|
Chandrayaan-2
Chandrayaan-2 (, ; ) is the second lunar exploration mission developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), after Chandrayaan-1. It consists of a lunar orbiter, and also included the ''Vikram'' lander, and the ''Pragyan'' lunar rover, all of which were developed in India. The main scientific objective is to map and study the variations in lunar surface composition, as well as the location and abundance of lunar water. The spacecraft was launched on its mission to the Moon from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh on 22 July 2019 at 09:13:12 UTC by a GSLV Mark III-M1. The craft reached the Moon's orbit on 20 August 2019 and began orbital positioning manoeuvres for the landing of the ''Vikram'' lander. The lander and the rover were scheduled to land on the near side of the Moon, in the south polar region at a latitude of about 70° south on 6 September 2019 and conduct scientific experiments for one lunar day, which approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragyan (rover)
''Pragyan'' ( sa, प्रज्ञान, translit=prajñana, lit=wisdom ) was the Rover (space exploration), rover of Chandrayaan-2, a lunar mission developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), that launched in July 2019. ''Pragyan'' was destroyed along with its lander, ''Vikram'', when it crash-landed on the Moon in September 2019 and never got the chance to deploy.Vikram lander located on lunar surface, wasn't a soft landing: Isro. ''Times of India''. 8 September 2019. Overview The rover's mass was about and was designed to operate on solar power. The rover was to move on 6 wheels traversing 500 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan Programme
The Chandrayaan programme (), also known as the Indian Lunar Exploration Programme is an ongoing series of outer space missions by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The programme incorporates lunar orbiter, impactor, soft lander and rover spacecraft. The name of the programme is from Sanskrit ' (). Programme structure The Chandrayaan (Indian Lunar Exploration Programme) programme is a multiple mission programme. , one orbiter with an impactor probe has been sent to the Moon, using ISRO's workhorse PSLV rocket. The second spacecraft consisting of orbiter, soft lander and rover was launched on 22 July 2019, by using a GSLV Mk III rocket. In a podcast from AT, VSSC director S. Somanath stated that there will be a Chandrayaan-3 and more follow up missions in Chandrayaan Program. The Chandrayaan-3 mission is expected to launch in 2023. Phase I: Orbiter and Impactor Chandrayaan-1 Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee announced the Chandrayaan project on course in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSLV Mark III
The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM 3), previously referred to as the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk3), is a three-stage medium-lift launch vehicle developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Primarily designed to launch communication satellites into geostationary orbit, it is also due to launch crewed missions under the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. GSLV Mk III has a higher payload capacity than it's predecessor, GSLV Mk II. After several delays and a sub-orbital test flight on 18 December 2014, ISRO successfully conducted the first orbital test launch of GSLV Mk III on 5 June 2017 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre. Total development cost of project was . In June 2018, the Union Cabinet approved to build 10 GSLV Mk III rockets over a five-year period. The GSLV Mk III has launched CARE, India's space capsule recovery experiment module, Chandrayaan-2, India's second lunar mission, and will be used to carry Gaganyaan, the first cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 (, ; ) is a planned third lunar exploration mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Following Chandrayaan-2, where a last-minute glitch in the soft landing guidance software led to the failure of the lander's soft landing attempt after a successful orbital insertion, another lunar mission for demonstrating soft landing was proposed. Chandrayaan-3 will be a mission repeat of Chandrayaan-2 but will only include a lander and rover similar to that of Chandrayaan-2. It will not have an orbiter, but its propulsion module will behave like a communications relay satellite. The spacecraft is scheduled to be launched in June 2023. Background In the second phase of the Chandrayaan programme to demonstrate soft landing on the Moon, ISRO launched Chandrayaan-2 onboard a Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM 3) launch vehicle consisting of an orbiter, a lander and a rover. The lander was scheduled to touchdown on the lunar surface in September 2019 to deploy the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods and the Chinese '' Yutus''. Three countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States and China. An Indian mission failed while Japan and Greece currently have planned missions. Past missions Lunokhod 1 Lunokhod 1 (Луноход) was the first of two polycrystalline-panel-powered robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program after a previous unsuccessful attempt of a launch probe with Lunokhod 0 (No.201) in 1969. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains on November 1970. Lunokhod was the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar South Pole
The lunar south pole is the southernmost point on the Moon, at 90°S. It is of special interest to scientists because of the occurrence of water ice in permanently shadowed areas around it. The lunar south pole region features craters that are unique in that the near-constant sunlight does not reach their interior. Such craters are cold traps that contain a fossil record of hydrogen, water ice, and other volatiles dating from the early Solar System. In contrast, the lunar north pole region exhibits a much lower quantity of similarly sheltered craters. Geography The lunar south pole is located on the center of the polar Antarctic Circle (80°S to 90°S).Lunar South Pole. NASA. 2017. Accessed on 16 July 2019. The lunar south pole has shifted 5 degrees from its original position billion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan-1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impactor. India launched the spacecraft using a PSLV-XL rocket on 22 October 2008 at 00:52 UTC from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. The mission was a major boost to India's space program, as India researched and developed indigenous technology to explore the Moon. The vehicle was inserted into lunar orbit on 8 November 2008. On 14 November 2008, the Moon Impact Probe separated from the Chandrayaan orbiter at 14:36 UTC and struck the south pole in a controlled manner, making India the fourth country to place its flag insignia on the Moon. The probe hit near the crater Shackleton at 15:01 UTC The location of impact was named Jawahar Point. The estimated cost for the project was . It was intended to survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions to the Moon. Its detailed mapping program is identifying safe landing sites, locating potential resources on the Moon, characterizing the radiation environment, and demonstrating new technologies. Launched on June 18, 2009, in conjunction with the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), as the vanguard of NASA's Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, LRO was the first United States mission to the Moon in over ten years. LRO and LCROSS were launched as part of the United States's Vision for Space Exploration program. The probe has made a 3-D map of the Moon's surface at 100-meter resolution and 98.2% coverage (excluding polar areas in deep shadow), including 0.5-meter resolution images of Apollo landing sites. The first images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
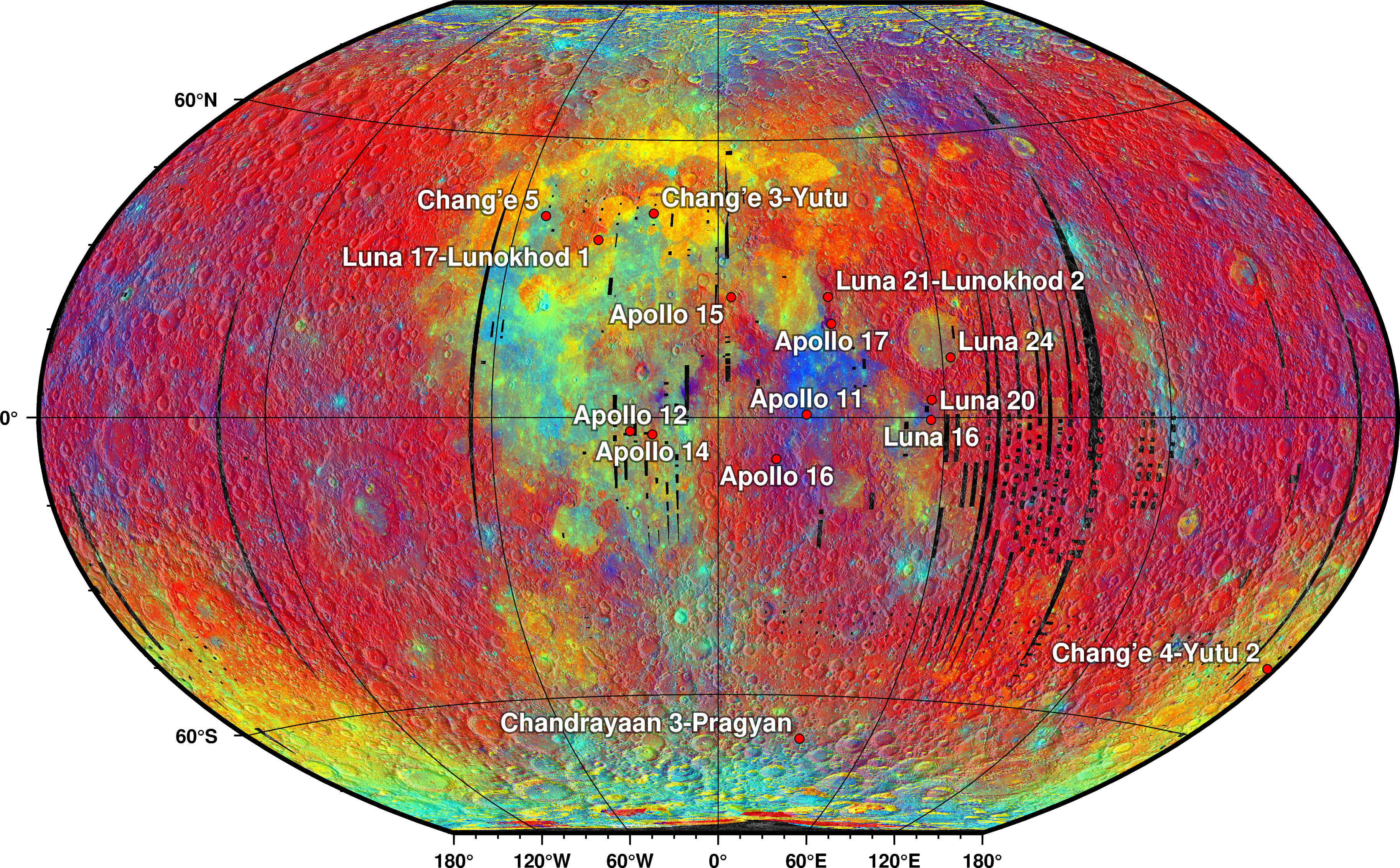
Exploration Of The Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made an impact on the surface of the Moon on September 14, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of exploration had been observation from Earth. The invention of the optical telescope brought about the first leap in the quality of lunar observations. Galileo Galilei is generally credited as the first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes; having made his own telescope in 1609, the mountains and craters on the lunar surface were among his first observations using it. NASA's Apollo program was the only program to successfully land humans on the Moon, which it did six times. The first landing took place in 1969, when Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong placed scientific instruments and returned lunar samples to Earth. The first unmanned landing on the far side of the Moon was made by the Chinese spacecraft Chang'e 4 in early 2019, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kailasavadivoo Sivan
Kailasavadivoo Sivan (born 14 April 1957) is an Indian space scientist who served as the Secretary of the Department of Space and chairman of Indian Space Research Organisation and Space Commission. He has previously served as the Director of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Center and the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre. Early life Sivan was born in Mela Sarakkalvilai, near Nagercoil in Kanyakumari district of Tamil Nadu state of India. His parents are Kailasavadivoo and mother Chellam. Education Sivan is son of a mango farmer and studied in a Tamil medium Government school in Mela Sarakkalvilai Village and later in Vallankumaranvilai in Kanyakumari district. He is the first graduate from his family. Later Sivan graduated with a bachelor's degree in aeronautical engineering from Madras Institute of Technology in 1980. He then got a master's degree in aerospace engineering from Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore in 1982, and started working in ISRO. He earned a doctoral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Orbiter Mission
The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called ''Mangalyaan'', was a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014. It was launched on 5 November 2013 by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was India's first interplanetary mission and it made ISRO the fourth space agency to achieve Mars orbit, after Roscosmos, NASA, and the European Space Agency. It made India the first Asian nation to reach Martian orbit and the first nation in the world to do so on its maiden attempt. The Mars Orbiter Mission probe lifted-off from the First Launch Pad at Satish Dhawan Space Centre ( Sriharikota Range SHAR), Andhra Pradesh, using a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) rocket C25 at 09:08 UTC on 5 November 2013. The launch window was approximately 20 days long and started on 28 October 2013. The MOM probe spent about a month in Earth orbit, where it made a series of seven apogee-raising orbital manoeuvres before trans-Mars injection on 30 November 2013 ( UTC). After a 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_launches_with_LRO_and_LCROSS.jpg)

