|
Capsidiol
Capsidiol is a terpenoid compound that accumulates in tobacco ''Nicotiana tabacum'' and chili pepper ''Capsicum annuum'' in response to fungal infection.Maldonado-Bonilla LD, Betancourt-Jiménez M,Lozoya-Gloria E (2008) "Local and systemic gene expression of sesquiterpene phytoalexin biosynthetic enzymes in plant leaves". ''European J. Plant Path.'' 121(4), 439-449. Capsidiol is categorized under the broad term of phytoalexin, a class of low molecular weight plant secondary metabolites that are produced during infection. Phytoalexins are also characterized as a part of a two pronged response to infection which involves a short term response consisting of production of free radicals near the site of infection and a long term response involving the production of hormones and an increase in enzymes to biosynthesize phyoalexins such as capsidiol. Mechanism of production Capsidiol is produced in the pepper fruit ''Capsicum annuum'' or tobacco ''Nicotiana tabacum'' after infe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoalexins
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized ''de novo'' by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection. Function Phytoalexins are produced in plants to act as toxins to the attacking organism. They may puncture the cell wall, delay maturation, disrupt metabolism or prevent reproduction of the pathogen in question. Their importance in plant defense is indicated by an increase in susceptibility of plant tissue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoalexin
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized ''de novo'' by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection. Function Phytoalexins are produced in plants to act as toxins to the attacking organism. They may puncture the cell wall, delay maturation, disrupt metabolism or prevent reproduction of the pathogen in question. Their importance in plant defense is indicated by an increase in susceptibility of plant tissue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant ''Salvia div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diols
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimeric and oligomeric derivatives. This reaction applies to glyoxal and related aldehydes. Vicinal diols In a vicinal diol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germacrene
Germacrenes are a class of volatile organic hydrocarbons, specifically, sesquiterpenes. Germacrenes are typically produced in a number of plant species for their antimicrobial and insecticidal properties, though they also play a role as insect pheromones. Two prominent molecules are germacrene A and germacrene D. Structures Germacrene has five isomers. Natural occurrences The essential oils of red deadnettle (''Lamium purpureum'') and hedgenettles (genus ''Stachys'') are characterized by their high contents of germacrene D, as is ''Clausena anisata :''Should not be confused with syzygium anisatum, a tree native to eastern Australian rainforests, used as a culinary herb.'' ''Clausena anisata'' ( Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth. is a deciduous shrub or small tree, belonging to the Rutaceae or Ci ...''. It is also a major component of patchouli oil. References Further reading General * Germacrene A * * * * * * Germacrene D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium Roqueforti
''Penicillium roqueforti'' is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus '' Penicillium''. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants. The major industrial use of this fungus is the production of blue cheeses, flavouring agents, antifungals, polysaccharides, proteases, and other enzymes. The fungus has been a constituent of Roquefort, Stilton, Danish blue, Cabrales, Gorgonzola, and other blue cheeses. Other blue cheeses are made with '' Penicillium glaucum''. Classification First described by American mycologist Charles Thom in 1906, ''P. roqueforti'' was initially a heterogeneous species of blue-green, sporulating fungi. They were grouped into different species based on phenotypic differences, but later combined into one species by Kenneth B. Raper and Thom (1949). The ''P. roqueforti'' group got a reclassification in 1996 due to molecular analysis of ribosomal DNA sequences. Formerly divided into two varieties―che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristolochene
Aristolochene is a bicyclic sesquiterpene produced by certain fungi including the cheese mold '' Penicillium roqueforti''. It is biosynthesized from farnesyl pyrophosphate by aristolochene synthase and is the parent hydrocarbon of a large variety of fungal toxins. , Chem 549, College of Pharmacy, University of Arizona The substance was first isolated from '' Penicillium roqueforti'', a fungus used to make blue cheeses like , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristolochene
Aristolochene is a bicyclic sesquiterpene produced by certain fungi including the cheese mold '' Penicillium roqueforti''. It is biosynthesized from farnesyl pyrophosphate by aristolochene synthase and is the parent hydrocarbon of a large variety of fungal toxins. , Chem 549, College of Pharmacy, University of Arizona The substance was first isolated from '' Penicillium roqueforti'', a fungus used to make blue cheeses like , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
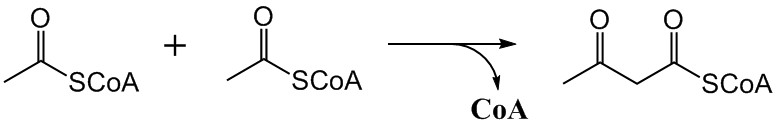
Mevalonate Pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farnesyl Pyrophosphate
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids such as sterols and carotenoids. It is also used in the synthesis of CoQ (part of the electron transport chain), as well as dehydrodolichol diphosphate (a precursor of dolichol, which transports proteins to the ER lumen for ''N''-glycosylation). Biosynthesis Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (a prenyl transferase) catalyzes sequential condensation reactions of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate with 2 units of 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate, as is shown in the following two steps: * Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate reacts with 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form geranyl pyrophosphate: * Geranyl pyrophosphate then reacts with another molecule of 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate Pharmacology The above reactions are inhibited by bisphosphonates (used for osteoporosis). Farnesyl pyrophosphate is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |