|
CCHCR1
Coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1, also known as CCHCR1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCHCR1'' gene. Gene The Human CCHCR1 gene is located at 6p21.33. It is also known as Coiled-Coil Alphahelical Rod Protein 1, C6orf18, Putative Gene 8 Protein, SBP, HCR (A-Helix Coiled-Coil Rod Homologue), pg8, StAR-Binding Protein, and Pg8. Homology Homologes for CCHCR1 are conserved through tetrapods. Paralogs Orthologs CCHCR1 has orthologs throughout vertebrates. Distant Homologs Homologous Domains Phylogeny Phylogenetic analysis with ClustalW indicated that CCHCR1 The CCHCR1 gene has Protein Structure The structure of CCHCR1 is primarily composed of alpha-helices, coils, and a small amount of beta sheets, according to PELE. Expression Function May be a regulator of keratinocyte proliferation or differentiation. Interacting Proteins CCHCR1 has been shown to interact with POLR2C, KRT17 , TOP3B, Steroidogenic acute regulatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POLR2C
DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''POLR2C'' gene. Function This gene encodes the third largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes. The product of this gene contains a cysteine rich region and exists as a heterodimer with another polymerase subunit, POLR2J. These two subunits form a core subassembly unit of the polymerase. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 21. Interactions POLR2C has been shown to interact with: * ATF4, * CCHCR1, * Myogenin, * POLR2A, * POLR2B, * POLR2E and * POLR2F, * POLR2G, * POLR2H, * POLR2J, * POLR2K, * POLR2L DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POLR2L'' gene. Function This gene encodes a subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in e ..., and * TAF15. References Further rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
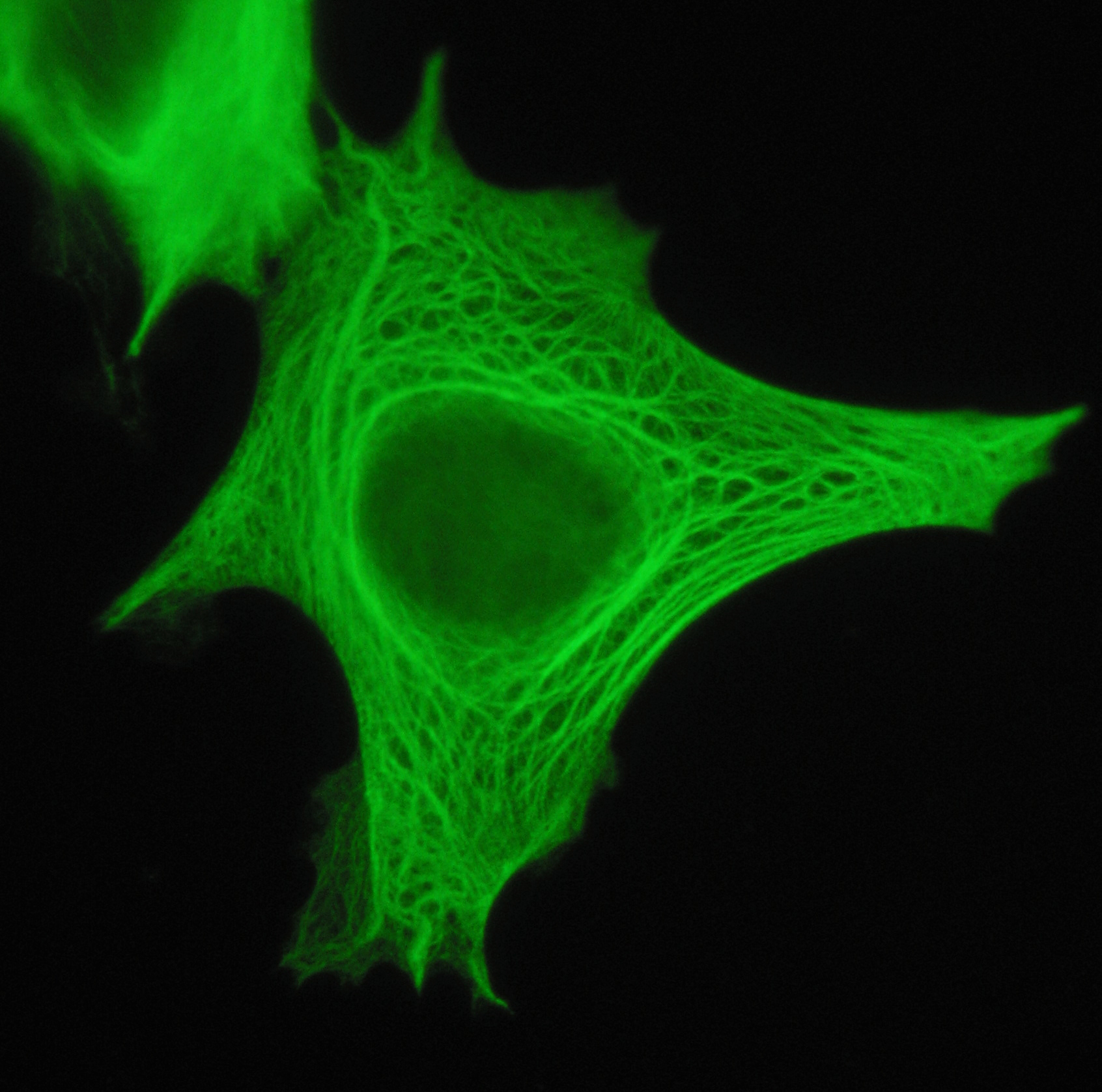
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEF1D
Elongation factor 1-delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EEF1D'' gene. Function This gene encodes a subunit of the elongation factor-1 complex, which is responsible for the enzymatic delivery of aminoacyl tRNAs to the ribosome. This subunit functions as guanine nucleotide exchange factor. It is reported that this subunit interacts with HIV-1 Tat, and thus it represses the translation of host-cell, but not HIV-1, mRNAs. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, however, the full length nature of only two variants has been determined. Interactions EEF1D has been shown to interact with Glycyl-tRNA synthetase, EEF1G Elongation factor 1-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EEF1G'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ... and KTN1, and is predicted to interact with TMEM63A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually be shed off, which happens every 40 to 56 days in humans. Function The primary function of keratinocytes is the formation of a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. Pathogens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornification
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only among sauro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 17
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT17'' gene. Keratin 17 is a type I cytokeratin. It is found in nail beds, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and other epidermal appendages. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein lead to PC-K17 (previously known as Jackson-Lawler) type pachyonychia congenita and steatocystoma multiplex. Interactions Keratin 17 has been shown to interact with CCDC85B Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 85B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCDC85B'' gene. Function Hepatitis delta virus (HDV) is a pathogenic human virus whose RNA genome and replication cycle resemble those of plant viroids. .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pachyonychia Congenita Keratins {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 16
Keratin 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT16'' gene. Keratin 16 is a type I cytokeratin. It is paired with keratin 6 in a number of epithelial tissues, including nail bed, esophagus, tongue, and hair follicle The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between ...s. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein are associated with the genetic skin disorders including pachyonychia congenita, non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma and unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus. References External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pachyonychia Congenita Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 6A
Keratin 6A is one of the 27 different type II keratins expressed in humans. Keratin 6A was the first type II keratin sequence determined. Analysis of the sequence of this keratin together with that of the first type I keratin led to the discovery of the four helical domains in the central rod of keratins. In humans Keratin 6A is encoded by the ''KRT6A'' gene. Keratins Keratins are the intermediate filament proteins that form a dense meshwork of filaments throughout the cytoplasm of epithelial cells. Keratins form heteropolymers consisting of a type I and a type II keratin. Keratins are generally expressed in particular pairs of type I and type II keratin proteins in a tissue-specific and cellular differentiation-specific manner. The keratin proteins of epithelial tissues are commonly known as "keratins" or are sometimes referred to as "epithelial keratins" or "cytokeratins". The specialized keratins of hair and nail are known as "hard keratins" or " trichocyte keratins". Tric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokeratin
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue. They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. Thus they are used clinically to identify the cell of origin of various human tumors. Naming The term ''cytokeratin'' began to be used in the late 1970s, when the protein subunits of keratin intermediate filaments inside cells were first being identified and characterized. In 2006 a new systematic nomenclature for mammalian keratins was created, and the proteins previously called ''cytokeratins'' are simply called ''keratins'' (human epithelial category). For example, cytokeratin-4 (CK-4) has been renamed keratin-4 (K4). However, they are still commonly referred to as cytokeratins in clinical practice. Types There are two categories of cytokeratins: the acidic type I cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (biology)
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Ford E.B. 1965. ''Genetic polymorphism''. Faber & Faber, London. Put simply, polymorphism is when there are two or more possibilities of a trait on a gene. For example, there is more than one possible trait in terms of a jaguar's skin colouring; they can be light morph or dark morph. Due to having more than one possible variation for this gene, it is termed 'polymorphism'. However, if the jaguar has only one possible trait for that gene, it would be termed "monomorphic". For example, if there was only one possible skin colour that a jaguar could have, it would be termed monomorphic. The term polyphenism can be used to clarify that the different forms arise from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEF1B2
Elongation factor 1-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EEF1B2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a translation elongation factor. The protein is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor involved in the transfer of aminoacylated tRNAs to the ribosome. Alternative splicing results in three transcript variants which differ only in the 5' UTR. Interactions EEF1B2 has been shown to interact with EEF1G Elongation factor 1-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EEF1G'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ... and HARS. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |