|
Cylinder Engine (PSF)
In an engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels. The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings, which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil. Steam engines The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. Internal combustion engines The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled by the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. In an air-cooled engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering Porting (engine)#Two-stroke porting, ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion piston engine, internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Ring
A piston ring is a metallic split ring that is attached to the outer diameter of a piston in an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The main functions of piston rings in engines are: # Sealing the combustion chamber so that there is minimal loss of gases to the crank case. # Improving heat transfer from the piston to the cylinder wall. # Maintaining the proper quantity of the oil between the piston and the cylinder wall # Regulating engine oil consumption by scraping oil from the cylinder walls back to the sump. Most piston rings are made from cast iron or steel. Design Piston rings are designed to seal the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. If this gap were too small, thermal expansion of the piston could mean the piston seizes in the cylinder, causing serious damage to the engine. On the other hand, a large gap would cause insufficient sealing of the piston rings against the cylinder walls, resulting in excessive blow-by (combustion gases entering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
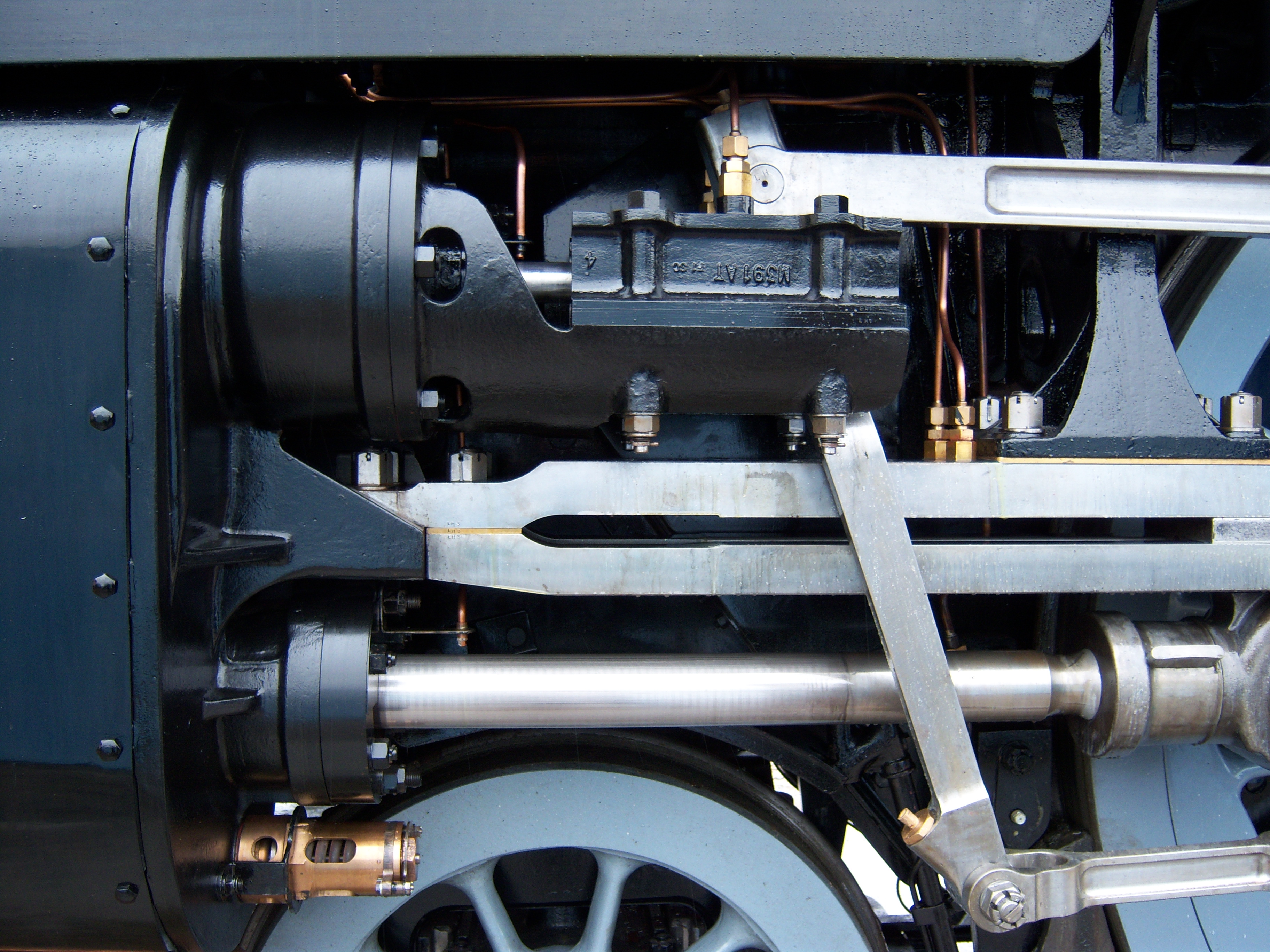
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed by a connecting rod and Crank (mechanism), crank into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including Boiler (power generation), boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder Engine (PSF)
In an engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels. The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings, which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil. Steam engines The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. Internal combustion engines The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled by the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. In an air-cooled engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-cooled Engine
Air-cooled engines rely on the circulation of air directly over heat dissipation fins or hot areas of the engine to cool them in order to keep the engine within operating temperatures. Air-cooled designs are far simpler than their liquid-cooled counterparts, which require a separate radiator, coolant reservoir, piping and pumps. Air-cooled engines are widely seen in applications where weight or simplicity is the primary goal. Their simplicity makes them suited for uses in small applications like chainsaws and lawn mowers, as well as small generators and similar roles. These qualities also make them highly suitable for aviation use, where they are widely used in general aviation aircraft and as auxiliary power units on larger aircraft. Their simplicity, in particular, also makes them common on motorcycles. Introduction Most modern internal combustion engines are cooled by a closed circuit carrying liquid coolant through channels in the engine block and cylinder head. A fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure that contains the cylinders and other components. The engine block in an early automotive engine consisted of just the cylinder block, to which a separate crankcase was attached. Modern engine blocks typically have the crankcase integrated with the cylinder block as a single component. Engine blocks often also include elements such as coolant passages and oil galleries. The term "cylinder block" is often used interchangeably with "engine block". However, technically, the block of a modern engine (i.e., multiple cylinders integrated with another component) would be classified as a monobloc. __TOC__ Construction The main structure of an engine typically consists of the cylinders, coolant passages, oil galleries, crankcase, and cylinder head(s). The first production engines of the 1880s to 1920s usually used separate components for each element, which were bolted together during engine assembly. Modern en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikasil
Nikasil is a trademarked electrodeposited lipophilic nickel matrix silicon carbide coating for engine components, mainly piston engine cylinder liners. Development Nikasil was introduced by Mahle in 1967 and was initially developed to allow Wankel engine apex seals to work directly against the aluminum block. This coating allowed aluminum cylinders and pistons to work directly against each other with low wear and friction. Unlike other methods, including cast iron cylinder liners, Nikasil allowed very large cylinder bores with tight tolerances. This made it possible for existing engine designs to be expanded easily. The aluminum cylinders also gave a much better heat conductivity and lower friction than cast iron liners, an important attribute for a high-output engine. The coating was further developed as a replacement for hard-chrome plated cylinder bores for Mercury Marine Racing, and Kohler Engines, and as a repair replacement for factory-chromed snowmobiles, dirt bik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaze (metallurgy)
Compacted oxide layer glaze describes the often shiny, wear-protective layer of oxide formed when two metals (or a metal and ceramic) are slid against each other at high temperature in an oxygen-containing atmosphere. The layer forms on either or both of the surfaces in contact and can protect against wear. Background A not often used definition of ''glaze'' is the highly sintered compacted oxide layer formed due to the sliding of either two metallic surfaces (or sometimes a metal surface and ceramic surface) at high temperatures (normally several hundred degrees Celsius) in oxidizing conditions. The sliding or tribological action generates oxide debris that can be compacted against one or both sliding surfaces and, under the correct conditions of load, sliding speed and oxide chemistry as well as (high) temperature, sinter together to form a 'glaze' layer. The 'glaze' formed in such cases is actually a crystalline oxide, with a very small crystal or grain size having been shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore (engine)
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds ( rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. In steam locomotives The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. Bore pitch Bore pitch is the distance between the centerline of a cylinder bore to the centerline of the next cylinder bore adjacent to it in an internal combustion engine. It's also referred to as the "mean cylinder width", "bore spacing", "bore center distance" and "cylinder spacing". The bore pitch is always larger than the inside diameter of the cylinder (the bore and piston diameter) sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder (engine), cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were initially cast iron, but later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of Stephenson's Rocket) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the Locomotive frame, main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Displacement
Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as an indicator of the power (through mean effective pressure and rotational speed) an engine might be capable of producing and the amount of fuel it should be expected to consume. For this reason displacement is one of the measures often used in advertising, as well as regulating, motor vehicles. It is usually expressed using the metric units of cubic centimetres (cc or cm3, equivalent to millilitres) or litres (l or L), orparticularly in the United States cubic inches (CID, cu in, or in3). Definition The overall displacement for a typical reciprocating piston engine is calculated by multiplying together three values; the distance travelled by the piston (the stroke length), the circular area of the cylinder, and the number of cylinders in the whole e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |