|
Castor Moving Group
The Castor Moving Group, or Castor stream, is a moving group of stars sharing similar velocities and directions. The stars that have been identified as part of the group include Castor, Fomalhaut, Vega, α Cephei and α Librae. While the reported group members are young (typically with ages of hundreds of millions of years), recent results suggest that the velocity differences amongst the moving group stars are too large for them to have possibly shared a common origin. Discovery and constituents The moving group was first proposed by J. P. Anosova, and V. V. Orlov in 1990. Anosova and Orlov originally proposed 15 members. In 1999, Barrado y Navascues presented a membership list of 16 stars, and estimated a group age of 200 million years. The membership of the group has not been well-established and varies quite a bit amongst studies. Physicality of the Group There is controversy over whether the Castor Moving Group constitutes a physical group of stars of shared origin (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more stars. The stars share a common origin, but have become gravitationally unbound and are still moving together through space. Associations are primarily identified by their common movement vectors and ages. Identification by chemical composition is also used to factor in association memberships. Stellar associations were first discovered by the Soviet Armenian astronomer Victor Ambartsumian in 1947. The conventional name for an association uses the names or abbreviations of the constellation (or constellations) in which they are located; the association type, and, sometimes, a numerical identifier. Types Victor Ambartsumian first categorized stellar associations into two groups, OB and T, based on the properties of their stars. A third category, R, was later suggested by Sidney van den Bergh for associations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Phoenicis
κ Phoenicis, Latinized as Kappa Phoenicis, is a single star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye as a white-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.94. The distance to this star is approximately 77.7 light years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +11 km/s. It is a member of the Castor Moving Group of co-moving stars. This object has a stellar classification of A5IVn, which matches the spectrum of an A-type subgiant star with "nebulous" lines due to rapid rotation. It is 348 million years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 245 km/s. The star has 1.7 times the mass of the Sun and 2.0 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 10.7 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 7,320 K. The star displays an infrared excess that matches the signature of a debris disk A debris dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
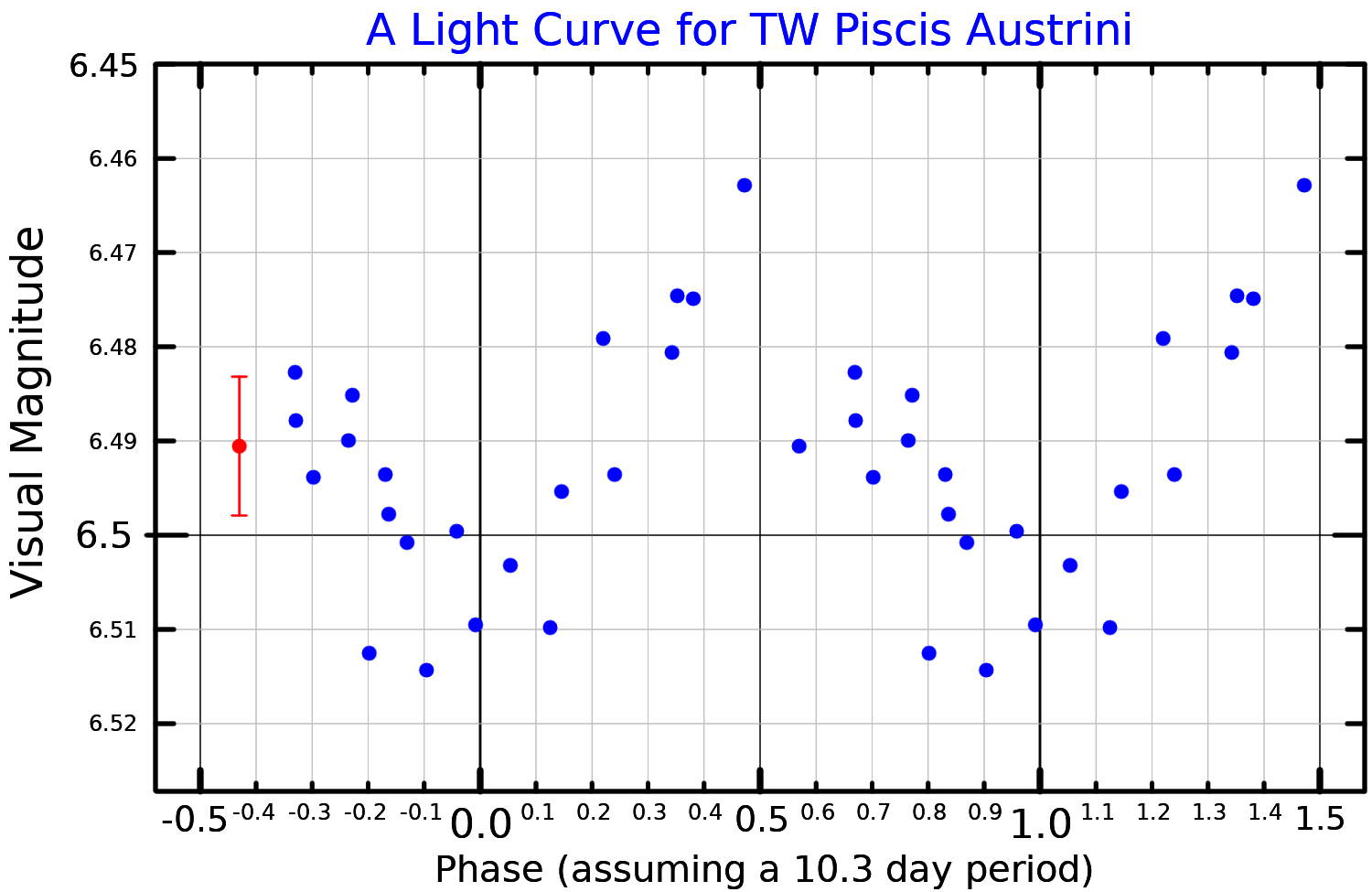
TW Piscis Austrini
TW Piscis Austrini (also Fomalhaut B) is a dwarf star in the constellation Piscis Austrinus. It lies relatively close to the Sun, at an estimated distance of 24.8 light-years. To an observer on Earth the star is visually separated from its larger companion Fomalhaut A by 2 degrees—the width of four full moons. The TW in the name is a variable star designation. This is a variable star of the type known as a BY Draconis variable, with surface brightness variations causing the changes as the star rotates. It varies slightly in apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's ..., ranging from 6.44 to 6.51 over a 10.3-day period. TW Piscis Austrini lies within a light-year of Fomalhaut A. Due to sharing the same proper motion, and the same estimated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 896 AB
Gliese may refer to: * Rochus Gliese (1891—1978), a German actor, director, production designer, and art director * Wilhelm Gliese (1915–1993), a German astronomer, best known for the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars * Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars, a modern star catalog of stars located within 25 parsecs of the Earth * Gliese 163, a red dwarf located 49 light years from the Sun * Gliese 229, a binary system composed of a red dwarf and a brown dwarf about 19 light years away in the constellation Lepus. * Gliese 581, a red dwarf orbited by several extra-solar planets, at least ** Gliese 581d, a planet in the star's habitable zone * Gliese 667, a triple star system in the constellation of Scorpius containing exoplanet GJ 667 Cc in one of the stars' habitable zone * Gliese 682, a red dwarf in the constellation of Scorpius with two candidate planets, one of which is in the star's habitable zone * Gliese 710, a star projected to pass through the Oort Cloud in 1.35 million y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 842
Gliese may refer to: * Rochus Gliese (1891—1978), a German actor, director, production designer, and art director * Wilhelm Gliese (1915–1993), a German astronomer, best known for the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars * Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars, a modern star catalog of stars located within 25 parsecs of the Earth * Gliese 163, a red dwarf located 49 light years from the Sun * Gliese 229, a binary system composed of a red dwarf and a brown dwarf about 19 light years away in the constellation Lepus. * Gliese 581, a red dwarf orbited by several extra-solar planets, at least ** Gliese 581d, a planet in the star's habitable zone * Gliese 667, a triple star system in the constellation of Scorpius containing exoplanet GJ 667 Cc in one of the stars' habitable zone * Gliese 682, a red dwarf in the constellation of Scorpius with two candidate planets, one of which is in the star's habitable zone * Gliese 710, a star projected to pass through the Oort Cloud in 1.35 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 119124
HD 119124 is a wide binary star system in the circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.3, it lies below the normal brightness limit of stars that are visible with the naked eye under most viewing conditions. An annual parallax shift of 39.24 mas for the A component provides a distance estimate of 83 light years. The pair are candidate members of the Castor Moving Group, which implies a relatively youthful age of around 200 million years. HD 119124 is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −12 km/s. This system was first identified as a double star by Friedrich von Struve (1793−1864) and catalogued as the 1774th entry in his list. As of 2015, the magnitude 10.5 K-type companion star was located at an angular separation of 18.10 arc seconds along a position angle of 135° from the brighter primary. They appear to be gravitationally bound with an estimated orbital period of around 7,000&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)