|
Cathal Mac Finguine
Cathal mac Finguine (died 742) was an Irish King of Munster or Cashel, and effectively High King of Ireland as well. He belonged to the Eóganacht Glendamnach sept of the dominant Eóganachta kin-group whose members dominated Munster from the 7th century to the 10th. His father, uncle, grandfather and great-grandfather had also been kings of Cashel, as were his son and grandson. Cathal's conflict with the Uí Néill kings, Fergal mac Máele Dúin, Flaithbertach mac Loingsig, and Áed Allán, son of Fergal mac Máele Dúin, is reported at some length in the Irish annals, and again northern and southern versions provide differing accounts. Cathal also appears as a character, not always portrayed sympathetically as in ''Aislinge Meic Con Glinne'' where he is possessed by a demon of gluttony, in a number of prose and verse tales in the Middle Irish language. Widely regarded as the most powerful Irish king of the first half of the 8th century, and the strongest (historical) ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Munster
The kings of Munster ( ga, Rí Mumhan), ruled from the establishment of Munster during the Irish Iron Age, until the High Middle Ages. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as the ''Book of Invasions'', the earliest king of Munster was Bodb Derg of the Tuatha Dé Danann. From the Gaelic peoples, an Érainn kindred known as the Dáirine (also known as Corcu Loígde and represented today in seniority by the Ó hEidirsceoil), provided several early monarchs including Cú Roí. In a process in the '' Cath Maige Mucrama'', the Érainn would lose out in the 2nd century AD to the Deirgtine, ancestors of the Eóganachta. Munster during this period was classified as part of ''Leath Moga'', or the southern-half, while other parts of Ireland were ruled mostly by the Connachta. After losing Osraige to the east, Cashel was established as the capital of Munster by the Eóganachta. This kindred ruled without interruption until the 10th century. Although the High K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faílbe Flann Mac Áedo Duib
Faílbe Flann mac Áedo Duib (died 639) was a King of Munster from the Eóganacht Chaisil branch of the Eoganachta. He succeeded Cathal mac Áedo Flaind Chathrach of the Glendamnach branch in 628. He was the younger brother of a previous king Fíngen mac Áedo Duib (d. 618). His sobriquet Flann meant "blood-red". Career In 629, he fought the Battle of Carn Feradaig (Cahernarry, County Limerick) versus Guaire Aidne mac Colmáin (d.663) of the Ui Fiachrach Aidhne of Connachta. Faílbe won the battle and Guaire was put to flight and his ally Conall mac Máele Dúib of the Uí Maine and many Connaught nobles were slain. Guaire ruled at the height of Ui Fiachrach power in south Connaught and sought to recover the lost Connaught territories in Thomond. Byrne believes that the true expansion of the Deisi into County Clare dates from this battle. The other important event of his reign was the Battle of Áth Goan in the western Liffey plain fought in 636. In this battle Faílbe i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eóganacht Chaisil
Eóganacht Chaisil were a branch of the Eóganachta, the ruling dynasty of Munster between the 5th and 10th centuries. They took their name from Cashel (County Tipperary) which was the capital of the early Catholic kingdom of Munster. They were descended from Óengus mac Nad Froích (died 489), the first Christian King of Munster, through his son Feidlimid mac Óengusa. In the seventh century, they split into two main clans. Cenél Fíngin descended from Fíngen mac Áedo Duib (d. 618) and became the O'Sullivans and MacGillycuddys. The McGillycuddy are a sept of the O'Sullivan's. A descendant of Fíngen was Feidlimid mac Cremthanin (d. 847). Clann Faílbe descended from Faílbe Flann mac Áedo Duib (d. 639) and became the MacCarthy dynasty, rulers of the Kingdom of Desmond following their displacement by the Normans. The O'Callaghans belong to the same line as the MacCarthys, while the MacAuliffes are a sept of the MacCarthys. The Eóganacht Chaisil were considered part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
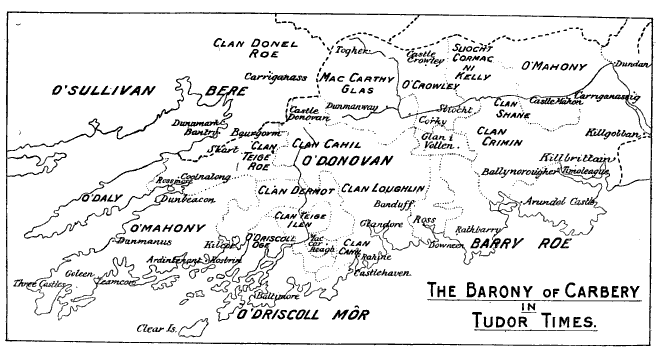
Corcu Loígde
The Corcu Loígde (Corcu Lóegde, Corco Luigde, Corca Laoighdhe, Laidhe), meaning Gens of the Calf Goddess, also called the Síl Lugdach meic Itha, were a kingdom centred in West County Cork who descended from the proto-historical rulers of Munster, the Dáirine, of whom they were the central royal sept. They took their name from Lugaid Loígde "Lugaid of the Calf Goddess", a King of Tara and High King of Ireland, son of the great Dáire Doimthech (a quo Dáirine). A descendant of Lugaid Loígde, and their most famous ancestor, is the legendary Lugaid Mac Con, who is listed in the Old Irish ''Baile Chuinn Chétchathaig''. Closest kin to the Corcu Loígde were the Dál Fiatach princes of the Ulaid. Overview The Corcu Loígde were the rulers of Munster, and likely of territories beyond the province, until the early 7th century AD, when their ancient alliance with the Kingdom of Osraige fell apart as the Eóganachta rose to power. Many peoples formerly subject to the Corcu Loíg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aimend
In Irish mythology and genealogy, Aimend is the daughter of Óengus Bolg, king of the Dáirine or Corcu Loígde. She marries Conall Corc, founder of the Eóganachta dynasties, and through him is an ancestor of the "inner circle" septs of Eóganacht Chaisil, Eóganacht Glendamnach, and Eóganacht Áine, who established the powerful kingship of Cashel. Details of the story imply she may have originally been a goddess (Byrne 2001: 166, 193). Etymology This name appears to be derived from Proto-Celtic *''aidu-mandā''. The name literally means "burning stain," which may have been a byword for the notion of ‘sunburn’ (q.v . The |
Conall Corc
Corc mac Luigthig (340-379),Genealogy of the House of Mac-Carthy formerly Sovereign of the Two Momonies or Southern Ireland, P. Louis Lainé, pg. 26, https://celt.ucc.ie/published/F830000-001.html also called Conall Corc, Corc of Cashel, and Corc mac Láire, is the hero of Irish language tales which form part of the origin legend of the Eóganachta, a group of kindreds which traced their descent from Conall Corc and took their name from his ancestor Éogan Mór. The early kindred they belonged to are known as the Deirgtine. He was probably a grandson of Ailill Flann Bec, and possible cousins were Dáire Cerbba and the famous Crimthann mac Fidaig. The latter is his opponent in a celebrated cycle of stories. Biography The name and identity of Corc's actual father is something of a mystery, however. While certainly belonging to the kindred of the proto-Eóganachta, he is inconsistently named in the genealogies and tales as Lugaid or Láre. Further confusion is caused by the fact tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uraicecht Becc
''Uraicecht Becc'' (Old Irish for "Small Primer"; ''uraicecht'' is a variant of ''airaiccecht'' 'air''- 'before' + ''aiccecht'' 'instruction,' from Latin ''acceptum'' 'primer') is an Old Irish legal tract on status. Of all status tracts, it has the greatest breadth in coverage, including not only commoners, kings, churchmen and poets, but also a variety of other professional groups, including judges. However, it does not go into as much detail for each group and level as do other status tracts. T.M. Charles-Edwards suggests that it is "almost certainly of Munster origin", as it asserts the supremacy of the king of Munster above other Irish kings and makes reference to the monasteries of Emly and Cork.T.M. Charles-Edwards, "Early Irish law." In ''A New History of Ireland'', p. 347. Poets The Small Primer goes into detail regarding the poets' place in Irish society. It lists the seven grades of poets, including their honor price, and the pay earned for the various meters they could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Érainn
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this settlement has the same name as the island as a whole, Ivernia (, '). It was probably once the name given to all the peoples of Ireland, but by Ptolemy's time had a more restricted usage applicable to the inhabitants of the south-west. These Iverni can be identified linguistically with the Érainn (Éraind, Érnai, Érna), a people attested in Munster and elsewhere in the early Middle Ages. The prehistoric Érainn royal dynasties are sometimes referred to as the Dáirine. Etymology The name Iverni has been derived from Archaic Irish ''*Īwernī'' meaning "folk of ''*Īweriū'' " (the island of Ireland). This is in turn derived from Proto-Celtic *''Φīwerjon-'' and further from Proto-Indo-European *''piHwerjon-'' (the fertile land), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dáirine
The Dáirine (Dárine, Dáirfine, Dáirfhine, Dárfine, Dárinne, Dairinne), later known dynastically as the Corcu Loígde and associated, were the proto-historical rulers of Munster before the rise of the Eóganachta in the 7th century AD. They were derived from or closely associated with the Darini of Ptolemy and were also related to the Ulaid and Dál Riata of Ulster and Scotland.O'Rahilly 1946 Their ancestors appear frequently in the Ulster Cycle. In historical times the Dáirine were represented, as stated, by the Corcu Loígde, the Uí Fidgenti and Uí Liatháin, as well as a few other early historical kindreds of both Munster and Ulster. In ancient genealogical schemes, the historical Dál Fiatach of Ulaid also belong to the Dáirine. History Dáirine can sometimes refer to the Érainn dynasties as a whole instead of the distinct royal septs mentioned above. The Dáirine of Munster were said to descend from a certain Dáire (''*Dārios''), both Dáire Doimthech (Sírc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulaid
Ulaid (Old Irish, ) or Ulaidh ( Modern Irish, ) was a Gaelic over-kingdom in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages made up of a confederation of dynastic groups. Alternative names include Ulidia, which is the Latin form of Ulaid, and in Cóiced, Irish for "the Fifth". The king of Ulaid was called the '' rí Ulad'' or ''rí in Chóicid''. Ulaid also refers to a people of early Ireland, and it is from them that the province of Ulster derives its name. Some of the dynasties in the over-kingdom claimed descent from the Ulaid, but others are cited as being of Cruithin descent. In historical documents, the term Ulaid was used to refer to the population group of which the Dál Fiatach was the ruling dynasty. As such, the title ''Rí Ulad'' held two meanings: over-king of Ulaid and king of the Ulaid, as in the Dál Fiatach. The Ulaid feature prominently in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. According to legend, the ancient territory of Ulaid spanned the whole of the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laigin
The Laigin, modern spelling Laighin (), were a Gaelic population group of early Ireland. They gave their name to the Kingdom of Leinster, which in the medieval era was known in Irish as ''Cóiced Laigen'', meaning "Fifth/province of the Leinstermen" (Modern Irish Cúige Laighean), where their descendants ruled till the 17th century. Their territory, located in south-east Ireland, is thought to have once extended from the River Shannon to the River Boyne. The surnames of those descended from the Laigin are still counted amongst the most numerous in Ireland. Etymology Laigin is a plural noun, indicating an ethnonym rather than a geographic term, but the Irish system of naming territories meant that an area tended to be named after an apical ancestor-figure even when the ruling dynasty had no links to that figure. The origin of their name is uncertain; however, it is traditionally assumed to derive from the Irish word ', meaning 'a spear'. Early texts use names ''Laigen'' and ''Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Tara
The term Kingship of Tara () was a title of authority in ancient Ireland - the title is closely associated with the archaeological complex at the Hill of Tara. The position was considered to be of eminent authority in medieval Irish literature and Irish mythology, although national kingship was never a historical reality in early Ireland. The term also represented a prehistoric and mythical ideal of sacred kingship in Ireland. Holding the title King of Tara invested the incumbent with a powerful status. Many Irish High Kings were simultaneously Kings of Tara. The title emerged in the ninth and tenth centuries. In later times, actual claimants to this title used their position to promote themselves in status and fact to the High Kingship. Prior to this, various branches of the Uí Néill dynasty appear to have used it to denote overlordship of their kindred and realms. It was associated with ''Feis Temro'' (Feast of Tara), a pagan inauguration rite. The titles King of Tara an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |