|
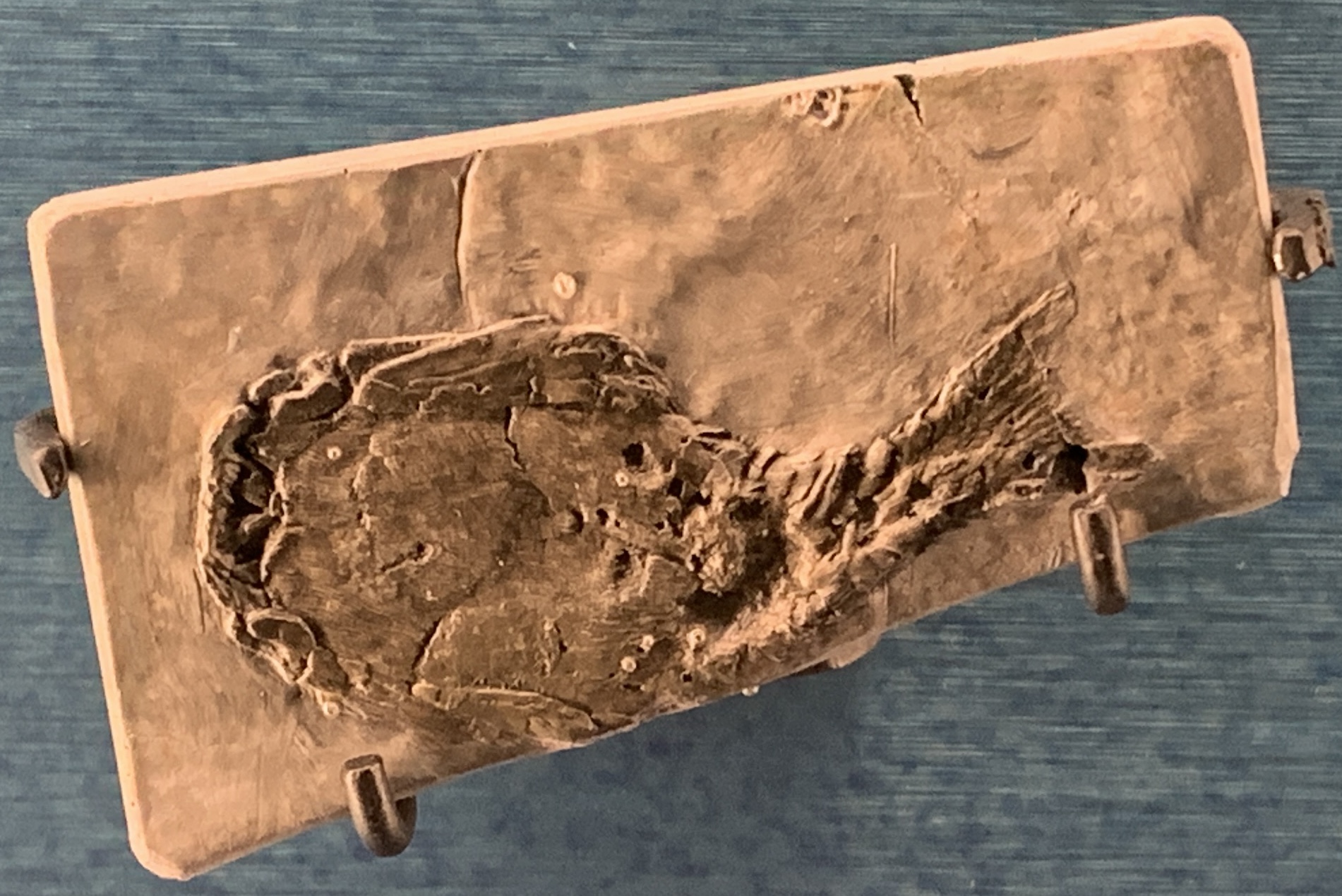
Heterostraci
Heterostraci (Ancient Greek, ἕτερος+ὄστρακον "those [with] a different shell" [-i is pl. of -us]) is an extinct subclass (biology), subclass of Pteraspidomorphi, pteraspidomorph, ostracoderm, jawless vertebrate that lived primarily in Marine (ocean), marine and estuary environments. Heterostraci existed from the mid-Ordovician to the conclusion of the Devonian. Description and anatomy The heterostracans differed from other Paleozoic agnathan taxa both in the arrangement and histology of their scales. Most heterostracans had two plates which form a large dorsal shield and a large ventral shield, and had series of scales arranged in various patterns on the sides of their bodies, the exact pattern differing from one group to another. In a few primitive forms, such as ''Lepidaspis'', the dorsal and ventral shields are composed of a mosaic of tiny scales. In most other known forms, though, these tiny scales have fused together to form the shield-plates. The scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostracoderm
Ostracodermi () or ostracoderms is an informal group of vertebrate animals that include all armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes and possibly the cyclostomes if anaspids are closer to them) and thus does not correspond to one evolutionary lineage. However, the term is still used as an informal way of loosely grouping together the armored jawless fishes. An innovation of ostracoderms was the use of gills not for feeding, but exclusively for respiration. Earlier chordates with gill precursors used them for both respiration and feeding. Ostracoderms had separate pharyngeal gill pouches along the side of the head, which were permanently open with no protective operculum. Unlike invertebrates that use ciliated motion to move food, ostracoderms used their muscular pharynx to create a suction that pulled small and slow-moving prey into their mouths. Swiss anatomist L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardipeltis
''Cardipeltis'' is an extinct genus of heterostracan agnathan from marine strata of early Devonian of Utah, and Wyoming Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ....Bryant, William L., and Rudolph Ruedemann. "The fish fauna of Beartooth Butte, Wyoming. Parts II and III." Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society (1934): 127-167.Denison, Robert Howland. Cardipeltis: an early Devonian agnathan of the Order Heterostraci. Field Museum of Natural History, 1966. Species of ''Cardipeltis'' superficially resemble those of cyathaspids in having a flattened body and indistinct head covered by a large, broad, guitar pick or heart-shaped dorsal shield, and a long, scaly tail. Unlike cyathaspids, which all have a single ventral plate, however, the ventral shield of ''Cardipelt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolypelepidida
Tolypelepidida is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates. These armored jawless fish superficially resemble their relatives, the cyathaspids, though, researchers place the tolypelepids as a sister group to the cyathaspids and the pteraspidids (and both groups' daughter taxa). Janvier, Philippe (1997Heterostraci''The Tree of Life Web Project''. A recent study by Lundgren and Blom in 2013 implies that the order is paraphyletic Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ..., with the type genus, ''Tolypelepis'', being the sister taxon of Cyathaspidiformes.Lundgren, Mette, and Henning Blom. "Phylogenetic relationships of the cyathaspidids (Heterostraci)." GFF 135.1 (2013): 74-84. The typical tolypelepid had a carapace formed from dorsal and ventral plates, and a scaly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidaspis
''Lepidaspis serrata'' ("serrated scaly shield") is an extinct heterostraci, heterostracan jawless fish from Early Devonian Canada. Its scientific name refers to the fact that the armor is composed of hundreds of tiny scales with serrated edges. Although it is regarded as a heterostracan, its exact placement within Heterostraci is regarded as ''incertae sedis'', as the fact that it is currently impossible to discern where its dorsal and ventral plates (which are made up of a mosaic of the aforementioned tiny scales) end or begin. Some experts regard it as being descended from the basal heterostracans of the Silurian. References External links Enigmatic Heterostraci taxa Heterostraci genera Devonian fish of North America {{Devonian-jawless-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panamintaspis
''Panamintaspis snowi'' is an extinct species of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathan which existed during the early Middle Devonian period of Death Valley, California.Elliott, David K., and Robert R. Ilyes. "New Early Devonian pteraspidids (Agnatha, Heterostraci) from Death Valley National Monument, southeastern California." Journal of Paleontology (1996): 152-161. Fossils are found in Late Emsian-aged marine strata of the Lost Burro Formation. ''P. snowi'' strongly resembles ''Pteraspis'', though while it was originally described as a member of the same family, Pteraspididae, a recent phylogenetic reassessment of the order Pteraspidiformes places ''P. snowi'' within the paraphyletic family "Protopeteraspidae," as the sister taxon of the suborder Pteraspidoidei (the super-taxon that contains Pteraspididae together with Protaspididae and '' Gigantaspis'').Pernegre, Vincent N., and David K. Elliott. "Phylogeny of the Pteraspidiformes (Heterostraci), Silurian–Devonian jawles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
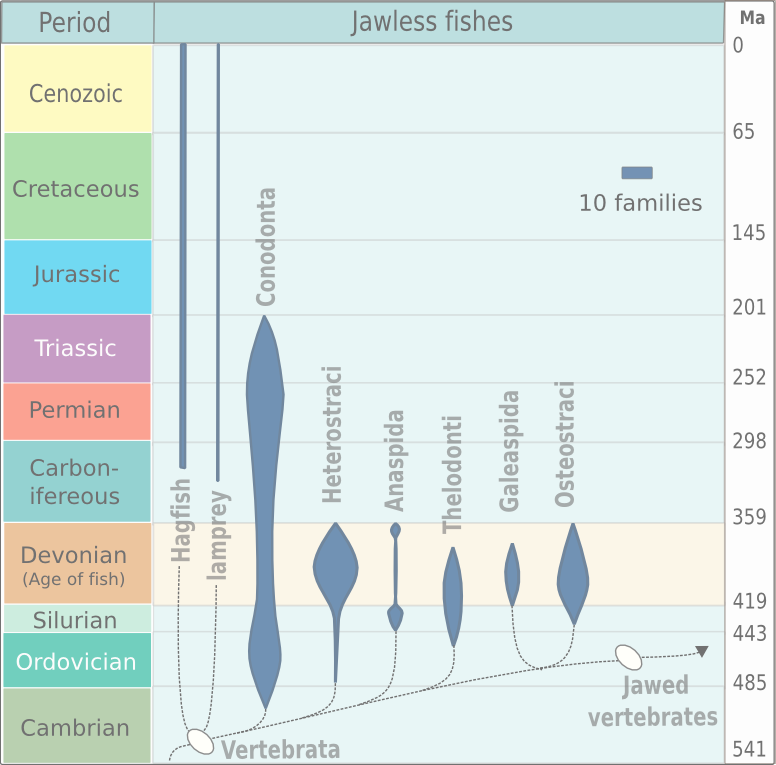
Agnathan
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both living ( cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to jawed fish, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish comprise about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidiformes
Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia. Anatomy Like their descendants, the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiform heterostracans had the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Thus, the living animals would have resembled tadpoles encased in massive armor. The majority of taxa have the rostral and pineal plates fused or merged with the dorsal plate, and in the amphiaspidids, all the plates of the cephalothorax were fused together into a single "muff-like" unit. Unlike the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiforms are thought to be almost uniformly benthic in lifestyle, though only the amphiaspids and the ctenaspids are thought to be burrowers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Cyathaspidif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteraspidomorphi
Pteraspidomorpha is an extinct class of early jawless fish. They have long been regarded as closely related or even ancestral to jawed vertebrates, but the few characteristics they share with the latter are now considered as basal traits for all vertebrates. Characteristics Pteraspidomorphs are characterized by their massive dermal head armour having large, median, ventral and dorsal plates or shields. Janvier, Philippe (1997Pteraspidomorphi''The Tree of Life Web Project''. The fossils show extensive shielding of the head. Many had hypocercal tails in order to generate lift to increase ease of movement through the water for their armoured bodies, which were covered in dermal bone. They also had sucking mouth parts and some species may have lived in fresh water. Most pteraspidomorphs were marine, but lived very near to the shore, in lagoons and deltas. Some groups are thought to have been fresh water-dwelling. They were certainly bottom-dwellers, as shown by traces of abrasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psammosteida
Psammosteida also called as Psammosteoidei is a suborder of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathans. The psammosteids had broad, flattened bodies, suggesting a predominantly benthic habit. The earliest unequivocal psammosteid is '' Drepanaspis'' of Early Devonian Germany, which is either included in the family Psammosteidae, or placed within its own family, Drepanaspididae. If the late Silurian/Early Devonian '' Weigeltaspis'' is a psammosteid, as opposed to being a traquairaspid, then that genus, instead, would be the oldest psammosteid. However, its placement within Heterostraci remains a matter of debate. Other notable psammosteids include '' Psammosteus'', and '' Obruchevia'', two genera of enormous species with dorsal shields around one meter in diameter. The Psammosteids were the only heterostracans to survive to the end of the Devonian, where they finally perish during the Hangenberg event The Hangenberg event, also known as the Hangenberg crisis or end-Devonian ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteraspidiformes
Pteraspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan agnathan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Early Devonian strata of Europe and North America, and from Upper Silurian Canada. Anatomy A pteraspidiform heterostracan has the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, rostral, pineal plates, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Many genera were benthic, others were apparently active swimming nekton.Botella, Hector, and Richard A. Farina. "Flow pattern around the rigid cephalic shield of the Devonian agnathan Errivaspis waynensis (Pteraspidiformes: Heterostraci)." Palaeontology 51.5 (2008): 1141-1150/ref> Delicate, finger-like components of the anterior end of the ventral plate forming the edges of the mouth suggest that pteraspidiform heterostracans were filter-feeding, filter-feeders that selectively filtered specific sized plankton from the water column.Purnell, Mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traquairaspidiformes
Traquairaspidiformes is an order of extinct heterostracan agnathan fish known from the Silurian and Early Devonian periods. Fossils are predominantly known from Late Silurian fluvial deposits from Wales and England: some species were also found in strata representing shallow water marine environment in Canada and North America North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri .... The head-shield and body armor of most traquairaspids form an almond shape. Plates have a distinctive ornamentation of tubercles: this ornamentation is very similar to the plate ornamentation of the heterostracan '' Weigeltaspis''. This similarity of ornamentation creates much confusion over the taxonomical placement of ''Weigeltaspis'', in addition to confusion over whether or not an isolated plate is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelodonti
Thelodonti (from Greek: "nipple teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct Palaeozoic jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor. There is much debate over whether the group represents a monophyletic grouping, or disparate stem groups to the major lines of jawless and jawed fish. Thelodonts are united in possession of " thelodont scales". This defining character is not necessarily a result of shared ancestry, as it may have been evolved independently by different groups. Thus the thelodonts are generally thought to represent a polyphyletic group, although there is no firm agreement on this point. On the basis that they are monophyletic, they are reconstructed as being ancestrally marine and invading freshwater on multiple occasions. "Thelodonts" were morphologically very similar, and probably closely related, to fish of the classes Heterostraci and Anaspida, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |