|
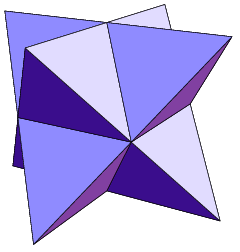
Toroidal Polyhedra
In geometry, a toroidal polyhedron is a polyhedron which is also a toroid (a -holed torus), having a topology (Mathematics), topological Genus (mathematics), genus () of 1 or greater. Notable examples include the Császár polyhedron, Császár and Szilassi polyhedron, Szilassi polyhedra. Variations in definition Toroidal polyhedra are defined as collections of polygons that meet at their edges and vertices, forming a manifold as they do. That is, each edge should be shared by exactly two polygons, and at each vertex the edges and faces that meet at the vertex should be linked together in a single cycle of alternating edges and faces, the link (geometry), link of the vertex. For toroidal polyhedra, this manifold is an orientability, orientable surface. Some authors restrict the phrase "toroidal polyhedra" to mean more specifically polyhedra topologically equivalent to the (genus 1) torus. In this area, it is important to distinguish embedding, embedded toroidal polyhedra, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Torus
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral polygon, equilateral and equiangular polygon, equiangular. In other words, a hexagon is said to be regular if the edges are all equal in length, and each of its internal angle is equal to 120°. The Schläfli symbol denotes this polygon as \ . However, the regular hexagon can also be considered as the Truncation (geometry), cutting off the vertices of an equilateral triangle, which can also be denoted as \mathrm\ . A regular hexagon is bicentric polygon, bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic polygon, cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential polygon, tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Polygon
In geometry, a star polygon is a type of non-convex polygon. Regular star polygons have been studied in depth; while star polygons in general appear not to have been formally defined, Decagram (geometry)#Related figures, certain notable ones can arise through truncation operations on regular simple or star polygons. Branko Grünbaum identified two primary usages of this terminology by Johannes Kepler, one corresponding to the regular star polygons with List of self-intersecting polygons, intersecting edges that do not generate new vertices, and the other one to the isotoxal Concave polygon, concave simple polygons.Grünbaum & Shephard (1987). Tilings and Patterns. Section 2.5 Polygram (geometry), Polygrams include polygons like the pentagram, but also compound figures like the hexagram. One definition of a ''star polygon'', used in turtle graphics, is a polygon having ''q'' ≥ 2 Turn (geometry), turns (''q'' is called the turning number or Density (polygon), density), like in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Hull
In geometry, the convex hull, convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space, or equivalently as the set of all convex combinations of points in the subset. For a Bounded set, bounded subset of the plane, the convex hull may be visualized as the shape enclosed by a rubber band stretched around the subset. Convex hulls of open sets are open, and convex hulls of compact sets are compact. Every compact convex set is the convex hull of its extreme points. The convex hull operator is an example of a closure operator, and every antimatroid can be represented by applying this closure operator to finite sets of points. The algorithmic problems of finding the convex hull of a finite set of points in the plane or other low-dimensional Euclidean spaces, and its projective duality, dual problem of intersecting Half-space (geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer either to a solid figure or to its boundary surface. The terms solid polyhedron and polyhedral surface are commonly used to distinguish the two concepts. Also, the term ''polyhedron'' is often used to refer implicitly to the whole structure formed by a solid polyhedron, its polyhedral surface, its faces, its edges, and its vertices. There are many definitions of polyhedron. Nevertheless, the polyhedron is typically understood as a generalization of a two-dimensional polygon and a three-dimensional specialization of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Polyhedra have several general characteristics that include the number of faces, topological classification by Euler characteristic, duality, vertex figures, surface area, volume, interior lines, Dehn invar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid, sometimes also known as a Johnson–Zalgaller solid, is a convex polyhedron whose faces are regular polygons. They are sometimes defined to exclude the uniform polyhedrons. There are ninety-two Solid geometry, solids with such a property: the first solids are the Pyramid (geometry), pyramids, Cupola (geometry), cupolas, and a Rotunda (geometry), rotunda; some of the solids may be constructed by attaching with those previous solids, whereas others may not. Definition and background A Johnson solid is a convex polyhedron whose faces are all regular polygons. The convex polyhedron means as bounded intersections of finitely many Half-space (geometry), half-spaces, or as the convex hull of finitely many points. Although there is no restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, some authors required that Johnson solids are not Uniform polyhedron, uniform. This means that a Johnson solid is not a Platonic solid, Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonnie Stewart
Bonnie Madison Stewart (July 10, 1914 – April 15, 1994) was a professor of mathematics at Michigan State University from 1940 to 1980. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1941, under the supervision of Cyrus Colton MacDuffee. Contributions Number theory In 1952, the first edition of his book, ''Theory of Numbers'', was published.Review of ''Theory of Numbers'' by H. Bergström, . Stewart's contributions to number theory also include a complete characterization of the practical numbers in terms of their factorizations, which he published in 1954, a year before Wacław Sierpiński's independent discovery of the same result. Geometry In 1970 he published a book, '' Adventures among the toroids. A study of orientable polyhedra with regular faces'', in which he discussed what are now called Stewart toroids. The book was handwritten in calligraphy with many formulas and illustrations. Like the Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, and Johnson solids, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either ''convex polygon, convex'' or ''star polygon, star''. In the limit (mathematics), limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a Line (geometry), straight line), if the edge length is fixed. General properties These properties apply to all regular polygons, whether convex or star polygon, star: *A regular ''n''-sided polygon has rotational symmetry of order ''n''. *All vertices of a regular polygon lie on a common circle (the circumscribed circle); i.e., they are concyclic points. That is, a regular polygon is a cyclic polygon. *Together with the property of equal-length sides, this implies that every regular polygon also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coplanar
In geometry, a set of points in space are coplanar if there exists a geometric plane that contains them all. For example, three points are always coplanar, and if the points are distinct and non-collinear, the plane they determine is unique. However, a set of four or more distinct points will, in general, not lie in a single plane. Two lines in three-dimensional space are coplanar if there is a plane that includes them both. This occurs if the lines are parallel, or if they intersect each other. Two lines that are not coplanar are called skew lines. Distance geometry provides a solution technique for the problem of determining whether a set of points is coplanar, knowing only the distances between them. Properties in three dimensions In three-dimensional space, two linearly independent vectors with the same initial point determine a plane through that point. Their cross product is a normal vector to that plane, and any vector orthogonal to this cross product through the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John H
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltahedron
A deltahedron is a polyhedron whose faces are all equilateral triangles. The deltahedron was named by Martyn Cundy, after the Greek capital letter delta resembling a triangular shape Δ. Deltahedra can be categorized by the property of convexity. The simplest convex deltahedron is the regular tetrahedron, a pyramid with four equilateral triangles. There are eight convex deltahedra, which can be used in the applications of chemistry as in the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory and chemical compounds. There are infinitely many concave deltahedra. Strictly convex deltahedron A polyhedron is said to be ''convex'' if a line between any two of its vertices lies either within its interior or on its boundary, and additionally, if no two faces are coplanar (lying in the same plane) and no two edges are collinear (segments of the same line), it can be considered as being strictly convex. Of the eight convex deltahedra, three are Platonic solids and five are Johnson solids. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conway Toroidal Deltahedron
Conway may refer to: Places United States * Conway, Arkansas * Conway County, Arkansas * Lake Conway, Arkansas * Conway, Florida * Conway, Iowa * Conway, Kansas * Conway, Louisiana * Conway, Massachusetts * Conway, Michigan * Conway Township, Michigan * Conway, Missouri * Conway, New Hampshire, a New England town ** Conway (CDP), New Hampshire, village in the town * Conway, North Dakota * Conway, North Carolina * Conway, Pennsylvania * Conway, South Carolina * Conway River (Virginia) * Conway, Washington Elsewhere * Conway, Queensland, a locality in the Whitsunday Region, Queensland, Australia * Conway River (New Zealand) * Conway, Wales, now spelt Conwy, a town with a castle in North Wales * River Conway, Wales, similarly respelt River Conwy Ships * HMS ''Conway'' (school ship) * HMS ''Conway'' (1832), a 26-gun sixth rate launched in 1832 * USS ''Conway'' (DD-70) or USS ''Craven'' (DD-70), a Caldwell class destroyer launched in 1918 * USS ''Conw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |