|
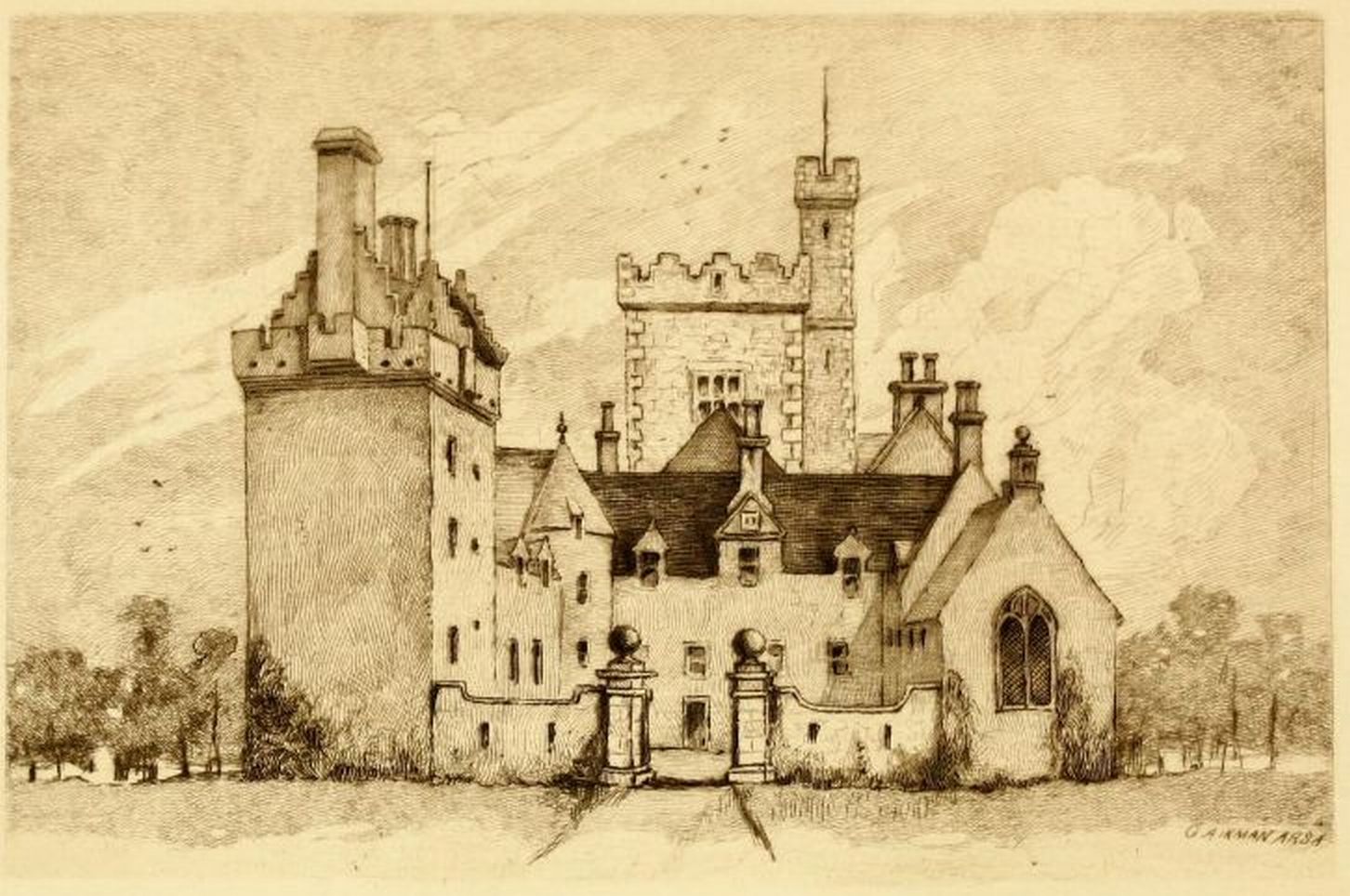
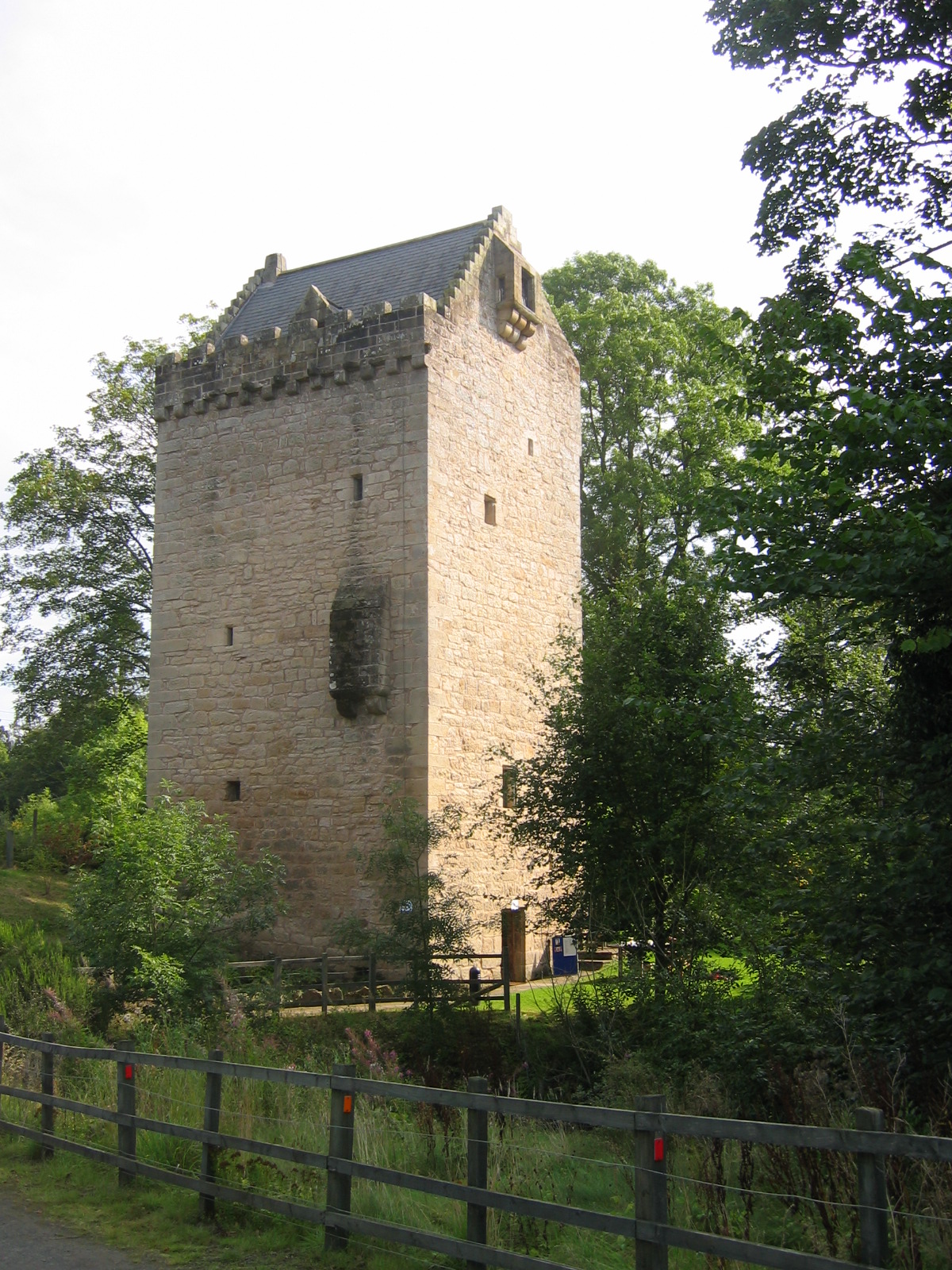
Cardoness Castle
Cardoness Castle is a well-preserved 15th-century tower house just south west of Gatehouse of Fleet, in the historical county of Kirkcudbrightshire in Scotland. It was originally owned by the MacCullochs of Myreton. They abandoned the castle in the late 17th century, following the execution of Sir Godfrey McCulloch for the murder of a Clan Gordon neighbour. It is now in the care of Historic Environment Scotland, and is a scheduled monument. History Around 1170 the lands of Anwoth were granted by Malcolm IV to David fitz Teri, a Cumbrian lord, who built a motte-and-bailey castle at Boreland, close to the present castle. In 1220 a Nicholas de Kerdenes and his wife Cicely were in dispute with the monastery at Dundrennan over Cicely's dowry—he eventually appealed to the Pope. In 1277, Bertram de Kerdennes was a witness to a charter by King Alexander III (reigned 1249–1286), confirming a grant by Devorguilla de Balliol to Glasgow Cathedral. On 18 June 1342 Malcolm Fleming, Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower House
A tower house is a particular type of stone structure, built for defensive purposes as well as habitation. Tower houses began to appear in the Middle Ages, especially in mountainous or limited access areas, in order to command and defend strategic points with reduced forces. At the same time, they were also used as an aristocrat's residence, around which a castle town was often constructed. Europe After their initial appearance in Ireland, Scotland, the Frisian lands, Basque Country and England during the High Middle Ages, tower houses were also built in other parts of western Europe, especially in parts of France and Italy. In Italian medieval communes, urban ''palazzi'' with a very tall tower were increasingly built by the local highly competitive patrician families as power centres during times of internal strife. Most north Italian cities had a number of these by the end of the Middles Ages, but few now remain, notably two towers in Bologna, twenty towers in Pavia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Fleming, Earl Of Wigtown
Malcolm Fleming, Earl of Wigtown (died c. 1363) was the son of Robert Fleming, a Stewart vassal and holder of the lands of Fulwood and Cumbernauld, who died sometime before 1314. He was the "foster-father" of King David II of Scotland and became the first man to hold the title Earl of Wigtown. Malcolm was given the barony of Kirkintilloch forfeited from the Comyns by King Robert I of Scotland during the First War of Scottish Independence and received other lands in Lennox and Wigtownshire. Malcolm became Sheriff of Dumbarton and keeper of the castle thereafter. Malcolm was on the defeated Bruce side at the Battle of Halidon Hill in July 1333, but managed to escape, and fled back to Dumbarton. He was partly responsible for sending the boy king, Robert's son David II from Dumbarton to exile in France. When David II returned to Scotland in 1341, David granted Malcolm much of western Galloway (Wigtownshire) and the burgh of Wigtown, and created for him the new title, "Earl of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Scotland Properties In Dumfries And Galloway
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Ancient Monuments In Dumfries And Galloway
A schedule or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are intended to take place. The process of creating a schedule — deciding how to order these tasks and how to commit resources between the variety of possible tasks — is called scheduling,Ofer Zwikael, John Smyrk, ''Project Management for the Creation of Organisational Value'' (2011), p. 196: "The process is called scheduling, the output from which is a timetable of some form". and a person responsible for making a particular schedule may be called a scheduler. Making and following schedules is an ancient human activity. Some scenarios associate this kind of planning with learning life skills. Schedules are necessary, or at least useful, in situations where individuals need to know what time they must be at a specific location to receive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Dumfries And Galloway
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Kirkcudbrightshire
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Maiden
The Maiden (also known as the Scottish Maiden) is an early form of guillotine, or gibbet, that was used between the 16th and 18th centuries as a means of execution in Edinburgh, Scotland. The device was introduced in 1564 during the reign of Mary Queen of Scots, and was last used in 1716. It long predates the use of the guillotine during the French Revolution. Manufactured in Edinburgh, the Maiden is built of oak, with a lead weight and iron blade. It is displayed at the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh. History Beheading machines were not a new idea: a European example is shown in a 1539 illustration by Lucas Cranach the Elder. By 1563, the sword used for executions in Edinburgh was worn out, and in February of that year funds were used to pay for the loan of a sword for a beheading. After this, the Maiden was constructed to an order from the Provost and Magistrates of Edinburgh in 1564,Maxwell, H Edinburgh, A Historical Study', Williams and Norgate (1916), pp. 137, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
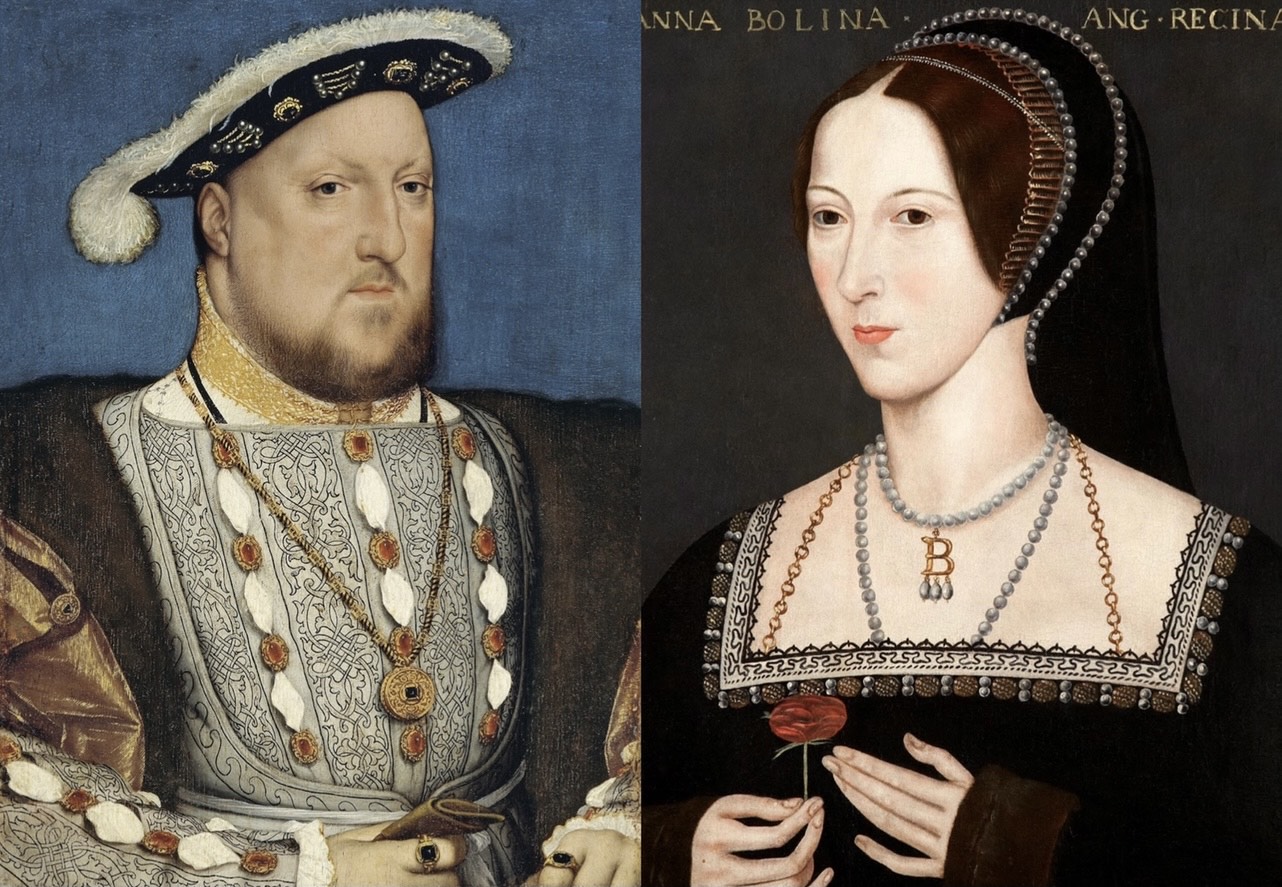
Elizabeth I Of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen". Elizabeth was the daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, his second wife, who was executed when Elizabeth was two years old. Anne's marriage to Henry was annulled, and Elizabeth was for a time declared illegitimate. Her half-brother Edward VI ruled until his death in 1553, bequeathing the crown to Lady Jane Grey and ignoring the claims of his two half-sisters, the Catholic Mary and the younger Elizabeth, in spite of statute law to the contrary. Edward's will was set aside and Mary became queen, deposing Lady Jane Grey. During Mary's reign, Elizabeth was imprisoned for nearly a year on suspicion of supporting Protestant rebels. Upon her half-sister's death in 1558, Elizabeth succeeded to the throne and set out to rule by good counsel. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Andrew Agnew, 8th Baronet
Sir Andrew Agnew, 8th Baronet DL (2 January 1818 – 25 March 1892) was a British politician and baronet. Early life Agnew was born in Edinburgh, Scotland on 2 January 1818 into the Scottish Lowlands Clan Agnew.George Edward Cokayne, editor, ''The Complete Baronetage, 5 volumes'' (); reprint, Gloucester, U.K.: Alan Sutton Publishing, 1983, volume II, page 370. He was the oldest son of Sir Andrew Agnew, 7th Baronet and his wife Madeline Carnegie. Among his siblings was younger brother Sir Stair Agnew, the Registrar General for Scotland. His paternal grandparents were Andrew Agnew (a son of Sir Stair Agnew of Lochnaw, 6th Baronet) and Hon. Martha de Courcy (the daughter of John de Courcy, 19th Baron Kingsale). His maternal grandparents were the former Agnes Murray Elliot (a daughter of Gov. Andrew Elliot) and Sir David Carnegie, 4th Baronet. The office of Sheriff of Wigtown was hereditary in the Agnew family for more than 400 years, until 1747, when the 5th Baronet was com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mochrum
Mochrum () is a coastal civil and Church of Scotland parish situated to the east of Luce Bay on the Machars peninsula and southwest of Wigtown and in the historical county of Wigtownshire in Galloway, Scotland. It covers and is approximately in length and in breadth. The parish contains the eponymous village of Mochrum, as well as Port William and the clachan of Elrig. Etymology Mochrum is recorded as ''Mochrumm'' in Blaeu as a hill-name. It is a Cumbric name formed of the elements ''moch'' 'pigs, swine' and ''drum'' 'ridge'. It is possible, but unlikely, that the name is Gaelic rather than Cumbric, formed of the cognate elements ''muc-druim''. Kirk of Mochrum Mochrum kirk was built on the site of a previous church building dating back to the 12th century. The former building was largely destroyed by fire in the 1770s, and the current building used most of the former building's rectangular walls in its construction in 1794, and was substantially altered again ca. 1840. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excambion
In Scots law, excambion is the exchange of land. The deed whereby this is effected is termed "Contract of Excambion". There is an implied real warranty in this contract, so that if one portion is evicted or taken away on a superior title, the party losing the property is entitled to demand the return of the other given in exchange. Entailed lands were allowed, under certain limitations and conditions, to be exchanged by the Act 10 Geo. III. c. 51, extended by the 6 and 7 Will. IV. c. 42, and still more so by 11 and 12 Vict. c. 36, s. 5 (1848). Alternate spellings include "excambie", "excamb", "excambiator" (an exchanger, a broker). The term is derived from Latin "''excambium''" (n. an exchange). See also * Tailzie *Property law Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property (land) and personal property. Property refers to legally protected claims to resources, such as land and personal property, including intellectual pro ... Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)