The etymology of "Guinea" is uncertain. The English term ''Guinea'' comes directly from the Spanish word ''Guinea'', which in turn derives from the Portuguese word ''Guiné''. The Portuguese term emerged in the mid-15th century to refer to the lands inhabited by the ''Guineus'', a generic term used by the Portuguese to refer to the 'black' African peoples living south of the Senegal River (in contrast to the 'tawny' Sanhaja Berbers, north of it, whom they called ''Azenegues''). The term "Guinea" is extensively used in the 1453 chronicle of Gomes Eanes de Zurara. King John II of Portugal took up the title of ''Senhor da Guiné'' (Lord of Guinea) from 1481. It is believed the Portuguese borrowed ''Guineus'' from the Berbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Goods
In economics, colonial goods are goods imported from European colonies, in particular coffee, tea, spices, rice, sugar, cocoa and chocolate, and tobacco. At a time when food and agriculture represented a relatively large proportion of overall economic activity, economic statistics often divided traded goods between "colonial goods", "domestic ( agricultural and extractive sectors) production" and "manufactured (secondary sector) production". The term "colonial goods" became less appropriate with the collapse of the western European empires that followed the Second World War. It nevertheless still appeared in books and articles in the 1970s, by now covering not merely agricultural output from (formerly) colonial countries but all long-life staple foods, regardless of provenance, as well as soap, washing powder and petrol/gasoline, and other newly important basic household supplies. Colonial goods stores Colonial goods stores were retailers specializing in colonial goods. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around the Indian Ocean by Portuguese explorers, soon after the Cape route was discovered. Nowadays, this term is broadly used to refer to the Malay Archipelago, which today comprises the Philippine Archipelago, Indonesian Archipelago, Malaysian Borneo, and New Guinea. Historically, the term was used in the Age of Discovery to refer to the coasts of the landmasses comprising the Indian subcontinent and the Indochinese Peninsula along with the Malay Archipelago. Overview During the era of European colonization, territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia were known as the Spanish East Indies for 333 years before the American conquest. Dutch occupied colonies in the area were known for about 300 years as the Dutch East Indies till Indonesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka."Indian subcontinent". ''Oxford Dictionary of English, New Oxford Dictionary of English'' () New York: Oxford University Press, 2001; p. 929: "the part of Asia south of the Himalayas which forms a peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Historically forming the whole territory of Greater India, the region is now divided into three countries named Bangladesh, India and Pakistan." The terms ''Indian subcontinent'' and ''South Asia'' are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indiaman
West Indiaman was a general name for any merchantman sailing ship making runs from the Old World to the West Indies and the east coast of the Americas. These ships were generally strong ocean-going ships capable of handling storms in the Atlantic Ocean. The term was used to refer to vessels belonging to the Danish (e.g. ), Dutch, English, and French (e.g. ) West India companies. Similarly, at the time (18th and 19th centuries) people also referred to East Indiamen (ships trading with the East Indies), Guineamen (slave ships), or Greenlandmen ( whalers in the North Seas whale fishery). British West Indiamen tended to be London-built and to sail directly from England (generally London), to the West Indies. Guineamen tended to be built (or owned) in Bristol and Liverpool, and to sail from Bristol or Liverpool via West Africa in what is now often referred to as the triangular trade in enslaved people. There were London-based Guineamen, (for example ), and Liverpool-based West India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Ships
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine. Early sailing ships were used for river and coastal waters in Ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean. The Austronesian peoples developed maritime technologies that included the fore-and-aft crab-claw sail and with catamaran and outrigger hull configurations, which enabled the Austronesian expansion into the islands of the Indo-Pacific. This expansion originated in Taiwan BC and propagated through Island Southeast Asia, reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |