|
CIT (gene)
Citron Rho-interacting kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CIT'' gene. Structure Citron is a 183 kDa protein that contains a C6H2 zinc finger, a PH domain, and a long coiled-coil forming region including 4 leucine zippers and a rho / rac binding site. It was discovered as a rho/rac effector in 1995, interacting only with the GTP bound forms of rho and rac 1. Displaying a distinctive protein organization, this protein defines a separate class of rho partners. Using a cloning approach based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a splice variant of citron, citron kinase (citron-K) has been identified with an alternative amino terminus. This N-terminal extension contains a protein kinase domain that has approximately 50% sequence identity to the sequences of ROCK, ROK, myotonic dystrophy protein kinase ( MDPK) and the CDC42 effector known as MRCK or GEK. Citron kinase, which resembles the ROCK family of kinases and by comparison to it, is therefore a multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, '' D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RHOA
Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOA'' gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 (Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1) and DIAPH1 (Diaphanous Homologue 1, a.k.a. hDia1, homologue to mDia1 in mouse, diaphanous in ''Drosophila'') are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
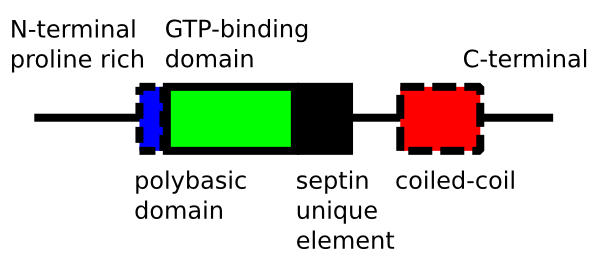
Septin
Septins are a group of GTP-binding proteins expressed in all eukaryotic cells except plants. Different septins form protein complexes with each other. These complexes can further assemble into filaments, rings and gauzes. Assembled as such, septins function in cells by localizing other proteins, either by providing a scaffold to which proteins can attach, or by forming a barrier preventing the diffusion of molecules from one compartment of the cell to another, or in the cell cortex as a barrier to the diffusion of membrane-bound proteins. Septins have been implicated in the localization of cellular processes at the site of cell division, and at the cell membrane at sites where specialized structures like cilia or flagella are attached to the cell body. In yeast cells, they compartmentalize parts of the cell and build scaffolding to provide structural support during cell division at the septum, from which they derive their name. Research in human cells suggests that septins buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
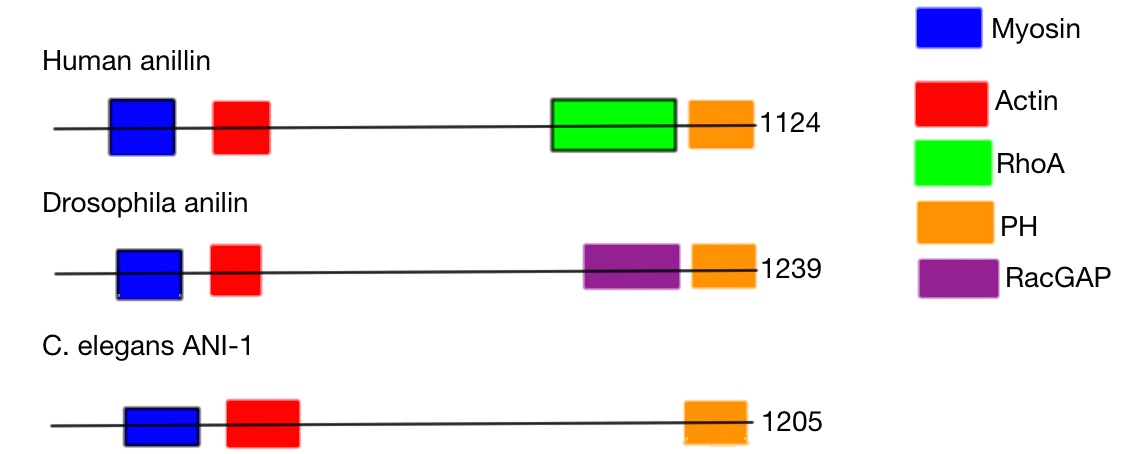
Anillin
Anillin is a conserved protein implicated in cytoskeletal dynamics during cellularization and cytokinesis. The ''ANLN'' gene in humans and the scraps gene in ''Drosophila'' encode Anillin. In 1989, anillin was first isolated in embryos of ''Drosophila melanogaster''. It was identified as an F-actin binding protein. Six years later, the anillin gene was cloned from cDNA originating from a Drosophila ovary. Staining with anti-anillin (Antigen 8) antibody showed the anillin localizes to the nucleus during interphase and to the contractile ring during cytokinesis. These observations agree with further research that found anillin in high concentrations near the cleavage furrow coinciding with RhoA, a key regulator of contractile ring formation. The name of the protein anillin originates from a Spanish word, ''anillo''. ''Anillo'' means ring and shows that the name anillin references the observed enrichment of anillins at the contractile ring during cytokinesis. Anillins are also enric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscission
Abscission () is the shedding of various parts of an organism, such as a plant dropping a leaf, fruit, flower, or seed. In zoology, abscission is the intentional shedding of a body part, such as the shedding of a claw, husk, or the autotomy of a tail to evade a predator. In mycology, it is the liberation of a fungal spore. In cell biology, abscission refers to the separation of two daughter cells at the completion of cytokinesis. In plants Function A plant will abscise a part either to discard a member that is no longer necessary, such as a leaf during autumn, or a flower following fertilisation, or for the purposes of reproduction. Most deciduous plants drop their leaves by abscission before winter, whereas evergreen plants continuously abscise their leaves. Another form of abscission is fruit drop, when a plant abscises fruit while still immature, in order to conserve resources needed to bring the remaining fruit to maturity. If a leaf is damaged, a plant may also abscise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HeLa Cell
HeLa (; also Hela or hela) is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, named after Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on October 4, 1951. The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific, which allows it to be used extensively in scientific study. The cells from Lacks's cancerous cervical tumor were taken without her knowledge or consent, which was common practice in the United States at the time. Cell biologist George Otto Gey found that they could be kept alive, and developed a cell line. Previously, cells cultured from other human cells would only survive for a few days. Cells from Lacks's tumor behaved differently. History Origin In 1951, a patient named Henrietta Lacks was admitted to the Johns Hopkins Hospital with symptoms of irregular vaginal bleeding, and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Spindle
The central spindle is a microtubule based structure, which forms in between segregating chromosomes during anaphase where the two sets of microtubules, emanating from opposite halves of the cell, overlap, and become arranged into antiparallel bundles by various microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) and motor proteins. The central spindle is widely regarded as a key regulating center for cytokinesis, recruiting proteins for successful cleavage furrow positioning and membrane abscission. For these important roles to be achieved successfully the central spindle has to be carefully regulated to control the size of the overlap region, the alignment of those overlaps and the overall length and symmetry of the structure. Without this regulation, signaling faults in cytokinesis can occur, resulting in unequal chromosome segregation or polyploid cells, greatly increasing the risk of cancer Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration. Cytokinesis typically begins before late telophase and, when complete, segregates the two daughter nuclei between a pair of separate daughter cells. Telophase is primarily driven by the dephosphorylation of mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) substrates. Dephosphorylation of Cdk substrates The phosphorylation of the protein targets of M-Cdks (Mitotic Cyclin-dependent Kinases) drives spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |