|
Cd46
CD46 complement regulatory protein also known as CD46 (cluster of differentiation 46) and Membrane Cofactor Protein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CD46'' gene. CD46 is an inhibitory complement receptor. Gene This gene is found in a cluster on chromosome 1q32 with other genes encoding structural components of the complement system. At least fourteen different transcript variants encoding fourteen different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane protein and is a regulatory part of the complement system. The encoded protein has cofactor activity for inactivation (through cleavage) of complement components C3b and C4b by serum factor I, which protects the host cell from damage by complement. The protein encoded by this gene may be involved in the fusion of the spermatozoa with the oocyte during fertilization. Clinical significance The encoded protein can act as a receptor for the Edmonston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Of Differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells. In terms of physiology, CD molecules can act in numerous ways, often acting as receptors or ligands important to the cell. A signal cascade is usually initiated, altering the behavior of the cell (see cell signaling). Some CD proteins do not play a role in cell signaling, but have other functions, such as cell adhesion. CD for humans is numbered up to 371 (). Nomenclature The CD nomenclature was proposed and established in the 1st International Workshop and Conference on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens (HLDA), which was held in Paris in 1982. This system was intended for the classification of the many monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated by different laboratories around the world against epitopes on the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Herpesvirus-6
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is the common collective name for '' human betaherpesvirus 6A'' (HHV-6A) and '' human betaherpesvirus 6B'' (HHV-6B). These closely related viruses are two of the nine known herpesviruses that have humans as their primary host. HHV-6A and HHV-6B are double-stranded DNA viruses within the ''Betaherpesvirinae'' subfamily and of the genus ''Roseolovirus''. HHV-6A and HHV-6B infect almost all of the human populations that have been tested. HHV-6A has been described as more neurovirulent, and as such is more frequently found in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis. HHV-6 (and HHV-7) levels in the brain are also elevated in people with Alzheimer's disease. HHV-6B primary infection is the cause of the common childhood illness exanthema subitum (also known as roseola infantum or sixth disease). It is passed on from child to child. It is uncommon for adults to contract this disease as most people have had it by kindergarten, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD151
CD151 molecule (Raph blood group), also known as CD151 (Cluster of Differentiation 151), is a human gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. This encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins and other transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins. It is involved in cellular processes including cell adhesion and may regulate integrin trafficking and/or function. This protein enhances cell motility, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode the same protein have been described for this gene. Abnormalities in CD151 have been implicated in a form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MV-NIS
Measles virus encoding the human thyroidal sodium iodide symporter or MV-NIS is an attenuated oncolytic Edmonston (Ed) strain of measles virus. MV-NIS will attach and fuse to host tumor cell membranes. After fusion, MV-NIS has been observed to kill the tumor cells. Due to the unique properties of iodine uptake in these cells, iodine 123 (I-123) may be used to image MV-NIS-infected tumor cells. Non-invasive imaging provides confirmation of targeted infection and allows for monitoring and visualization of treatment progression. The human CD46 antigen is known to be the functional cellular receptor for Measles virus. This type 1 integral membrane glycoprotein is a normal part of human tissue but may be overexpressed on some cancer cell types. MV-NIS is the first targeted engineered virus therapy to have shown remission in published cancer clinical trials. PET/CT Imaging A few days after infection, the host animal may be injected with radioiodine which is then selectively captured by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa. The brain is divided into two main parts, the larger cerebrum on top and the smaller cerebellum below towards the back. They are separated by a membrane called the tentorium. Tumors that originate in the cerebellum or the surrounding region below the tentorium are, therefore, called infratentorial. Historically medulloblastomas have been classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), but it is now known that medulloblastoma is distinct from supratentorial PNETs and they are no longer considered similar entities. Medulloblastomas are invasive, rapidly growing tumors that, unlike most brain tumors, spread through the cerebrospinal fluid and frequently metastasize to different locations along the surface of the brain and spinal cord. Metastasis all the way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-barrel
In protein structures, a beta barrel is a beta sheet composed of tandem repeats that twists and coils to form a closed toroidal structure in which the first strand is bonded to the last strand (hydrogen bond). Beta-strands in many beta-barrels are arranged in an antiparallel fashion. Beta barrel structures are named for resemblance to the barrels used to contain liquids. Most of them are water-soluble proteins and frequently bind hydrophobic ligands in the barrel center, as in lipocalins. Others span cell membranes and are commonly found in porins. Porin-like barrel structures are encoded by as many as 2–3% of the genes in Gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown that more than 600 proteins with various function (e.g., oxidase, dismutase, amylase) contain the beta barrel structure. In many cases, the strands contain alternating polar and non-polar (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) amino acids, so that the hydrophobic residues are oriented into the interior of the barrel to form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
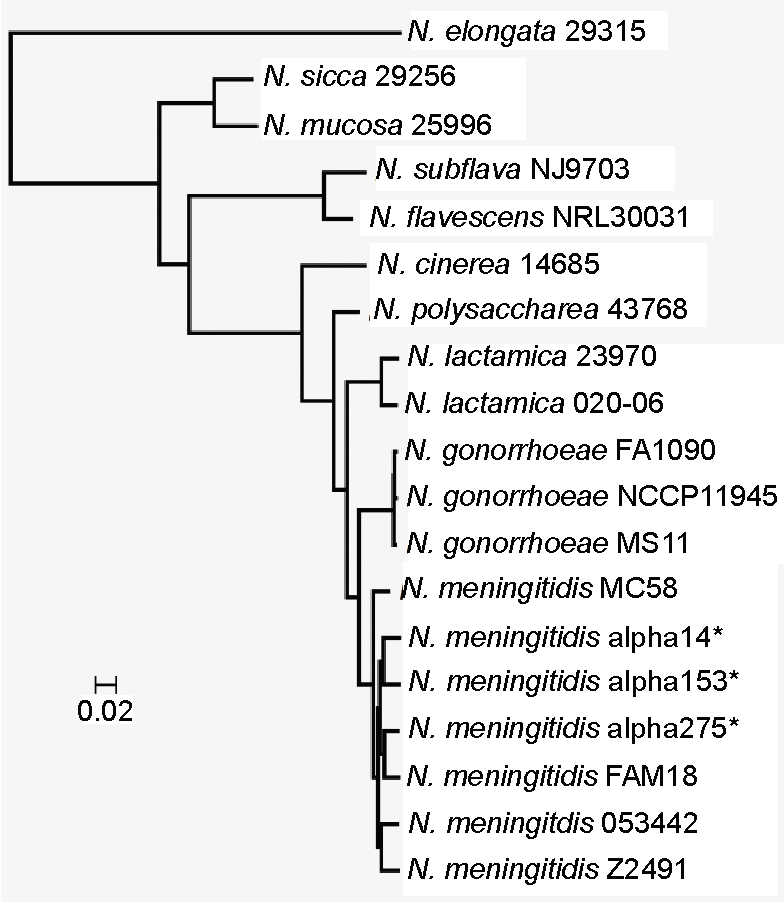
Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''. ''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negative bacteria included among the Pseudomonadota, a large group of Gram-negative forms. ''Neisseria'' diplococci resemble coffee beans when viewed microscopically. Pathogenesis and classification Pathogens Species of this genus (family Neisseriaceae) of parasitic bacteria grow in pairs and occasionally tetrads, and thrive best at 98.6 °F (37 °C) in the animal body or serum media. The genus includes: * ''N. gonorrhoeae'' (also called the gonococcus) causes gonorrhea. * '' N. meningitidis'' (also called the meningococcus) is one of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis and the causative agent of meningococcal septicaemia. These two species have the ability of 'breaching' the barrier. Local cytokines of the area become secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles Virus
''Measles morbillivirus'' (MeV), also called measles virus (MV), is a single-stranded, negative-sense, enveloped, non-segmented RNA virus of the genus '' Morbillivirus'' within the family '' Paramyxoviridae''. It is the cause of measles. Humans are the natural hosts of the virus; no animal reservoirs are known to exist. Disease The virus causes measles, a highly contagious disease transmitted by respiratory aerosols that triggers a temporary but severe immunosuppression. Symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes and a generalized, maculopapular, erythematous rash and a pathognomic Koplik spot seen on buccal mucosa opposite to lower 1 st and 2 nd molars . The virus is spread by coughing and sneezing via close personal contact or direct contact with secretions. Replication cycle Entry The measles virus has two envelope glycoproteins on the viral surface – hemagglutinin (H) and membrane fusion protein (F). These proteins are responsible for host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
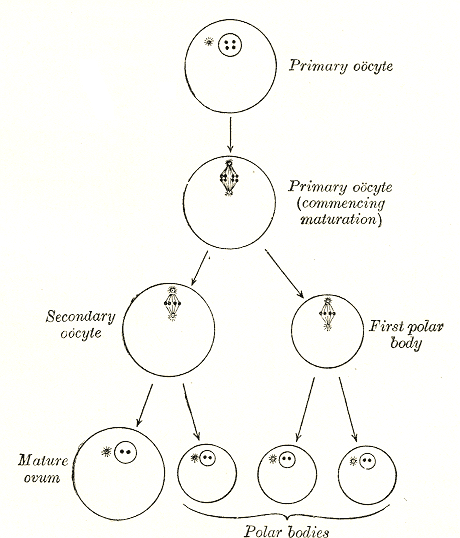
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, that normally develops into an embryo.) Sperm cells contribute approximately half of the nuclear genetic information to the diploid offspring (excluding, in most cases, mitochondrial DNA). In mammals, the sex of the offspring is determined by the sperm cell: a spermatozoon bearing an X chromosome will lead to a female (XX) offspring, while one bearing a Y chromosome will lead to a male (XY) offspring. Sperm cells were first observed in Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's laboratory in 1677. Mammalian spermatozoon structure, function, and size Humans The human sperm cell is the reproductive cell in males and will only survive in warm environments; once it leaves the male body the sperm's survival likelihood is reduced and it may d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |