|
Netherlandish Renaissance Art
The Low Countries comprise the coastal Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta region in Western Europe, whose definition usually includes the modern countries of Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands and parts of French Flanders, Northern France. Both Belgium and the Netherlands derived their names from earlier names for the region, due to ''nether'' meaning "low" and ''Belgica'' being the Latinization of names, Latinized name for all the Low Countries, a nomenclature that became obsolete after Belgian Revolution, Belgium's secession in 1830. The Low Countries—and the Netherlands and Belgium—had in their history exceptionally many and widely varying names, resulting in equally varying names in different languages. There is diversity even within languages: the use of one word for the country and another for the adjective form is common. This holds for English, where ''Dutch'' is the adjective form for the country "the Netherlands". Moreover, many languages have the same word for both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Belgicus (Dutch-Belgic Lion Of The Low Countries) Famiano Strada C1647
The Leo Belgicus (Latin, 'wikt:Belgic, Belgic Lion') was used in both heraldry and map design to symbolize the former Low Countries (current day Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium and a small part of northern France) with the shape of a lion. When not in map form, the Leo Belgicus often accompanies the Dutch Maiden, the national personification of the Dutch Republic. Often both sit in a circular fenced enclosure, the "Garden of Holland". Europa regina, showing Europe as a queen, was a comparable schematic. The Leo Belgicus is also the name of the Belgian lion or the Brabantian lion, this lion is seen on the coat of arms of Belgium and the flag of the provinces of Flemish and Walloon Brabant. Terminology The names derived from the Belgae (and thus including ''Belgica (other), Belgica'') are now mostly identified with the country Belgium; yet before the division of the Low Countries into a southern and a northern half in the 16th century, it was a common name for the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania Inferior
''Germania Inferior'' ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed ''Germania Secunda'' in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium (modern-day Cologne). Geography According to Ptolemy (2.9), Germania Inferior included the Rhine from its mouth up to the mouth of the ''Obringa'', a river identified with either the Aar or the Moselle. The territory included modern-day Luxembourg, the southern Netherlands, part of Belgium, and part of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany, west of the Rhine. The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum ( Heerlen), Albaniana ( Alphen aan den Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum ( Katwijk), Forum Hadriani ( Voorburg), Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum ( Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum ( Tongeren), Bona ( Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ..., and affiliated with Columbia University. Founded in 1893, it is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fields of literary and cultural studies, history, social work, sociology, religion, film, and international studies. History Columbia University Press was founded in May 1893. In 1933, the first four volumes of the ''History of the State of New York'' were published. In the early 1940s, the Press' revenues rose, partially thanks to the ''Encyclopedia'' and the government's purchase of 12,500 copies for use by the military. Columbia University Press is notable for publishing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier'' . In Davenport, Frances G. ''European Treaties Bearing on the History of the United States and Its Dependencies''. The Lawbook Exchange, Ltd., 2004. in titles), was a stem duchy of the medieval Kingdom of Germany established in 959, which encompassed almost all of modern , |
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as Roman emperor in return for political protection, disregarding the universalist claims of the weakened Byzantine Empire. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. After a civil war from 840 to 843 following the death of Emperor Louis the Pious, the empire was divided into autonomous kingdoms, with one king still recognised as emperor, but with little authority outside his own kingdom. The unity of the empire and the hereditary right of the Carolingians continued to be acknowledged. In 884, Charles the Fat reunited all the Carolingian kingdoms for the last time, but he was deposed by the Frankis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical effects on both the sound and the meaning of a word, cognates may not be obvious, and it often takes rigorous study of historical sources and the application of the comparative method to establish whether lexemes are cognate. Cognates are distinguished from loanwords, where a word has been borrowed from another language. Name The English term ''cognate'' derives from Latin , meaning "blood relative". Examples An example of cognates from the same Indo-European root are: ''night'' ( English), ''Nacht'' ( German), ''nacht'' ( Dutch, Frisian), ''nag'' (Afrikaans), ''Naach'' ( Colognian), ''natt'' ( Swedish, Norwegian), ''nat'' ( Danish), ''nátt'' ( Faroese), ''nótt'' ( Icelandic), ''noc'' ( Czech, Slovak, Polish), ночь, ''noch'' ( Russian), но� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, cleric, ecclesiastic, and vicegerent while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, cardinals, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, sheikh, mullah, muezzin, and ulema. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch ( Modern Dutch: ') or Old Low Franconian (Modern Dutch: ') is the set of dialects that evolved from Frankish spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from around the 6th Page 55: "''Uit de zesde eeuw dateren de oudst bekende geschreven woorden en tekstjes in de Lage Landen, waarmee de periode van het oud-Nederlands begint.''" rom the 6th century date the oldest known text from the Low Countries, with which the period of Old Dutch begins./ref> to the 12th century. Old Dutch is mostly recorded on fragmentary relics, and words have been reconstructed from Middle Dutch and Old Dutch loanwords in French. Old Dutch is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language. It was spoken by the descendants of the Salian Franks who occupied what is now the southern Netherlands, northern Belgium, part of northern France, and parts of the Lower Rhine regions of Germany. It evolved into Middle Dutch around the 12th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
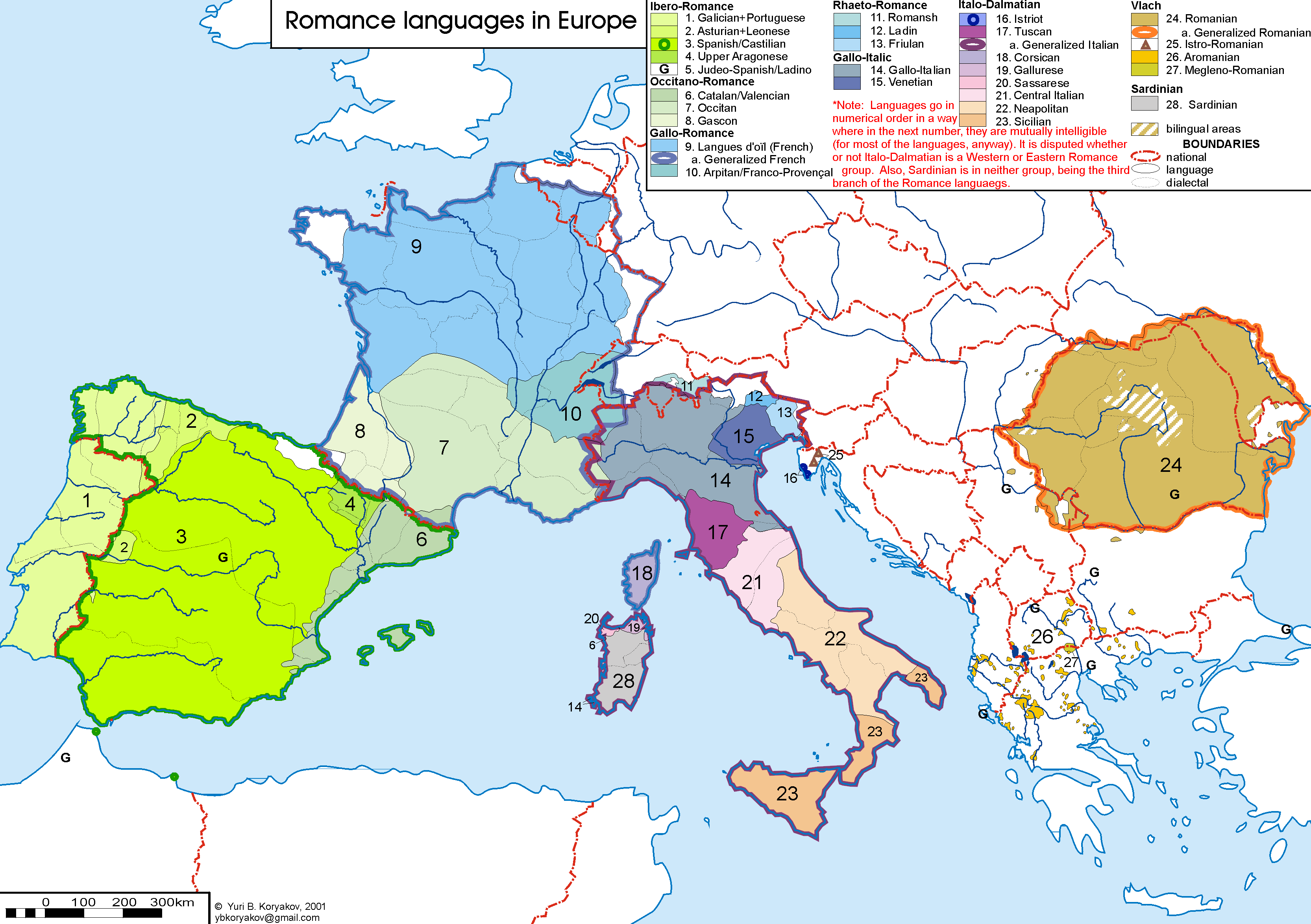
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Language
Frankish (language reconstruction, reconstructed endonym: *), also known as Old Franconian or Old Frankish, was the West Germanic language spoken by the Franks from the 5th to 10th centuries. Franks under king Chlodio settled in Roman Gaul in the 5th century. One of his successors, named Clovis I, took over the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis (in modern day France). Outnumbered by the local populace, the ruling Franks there adapted to its language which was a Vulgar Latin, Proto-Romance dialect. However, many modern French language, French words and place names are still of Frankish origin. Between the 5th and 10th centuries, Frankish spoken in Northeastern France, present-day Belgium, and the Netherlands is subsequently referred to as Old Dutch, whereas the Frankish varieties spoken in the Rhineland were heavily influenced by Elbe Germanic, Elbe Germanic dialects and the Second Germanic consonant shift and formed part of the modern Central Franconian and Rhine Franco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as Roman emperor in return for political protection, disregarding the universalist claims of the weakened Byzantine Empire. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. After a Carolingian civil war, civil war from 840 to 843 following the death of Emperor Louis the Pious, the empire was divided into autonomous kingdoms, with one king still recognised as emperor, but with little authority outside his own kingdom. The unity of the empire and the hereditary right of the Carolingians continued to be acknowledged. In 884, Charles the Fat reunited all the Carolingian kingdoms f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |