|
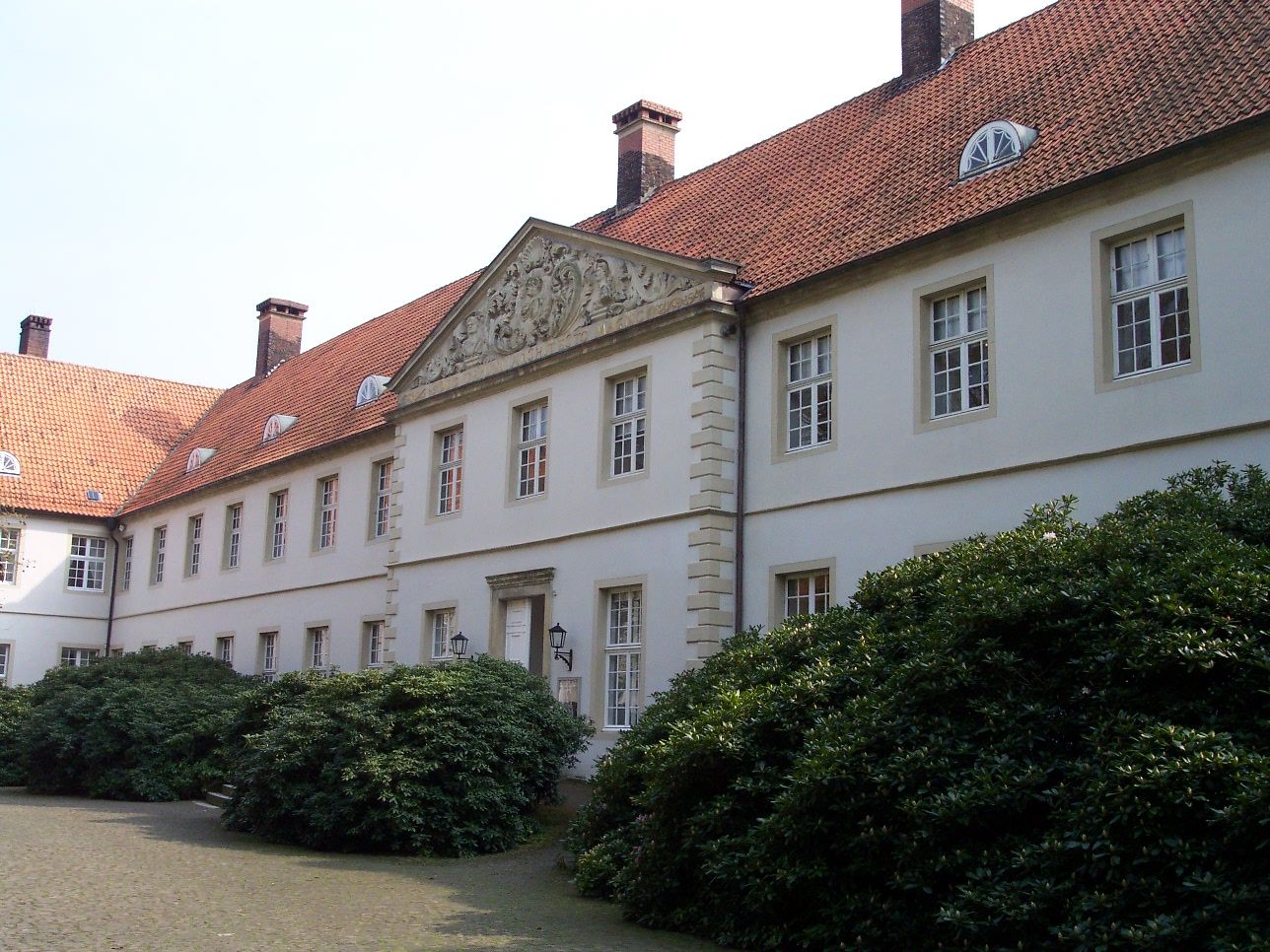
Cappenberg Castle
Cappenberg Castle (german: Schloss Cappenberg) is a former Premonstratensian monastery, Cappenberg Abbey (german: Kloster Cappenberg) in Cappenberg, a part of Selm, North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It stands on an elevation, the Cappenberg, near Lünen and Werne, and is a vantage point offering views over the eastern Ruhrgebiet. In the castle grounds is a water tower constructed in 1899, now a protected monument, which was restored in 1992. The approach from the north-west to the main gate is marked by two stone lions on pedestals, standing at the entrance to an avenue between clipped oaks. On the adjacent castle grounds are a wildlife reserve and a bird of prey sanctuary. History The Counts of Cappenberg, who were related to the Salians and the Staufers, were a rich and powerful family. During the Investiture Controversy, when they supported Duke Lothar von Supplinburg against Emperor Heinrich V, Count and his brother led their armies against Münster in February 1121 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selm Schloss Cappenberg Zentralgebäude
Selm is a town in the district of Unna, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated approximately 20 kilometers north of Dortmund and 25 kilometers west of Hamm. Geography The town belongs to the southern part of the Münsterland. It is surrounded by (beginning in the west) Olfen, Lüdinghausen, Nordkirchen (all in the district of Coesfeld), Werne, Lünen (both in the district of Unna), Waltrop, and Datteln (both belonging to the district of Recklinghausen). History The first traces of living people in the area date from the younger half of the Stone Age. In 858 it was mentioned as ''Seliheim'' in the Dreingau. In the early Middle Ages Selm was ruled by the count of Cappenberg, then by the bishop of Münster. In the beginning of the 19th century it was transferred to Prussia, to which it remained, as part of the province of Westphalia, until 1946. In 1906 the coal mine ''Zeche Hermann'' was established, transferring coal from 1,200 m under underground. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
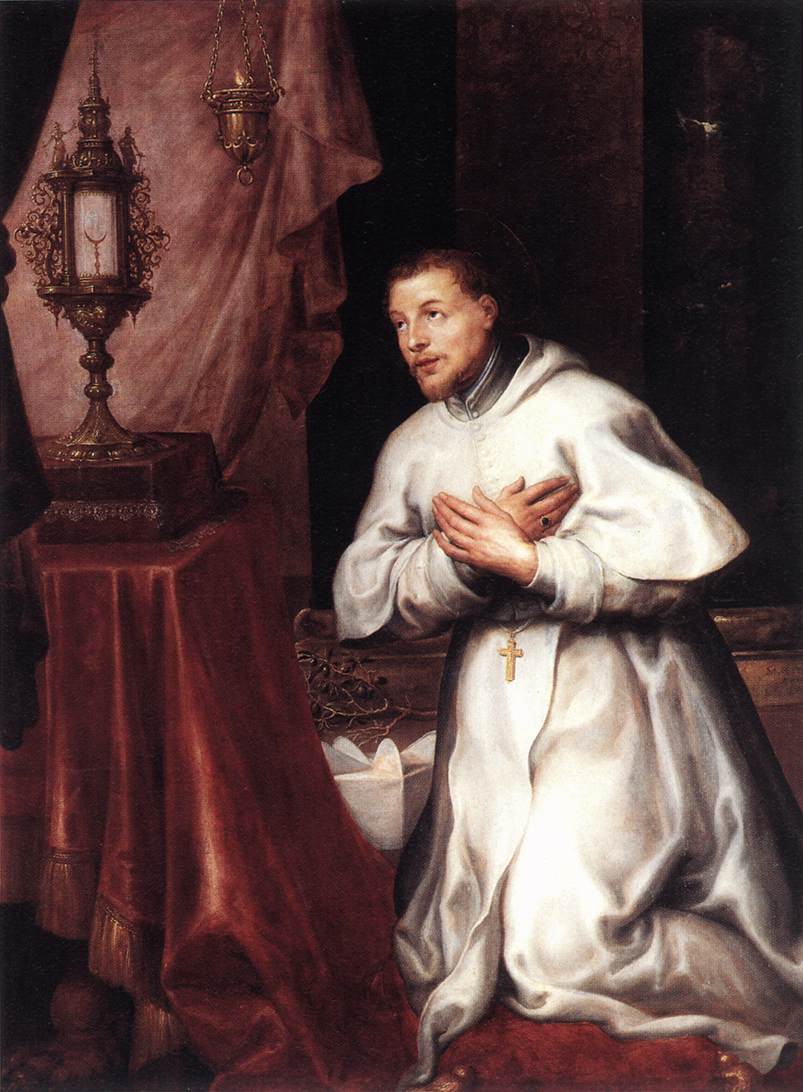
Norbert Of Xanten
Norbert of Xanten, O. Praem (c. 1075 – 6 June 1134) (Xanten-Magdeburg), also known as Norbert Gennep, was a bishop of the Catholic Church, founder of the Premonstratensian order of canons regular, and is venerated as a saint. Norbert was canonized by Pope Gregory XIII in the year 1582, and his statue appears above the Piazza colonnade of St. Peter's Square in Rome. Early priesthood He adopted such strict discipline that it killed his first three disciples. This may be why he failed to reform the canons of Xanten, who denounced him as an innovator at the Council of Fritzlar in 1118. He then resigned his benefice, sold all his property and gave the proceeds to the poor. He visited Pope Gelasius II, who gave him permission to become an itinerant preacher and he preached throughout lands in what is now western Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands and northern France, being credited with a number of miracles. In settlement after settlement he encountered a demoralized clergy, lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreis Unna
The Unna () district is a Kreis (district) in central North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring authorities are the district of Coesfeld, the city of Hamm, the districts of Soest and Märkischer Kreis, the cities of Hagen and Dortmund, and the district of Recklinghausen. History The area of the present district of Unna was formerly part of the County of the Mark, which later belonged to Prussia. In 1753 local government of the area was reformed, creating the first district of Hamm. During the French occupation of the Napoleonic period it was included in the Ruhr département, but once returned to the rule of Prussia, the district of Hamm was recreated, although with several changes. In 1901 the town of Hamm itself became a separate urban authority, but the district retained the name of, and its administration continued to be located in Hamm until 1929. In that year the administration was moved to Unna, when the district name also changed to Unna to reflect the new administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund
Dortmund (; Westphalian nds, Düörpm ; la, Tremonia) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the eighth-largest city of Germany, with a population of 588,250 inhabitants as of 2021. It is the largest city (by area and population) of the Ruhr, Germany's largest urban area with some 5.1 million inhabitants, as well as the largest city of Westphalia. On the Emscher and Ruhr rivers (tributaries of the Rhine), it lies in the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region and is considered the administrative, commercial, and cultural center of the eastern Ruhr. Dortmund is the second-largest city in the Low German dialect area after Hamburg. Founded around 882, Wikimedia Commons: First documentary reference to Dortmund-Bövinghausen from 882, contribution-list of the Werden Abbey (near Essen), North-Rhine-Westphalia, Germany Dortmund became an Imperial Free City. Throughout the 13th to 14th centuries, it was the "chief city" of the Rhine, Westph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marienkirche, Dortmund
Marienkirche (St. Mary's Church) is a church in Dortmund, North Rhine-Westphalia state, Germany, located in the inner city. Since the Reformation, it has been a Lutheran parish church of St. Marien. The church was destroyed in World War II, but rebuilt. It also serves as a concert venue for sacred music. The church was built on the Hellweg, opposite of the Reinoldikirche, for the town's council and jurisdiction. It shows elements of Romanesque and Gothic architecture, and houses notable Medieval art, such as the by Conrad von Soest and the . History The church was built on the Hellweg, a main Medieval road connecting the free imperial town Dortmund with others. It was erected between 1170 and 1200 in Romanesque style to serve the town's council and jurisdiction. It is the oldest extant church in Dortmund's inner city. Around 1350, a choir in Gothic architecture was built. It served as a model for the Reinoldikirche, which was built opposite of the road. The Marienkirche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
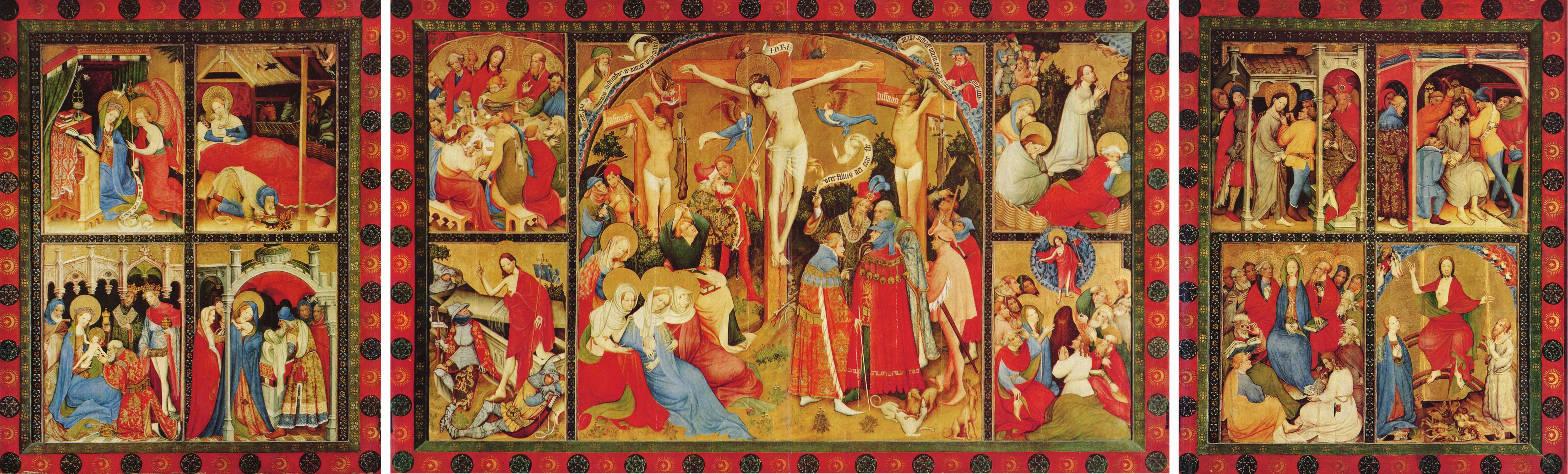
Conrad Von Soest
Conrad von Soest, also ''Konrad'' in modern texts, or in Middle High German ''Conrad van Sost'' or "von Soyst", (born around 1370 in Dortmund; died soon after 1422) was the most significant Westphalian artist and painted in the so-called ''soft style'' of International Gothic. He played a leading role in the introduction of this International Courtly Style to Northern Germany around 1390 and influenced German and Northern European painting into the late 15th century. He was the master of a thriving workshop and was accepted into the social circle of the cosmopolitan patrician elite of Dortmund. Dortmund was then a leading and very prosperous member of the influential Hanseatic League. Works Conrad von Soest's main surviving works are influenced by French illuminated manuscripts and certain early Parisian examples of Early Netherlandish painting; his detailed knowledge of Parisian patterns and techniques points towards a sojourn in Paris as a journeyman in the 1380s: * Niederw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Für Kunst Und Kulturgeschichte
The Museum für Kunst und Kulturgeschichte or MKK (''Museum of Art and Cultural History'') is a municipal museum in Dortmund, Germany. It is currently located in an Art Deco building which was formerly the Dortmund Savings Bank. The collection includes paintings, sculptures, furniture and applied art, illustrating the cultural history of Dortmund from early times to the 20th century. There are regular temporary exhibitions of art and culture, as well as a permanent exhibition on the history of surveying, with rare geodetic instruments.Das Museum History It was founded in 1883 as a collection of historical and artistic objects. It changed location several times in the early years, and came to include |
Allies Of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China. Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom, France, and Poland, as well as their respective dependencies, such as British India. They were soon joined by the independent dominions of the British Commonwealth: Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled that of the First World War. As Axis forces began invading northern Europe and the Balkans, the Allies added the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Greece, and Yugoslavia. The Soviet Union, which initially had a nonaggression pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Friedrich Karl Vom Und Zum Stein
Heinrich Friedrich Karl Reichsfreiherr vom und zum Stein (25 October 1757 – 29 June 1831), commonly known as Baron vom Stein, was a Prussian statesman who introduced the Prussian reforms, which paved the way for the unification of Germany. He promoted the abolition of serfdom, with indemnification to territorial lords; subjection of the nobles to manorial imposts; and the establishment of a modern municipal system. Stein was from an old Franconian family. He was born on the family estate near Nassau, studied at Göttingen, and entered the civil service. Prussian conservatism hampered him in his efforts to bring about changes. In 1807, he was removed from office by the King for refusing to accept the post of Minister of Foreign Affairs but was recalled after the Peace of Tilsit. After it became known that he had written a letter in which he criticised Napoleon, Stein was obliged to resign, which he did on 24 November 1808 and retired to the Austrian Empire, from which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Berg
Berg was a state—originally a county, later a duchy—in the Rhineland of Germany. Its capital was Düsseldorf. It existed as a distinct political entity from the early 12th to the 19th centuries. The name of the county lives on in the modern geographic term Bergisches Land, often misunderstood as ''bergiges Land'' (hilly country). History Ascent The Counts of Berg emerged in 1101 as a junior line of the dynasty of the Ezzonen, which traced its roots back to the 9th-century Kingdom of Lotharingia, and in the 11th century became the most powerful dynasty in the region of the lower Rhine. In 1160, the territory split into two portions, one of them later becoming the County of the Mark, which returned to the possession of the family line in the 16th century. The most powerful of the early rulers of Berg, Engelbert II of Berg died in an assassination on November 7, 1225. In 1280 the counts moved their court from Schloss Burg on the Wupper river to the town of Düsseldorf. Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |