|
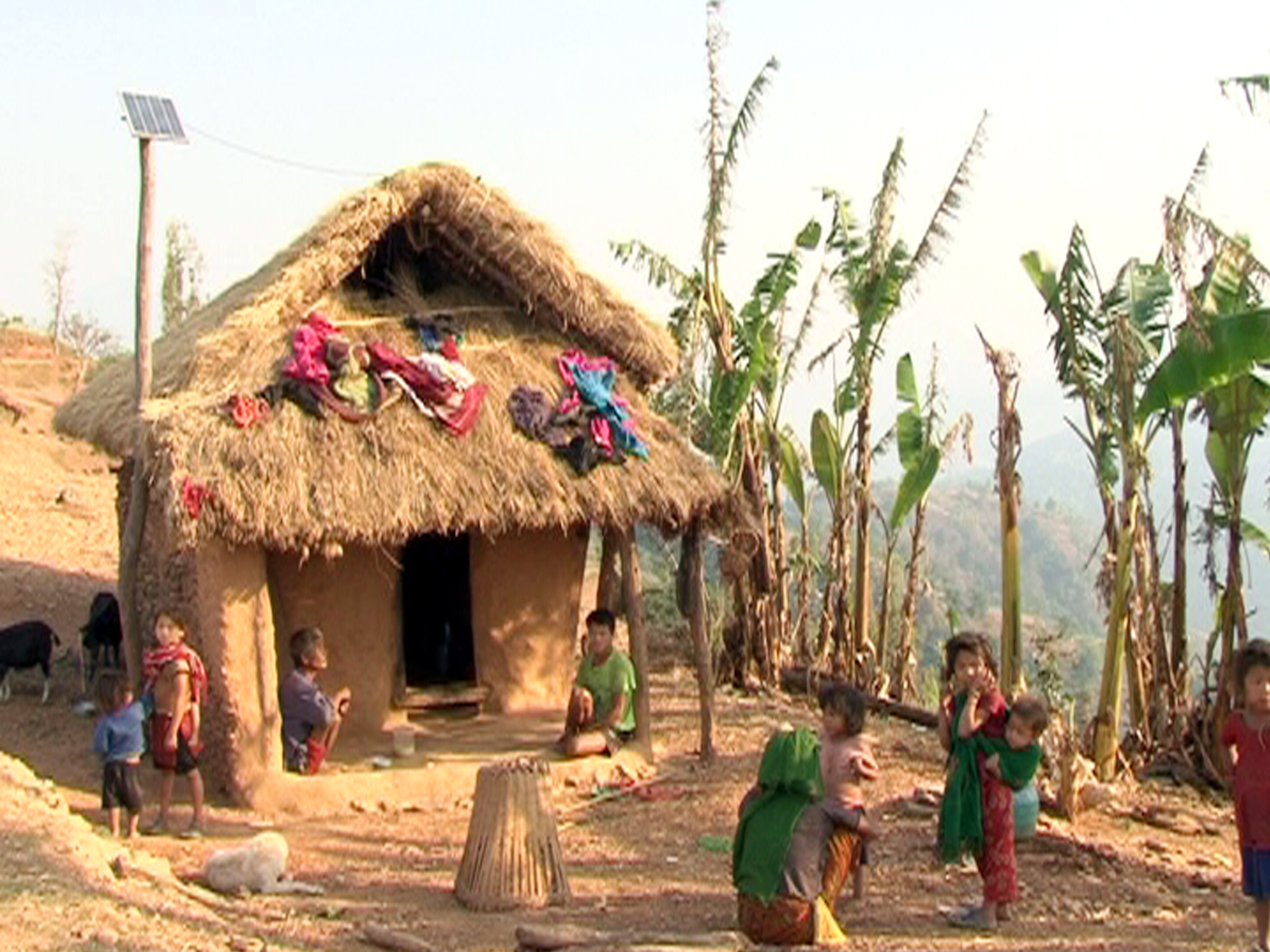
Chepang People
The Chepang, also known as Chewang, are an Tibeto-Burman ethnic group from the rugged ridges of the Mahabharat mountain range of central Nepal.Beine, Caughley and Shrestha. 2012. Chepang Then and Now: Life and Change Among the Chepang of Nepal. Blurb Books. With increasing populations, lack of arable land and few irrigation options, malnutrition has been a historic problem for the Chepang despite forest supplements. The Chepang have often been characterized as the poorest of Nepal's poor. Forced teenage pregnancies are common. Chepang men and women are basically egalitarian and no social ranking exists as it does in caste Nepalese society. Many Chepang cannot read and write due to a lack of education beyond elementary school, and this illiteracy stands in contrast to the great gains Nepal has been making in reducing illiteracy. They are mostly located in Dhading District, Chitwan District, Gorkha District, Makwanpur District, and Tanahu District. Livelihood Over the past two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office. The 2010 Human Development Report introduced an Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI). While the simple HDI remains useful, it stated that "the IHDI is the actual level of human development (accounting for inequality), while the HDI can be viewed as an index of 'potential' human development (or the maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2015 Nepal Blockade
: The 2015 Nepal blockade, which began on 23 September 2015 and lasted about six months, was an economic and humanitarian crisis which severely affected Nepal and its economy. Nepal has accused India of imposing an undeclared blockade triggered by Indian concern about changes to the Nepali constitution, violent ethnic conflict, and Nepal's increasing cooperation with China. India has denied the allegations, stating the supply shortages have been imposed by Madheshi protesters within Nepal. As a landlocked nation, Nepal imports all of its petroleum supplies from India. Roughly 300 fuel trucks enter from India on a normal day, but this had dwindled to a sporadic passage of 5–10 fuel trucks daily since the start of the crisis, though shipments of perishables like fruits and vegetables had generally been allowed to pass. Moreover, India had also been stopping some Nepalese trucks at the Kolkata harbour. The blockade choked imports of not only petroleum, but also medicines a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
April 2015 Nepal Earthquake
The April 2015 Nepal earthquake (also known as the Gorkha earthquake) killed 8,964 people and injured 21,952 more. It occurred at on Saturday, 25 April 2015, with a magnitude of 7.8 Mw or 8.1 Ms and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of X (''Extreme''). Its epicenter was east of Gorkha District at Barpak, Gorkha, roughly northwest of central Kathmandu, and its hypocenter was at a depth of approximately . It was the worst natural disaster to strike Nepal since the 1934 Nepal–Bihar earthquake. The ground motion recorded in Kathmandu, capital of Nepal, was of low frequency, which, along with its occurrence at an hour where many people in rural areas were working outdoors, decreased the loss of property and human lives. The earthquake triggered an avalanche on Mount Everest, killing 22, the deadliest incident on the mountain on record. The earthquake triggered another huge avalanche in the Langtang valley, where 250 people were reported missing. Hundreds of thousands of Nepalese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A ''decimal numeral'' (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the #Decimal fractions, decimal fractions. That is, fraction (mathematics), fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodecimal
The duodecimal system (also known as base 12, dozenal, or, rarely, uncial) is a positional notation numeral system using twelve as its base. The number twelve (that is, the number written as "12" in the decimal numerical system) is instead written as "10" in duodecimal (meaning "1 dozen and 0 units", instead of "1 ten and 0 units"), whereas the digit string "12" means "1 dozen and 2 units" (decimal 14). Similarly, in duodecimal, "100" means "1 gross", "1000" means "1 great gross", and "0.1" means "1 twelfth" (instead of their decimal meanings "1 hundred", "1 thousand", and "1 tenth", respectively). Various symbols have been used to stand for ten and eleven in duodecimal notation; this page uses and , as in hexadecimal, which make a duodecimal count from zero to twelve read 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, , , 10. The Dozenal Societies of America and Great Britain (organisations promoting the use of duodecimal) use turned digits in their published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raji Language
Raji is a small Sino-Tibetan language of Nepal and Uttarakhand, India. Speakers were until recently nomadic. Distribution Raji is spoken in the following areas of southwestern Nepal: *Lumbini Province: Banke and Bardiya districts *Karnali Province: Surkhet *Sudurpashchim Province: Kailali and Kanchanpur districts It is also spoken by Raji people of Uttarakhand, India, primarily living in Pithoragarh district. In Pithoragarh district, Rastogi (2015) reports that Raji is spoken in the hamlets of Kimkhola, Bhogtirua, Ganagaon, Chipaltara, Madanbori, Kutachaurani, Altodi, Jamtadi, Khirdwari and Chakarpur. Dialects Khatri (2008)Khatri, Ramesh. 2008. ''The structure of verbs and sentences of Raji''. MA thesis, Kirtipur: Tribhuvan University. divides Raji into 3 main regional dialects, for which he also provides word lists. *Barabandale: spoken in Jyotinagar, Katasi, Lalbojhi, Kuti, Bhuruwa, Solta, Khairehi, and Keodi of Kailali District; Sundarpur, Bandevi Sibir, Daiji, krishan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raute Language
Raute is a small Sino-Tibetan language of Dadeldhura District, Sudurpashchim Province, Nepal. Some speakers are nomadic. Alternate names include Boto boli, Khamchi, Raji, Rajwar, Ra’te, Rautya, Rautye (''Ethnologue''). Geographical distribution ''Ethnologue'' lists the following locations for historical and present locations of the Raute. *Jogbudha and Sirsa VDC's, Dadeldhura District, Sudurpashchim Province: in Karnali and Mahakali (Kali) rivers watershed regions (800 settled) *Former nomadic camp in Surkhet district, Karnali Province Karnali Province ( ne, कर्णाली प्रदेश) is one of the seven federal provinces of Nepal formed by the new constitution which was adopted on 20 September 2015. The total area of the province is covering 18.97% of the cou ... *Midwest and far west forest regions (about 25 nomads). References Raji–Raute languages Languages of Nepal Languages of Sudurpashchim Province Languages of Karnali Province { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Language
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang
The Tamang (; Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāṅ'') are an Tibeto-Burmese ethnic group of Nepal. In Nepal Tamang/Moormi people constitute 5.6% of the Nepalese population at over 1.3 million in 2001, increasing to 1,539,830 as of the 2011 census. Tamang people are also found in significant numbers in the Indian state of Sikkim and districts of Darjeeling and Kalimpong in West Bengal state of India and various districts in the southern foothills of the Kingdom of Bhutan. Such districts include the Tsirang District, the Dagana District, the Samtse District, the Chukha District, the Sarpang District and the Samdrup Jongkhar District. Emergent North-East : A Way Forward By H. C. Sadangi Tamang language is the fifth most-spoken language in Nepal. Etymology ''Tamang'' may be derived from the word ''Tamang'', where ''Ta'' means "horse" and ''Mak'' means "warrior" in Tibetan. However, there are no written documentations of Horse Riders. Some scientific research claims Tamangs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in History of India, northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a Bhavana, training of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |