|
Overthrow Of Slobodan Milošević
The Overthrow of Slobodan Milošević began in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia after the general election on 24 September 2000 and culminated in the downfall of Slobodan Milošević's government on 5 October 2000. As such, it is commonly referred to as the 5 October Revolution () or colloquially the Bulldozer Revolution (), after one of the most memorable episodes from the day-long protest in which a heavy equipment operator charged the Radio Television of Serbia building, considered to be symbolic of the Milošević regime's propaganda. Prelude Milošević's rule has been described by observers as authoritarian or autocratic, as well as kleptocratic, with numerous accusations of electoral fraud, political assassinations, suppression of media freedom and police brutality. He became the first sitting head of state to be charged with war crimes. His role in the Yugoslav Wars led to international sanctions against Yugoslavia, which had a devastating impact on the Yugo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related#Naimark, Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and Insurgency, insurgencies that took place from 1991 to 2001 in what had been the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFR Yugoslavia). The conflicts both led up to and resulted from the breakup of Yugoslavia, which began in mid-1991, into six independent countries matching the six Republics of Yugoslavia, entities known as republics that had previously constituted Yugoslavia: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, and North Macedonia, Macedonia (now Macedonia naming dispute, called North Macedonia). SFR Yugoslavia's constituent republics declared independence due to rising nationalism. Unresolved tensions between ethnic minorities in the new countries led to the wars. While most of the conflicts ended through peace accords that involved full international recognition of new states, they resulted in a massive number of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otpor!
Otpor ( sr-Cyrl, Отпор!, , stylized as Otpor!) was a political organization in Serbia (then part of FR Yugoslavia) from 1998 until 2004. In its initial period from 1998 to 2000, Otpor began as a civic protest group, eventually turning into a movement, which adopted the ''Narodni pokret'' (the People's Movement) title, against the policies of the Serbian authorities under the influence of Yugoslav president Slobodan Milošević. Following Milošević's overthrow in October 2000, Otpor became a political watchdog organization monitoring the activities of the post-Milošević period of the DOS coalition. Finally, during fall 2003, Otpor briefly became a political party which, due to its failure to pass the 5% threshold needed to get any seats in the Serbian parliament, soon merged with another party. Founded and best known as an organization employing nonviolent struggle as a course of action against the Milošević-controlled Serbian authorities, Otpor grew into a civic yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
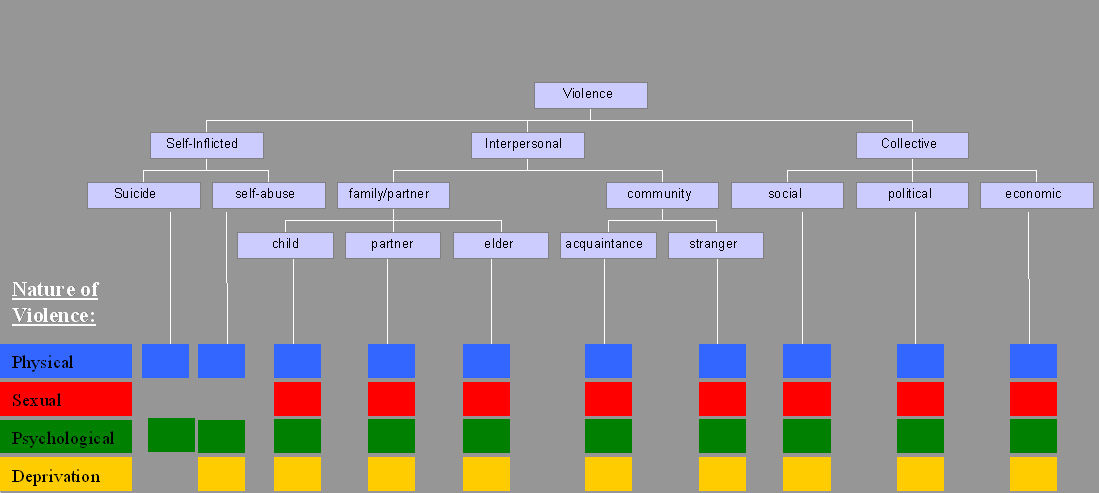
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property Damage
Property damage (sometimes called damage to property) is the damage or destruction of real or tangible personal property, caused by negligence, willful destruction, or an act of nature. Destruction of property (sometimes called property destruction, or criminal damage in England and Wales Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...) is a sub-type of property damage that involves damage to property that results from willful misconduct and is punishable as a crime. Destruction of property encompasses vandalism (deliberate damage, destruction, or defacement), building implosion (destroying property with explosives), and arson (destroying property with fire), and similar crimes that involve unlawful infliction of damage to or destruction of personal property or real pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barricades
Barricade (from the French '' barrique'' - 'barrel') is any object or structure that creates a barrier or obstacle to control, block passage or force the flow of traffic in the desired direction. Adopted as a military term, a barricade denotes any improvised field fortification, such as on city streets during urban warfare. Barricades also include temporary traffic barricades designed with the goal of dissuading passage into a protected or hazardous area or large slabs of cement whose goal is to prevent forcible passage by a vehicle. Stripes on barricades and panel devices slope downward in the direction traffic must travel. There are also pedestrian barricades - sometimes called bike rack barricades for their resemblance to a now obsolete form of bicycle stand, or police barriers. They originated in France approximately 50 years ago and are now used around the world. They were first used in the U.S. 40 years ago by Friedrichs Mfg for New Orleans's Mardi Gras parades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation (protest)
As an act of protest, occupation is a strategy often used by social movements and other forms of collective social action in order to squat and hold public and symbolic spaces, buildings, critical infrastructure such as entrances to train stations, shopping centers, university buildings, squares, and parks. Occupation attempts to use space as an instrument in order to achieve political and economic change, and to construct counter-spaces in which protesters express their desire to participate in the production and re-imagination of urban space. Often, this is connected to the right to the city, which is the right to inhabit and be in the city as well as to redefine the city in ways that challenge the demands of capitalist accumulation. That is to make public spaces more valuable to the citizens in contrast to favoring the interests of corporate and financial capital. Unlike other forms of protest like demonstrations, marches and rallies, occupation is defined by an extended te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Resistance
Civil resistance is a form of political action that relies on the use of nonviolent resistance by ordinary people to challenge a particular power, force, policy or regime. Civil resistance operates through appeals to the adversary, pressure and coercion: it can involve systematic attempts to undermine or expose the adversary's sources of power (or pillars of support, such as police, military, clergy, business elite, etc.). Forms of action have included demonstrations, vigils and petitions; strikes, go-slows, boycotts and emigration movements; and sit-ins, occupations, constructive program, and the creation of parallel institutions of government. Some civil resistance movements' motivations for avoiding violence are generally related to context, including a society's values and its experience of war and violence, rather than to any absolute ethical principle. Civil resistance cases can be found throughout history and in many modern struggles, against both tyrannical rulers and demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Disobedience
Civil disobedience is the active and professed refusal of a citizenship, citizen to obey certain laws, demands, orders, or commands of a government (or any other authority). By some definitions, civil disobedience has to be nonviolent to be called "civil". Hence, civil disobedience is sometimes equated with peaceful protests or nonviolent resistance. Henry David Thoreau's essay ''Resistance to Civil Government'', first published in 1849 and then published posthumously in 1866 as ''Civil Disobedience (Thoreau), Civil Disobedience'', popularized the term in the US, although the concept itself was practiced long before this work. Various forms of civil disobedience have been used by prominent activists, such as Women's suffrage in the United States, American women's suffrage leader Susan B. Anthony in the late 19th century, Egyptian nationalist Saad Zaghloul during the 1910s, and Indian nationalist Mahatma Gandhi in 1920s British Raj, British India as part of his leadership of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rioting
A riot or mob violence is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups (race riot) or religions (e.g., sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (e.g., sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganized groups that are fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstration (people)
A political demonstration is an action by a mass group or collection of groups of people in favor of a political or other cause or people partaking in a protest against a cause of concern; it often consists of walking in a mass march formation and either beginning with or meeting at a designated endpoint, or rally, in order to hear speakers. It is different from mass meeting. Demonstrations may include actions such as blockades and sit-ins. They can be either nonviolent or violent, with participants often referring to violent demonstrations as " militant." Depending on the circumstances, a demonstration may begin as nonviolent and escalate to violence. Law enforcement, such as riot police, may become involved in these situations. Police involvement at protests is ideally to protect the participants and their right to assemble. However, officers don't always fulfill this responsibility and it's well-documented that many cases of protest intervention result in power abus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protests
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration, or remonstrance) is a public act of objection, disapproval or dissent against political advantage. Protests can be thought of as acts of cooperation in which numerous people cooperate by attending, and share the potential costs and risks of doing so. Protests can take many different forms, from individual statements to mass political demonstrations. Protesters may organize a protest as a way of publicly making their opinions heard in an attempt to influence public opinion or government policy, or they may undertake direct action in an attempt to enact desired changes themselves. When protests are part of a systematic and peaceful nonviolent campaign to achieve a particular objective, and involve the use of pressure as well as persuasion, they go beyond mere protest and may be better described as civil resistance or nonviolent resistance. Various forms of self-expression and protest are sometimes restricted by governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000 Serbian Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 23 December 2000, to elect members of the National Assembly.Janusz Bugajski (2002) ''Political Parties of Eastern Europe: A Guide to Politics in the Post-Communist Era'', pp434 They were the first free and fair parliamentary elections since the introduction of a multi-party system in 1990 and the overthrow of Slobodan Milošević. The result was a victory for the Democratic Opposition of Serbia, which won 176 of the 250 seats in the National Assembly. Electoral lists Following electoral lists took part in the 2000 parliamentary election: Results References {{Serbian elections Overthrow of Slobodan Milošević Parliamentary elections in Serbia Elections in Serbia and Montenegro Serbia Serbia Parliamentary In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |