|
Capsulorhexis
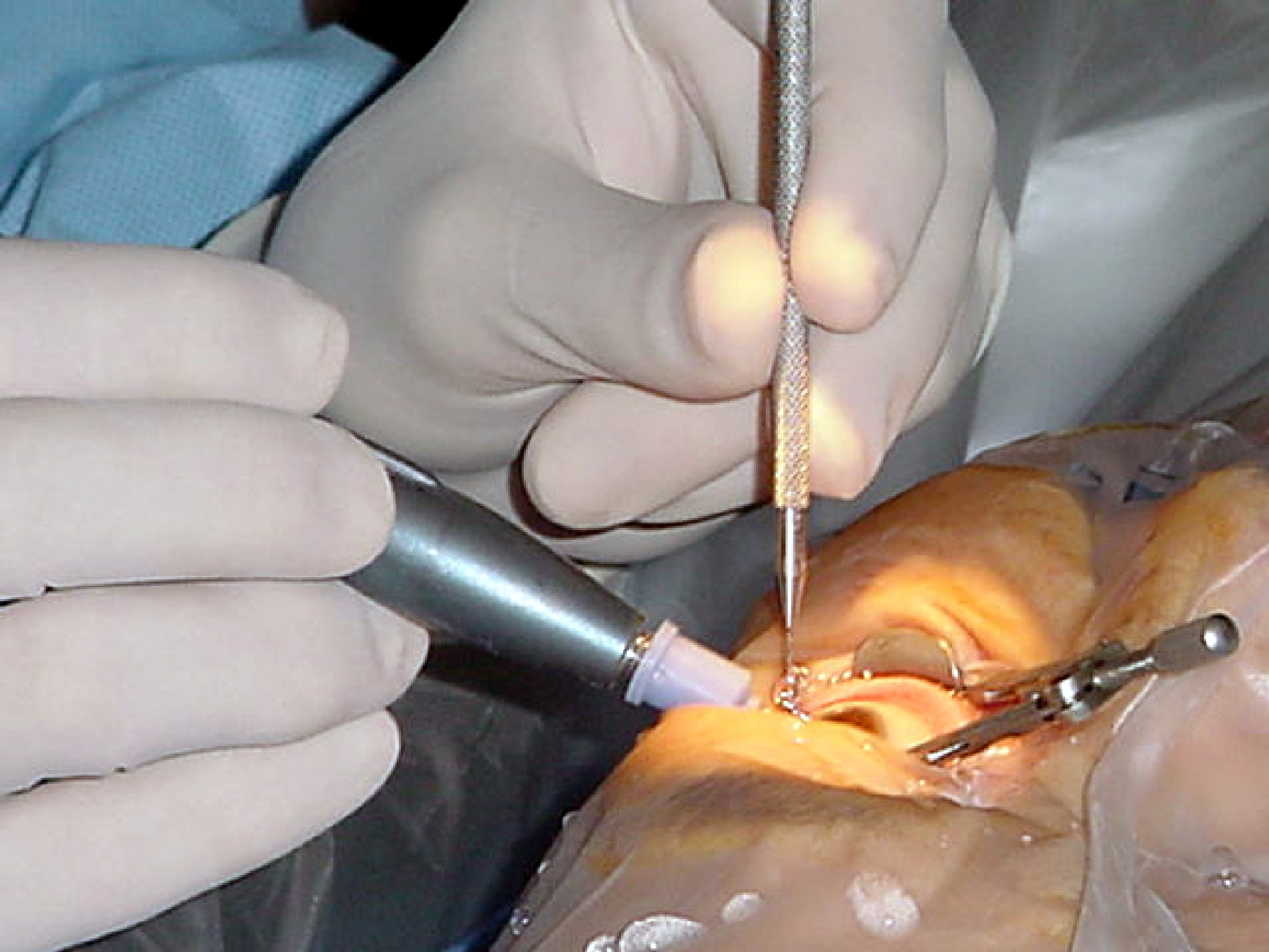
Capsulorhexis or capsulorrhexis, and the commonly used technique known as continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC), is a surgical technique used to remove the central anterior part of the capsule of the lens from the eye during cataract surgery by shear and tensile forces. It generally refers to removal of the central part of the anterior lens capsule, but in situations like a developmental cataract a part of the posterior capsule is also removed by a similar technique. In order to remove a cataract by extracapsular techniques, the capsule of the lens must be opened. In earlier intracapsular cataract extraction, the whole lens and capsule was removed at the same time. This was done to prevent the inflammatory response to leftover lens material. Since it was all removed ''en-bloc'', there was no residual lens material. With effective aspiration practically all the material can be removed while leaving the posterior capsule intact. This provides a barrier between the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract, and its replacement with an intraocular lens. Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over time lead to the development of the cataract, causing impairment or loss of vision. Some infants are born with congenital cataracts, and certain environmental factors may also lead to cataract formation. Early symptoms may include strong glare from lights and small light sources at night, and reduced acuity at low light levels. During cataract surgery, a patient's cloudy natural cataract lens is removed, either by emulsification in place or by cutting it out. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted in its place. Cataract surgery is generally performed by an ophthalmologist in an ambulatory setting at a surgical center or hospital rather than an inpatient settin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens that reduces transmission of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Gimbel
Howard V. Gimbel FRCSC, AOE, FACS, CABES, (born January 17, 1934) is a Canadian ophthalmologist, university professor, senior editor, and amateur musician. He is better known for his invention, along with Thomas Neuhann, of the continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC), a technique employed in modern cataract surgery. Early life Gimbel was born in Calgary, Alberta. The son of Jacob and Ruth Gimbel, he grew up along with five siblings on a grain and dairy farm east of Calgary near the small town of Beiseker. In 1952, he graduated from high school at Canadian University College near Lacombe (Alberta). He attended Walla Walla University in Washington, and graduated with a degree in physics. It was here where he met his wife and lifetime companion, Judy Carl, whom he married on the evening of his graduation day. Education Gimbel attended medical school at Loma Linda University School of Medicine (California), and graduated in 1960. Given his physics background and interest in opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsule Of Lens
The lens capsule is a component of the globe of the eye. It is a clear, membrane-like structure composed of collagen IV and laminin that is quite elastic, a quality that keeps it under constant tension. As a result, the lens naturally tends towards a rounder or more globular configuration, a shape it must assume for the eye to focus at a near distance. Lens capsule is the thickest basement membrane in the body. Normally, the lens capsule serves as a diffusion barrier. It is permeable to low molecular weight compounds but restricts the movement of large colloidal particles. Anatomy The lens capsule is a transparent membrane that surrounds the entire lens. The capsule is thinnest at the posterior pole with approximate thickness of 3.5μm. Average thickness at the equator is 7μm. Anterior pole thickness increases with age from 11-15μm. The thickest portion of is annular region surrounding the anterior pole. This will also increases with age (from 13.5-16μm). Even though the cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (anatomy)
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. By changing shape, it functions to change the focal length of the eye so that it can focus on objects at various distances, thus allowing a sharp real image of the object of interest to be formed on the retina. This adjustment of the lens is known as '' accommodation'' (see also below). Accommodation is similar to the focusing of a photographic camera via movement of its lenses. The lens is flatter on its anterior side than on its posterior side. In humans, the refractive power of the lens in its natural environment is approximately 18 dioptres, roughly one-third of the eye's total power. Structure The lens is part of the anterior segment of the human eye. In front of the lens is the iris, which regulates the amount of light entering into the eye. The lens is suspended in place by the suspensory ligament of the lens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Response
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. In contrast, too much inflammation, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Humour
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor (also spelled humour, from Latin meaning liquid) or simply "the vitreous". Vitreous fluid or "liquid vitreous" is the liquid component of the vitreous gel, found after a vitreous detachment. It is not to be confused with the aqueous humor, the other fluid in the eye that is found between the cornea and lens. Structure The vitreous humor is a transparent, colorless, gelatinous mass that fills the space in the eye between the lens and the retina. It is surrounded by a layer of collagen called the vitreous membrane (or hyaloid membrane or vitreous cortex) separating it from the rest of the eye. It makes up four-fifths of the volume of the eyeball. The vitreous humour is fluid-like near the centre, and gel-like near the edges. The vitreous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects needed to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively in the fields of biology and medicine. Outside biology and medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps. Mechanically, forceps employ the principle of the lever to grasp and apply pressure. Depending on their function, basic surgical forceps can be categorized into the following groups: # Non-disposable forceps. They should withstand various kinds of physical and chemical effects of body fluids, secretions, cleaning agents, and sterilization methods. # Disposable forceps. They are usually mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YAG Laser )
{{disambig ...
YAG laser may refer to two types of lasers that use yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG): * Nd:YAG laser (doped with neodymium) * Er:YAG laser (doped with erbium Erbium is a chemical element with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_PHIL_4284_lores.jpg)


.jpg)
