|
Chico Formation
The Chico Formation is a geologic formation of the Campanian Age during the Cretaceous Period, found in California and southern Oregon. Geology The MesozoicEra formation can regionally overlie the Vaqueros Formation, and can regionally underlie the Martinez Formation or Tejon Formation. The Chico Formation is exposed in the Southern California Coast Ranges, western San Joaquin Valley, north of Mount Diablo, and in the Chico area of the northeastern Sacramento Valley. Google Books: "The stratigraphic and faunal relations of the Martinez forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacramento Valley
, photo =Sacramento Riverfront.jpg , photo_caption= Sacramento , map_image=Map california central valley.jpg , map_caption= The Central Valley of California , location = California, United States , coordinates = , boundaries = Sierra Nevada (east), Cascade Range, Klamath Mountains (north), Coast Range (west), Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta (south) , towns = Redding, Chico, Yuba City, Sacramento , watercourses = Sacramento River The Sacramento Valley is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies north of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the Sacramento River. It encompasses all or parts of ten Northern California counties. Although many areas of the Sacramento Valley are rural, it contains several urban areas, including the state capital, Sacramento. Since 2010, statewide droughts in California have further strained both the Sacramento Valley's and the Sacramento metropolitan region's water security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dinosaur-bearing Rock Formations
This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with few dinosaur genera ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils Containing trace fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur trace fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with ornithischian tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with sauropodomorph tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with theropod tracks See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units * List of fossil sites * Mesozoic The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ... {{DEFAUL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In California
This article contains a list of fossil-bearing stratigraphic units in the state of California, California, U.S. Sites See also * Paleontology in California References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in California Fossiliferous stratigraphic units of the United States, California Paleontology in California, Stratigraphic units Stratigraphy of California, Fossiliferous stratigraphic units California geography-related lists United States geology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteranodontidae
The Pteranodontidae are a family of large pterosaurs of the Cretaceous Period of North America and Africa. The family was named in 1876 by Othniel Charles Marsh. Pteranodontids had a distinctive, elongated crest jutting from the rear of the head (most famously seen in ''Pteranodon'' itself). The spectacularly-crested '' Nyctosaurus'' is sometimes included in this family, though usually placed in its own family, the Nyctosauridae (Nicholson & Lydekker, 1889). Modern researchers differ in their use of the concept. S. Christopher Bennett and Alexander Kellner have concluded that ''Nyctosaurus'' was not a pteranodontid. In 1994 Bennett defined a clade Pteranodontidae, also including species of the Anhangueridae. However, this definition has not been accepted by other workers. Alexander Kellner, for example, named several additional species for specimens previously classified as ''Pteranodon'', and placed ''P. sternbergi'' in a distinct genus, ''Geosternbergia''. Kellner re-defined Pt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
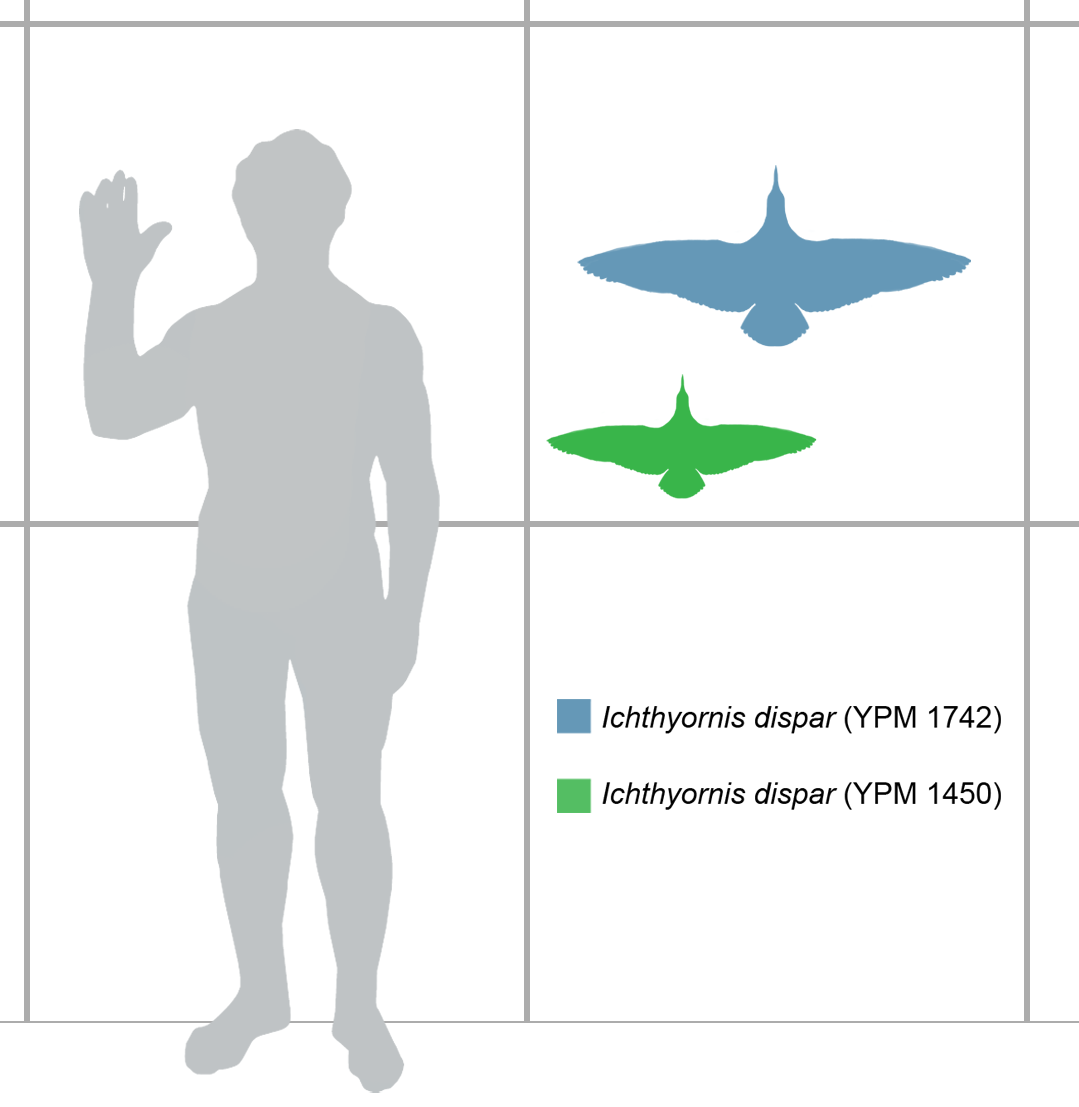
Ichthyornis
''Ichthyornis'' (meaning "fish bird", after its fish-like vertebrae) is an extinct genus of toothy seabird-like ornithuran from the late Cretaceous period of North America. Its fossil remains are known from the chalks of Alberta, Alabama, Kansas (Greenhorn Limestone), New Mexico, Saskatchewan, and Texas, in strata that were laid down in the Western Interior Seaway during the Turonian through Campanian ages, about 95–83.5 million years ago. ''Ichthyornis'' is a common component of the Niobrara Formation fauna, and numerous specimens have been found. ''Ichthyornis'' has been historically important in shedding light on bird evolution. It was the first known prehistoric bird relative preserved with teeth, and Charles Darwin noted its significance during the early years of the theory of evolution. ''Ichthyornis'' remains important today as it is one of the few Mesozoic era ornithurans known from more than a few specimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornis
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornis BW (white Background)
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clidastes
''Clidastes'' is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like ''Mosasaurus'' and ''Prognathodon''. ''Clidastes'' is known from deposits ranging in age from the Coniacian to the early Campanian in the United States. ''Clidastes'' means "locked vertebrae", which originates from the Greek noun κλειδί, or kleid meaning key (akin to Latin ''claudere'' meaning to shut). This refers to how the vertebral processes allow the proximal heads of the vertebrae to interlock for stability and strength during swimming. It was one of the earliest hydropedalIn mosasaurs, the terms "hydropedal" and "plesiopedal" refers to varying limb conditions and varying degrees of adaptations for marine life. Plesiopedal mosasaurs, such as '' Dallasaurus'' or '' Tethysaurus'' were primitive and largely coastal, while later hydropedal mosasaurs were streamlined and well-adapted to marine life. mosasaurs, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do not have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)