|
Curette
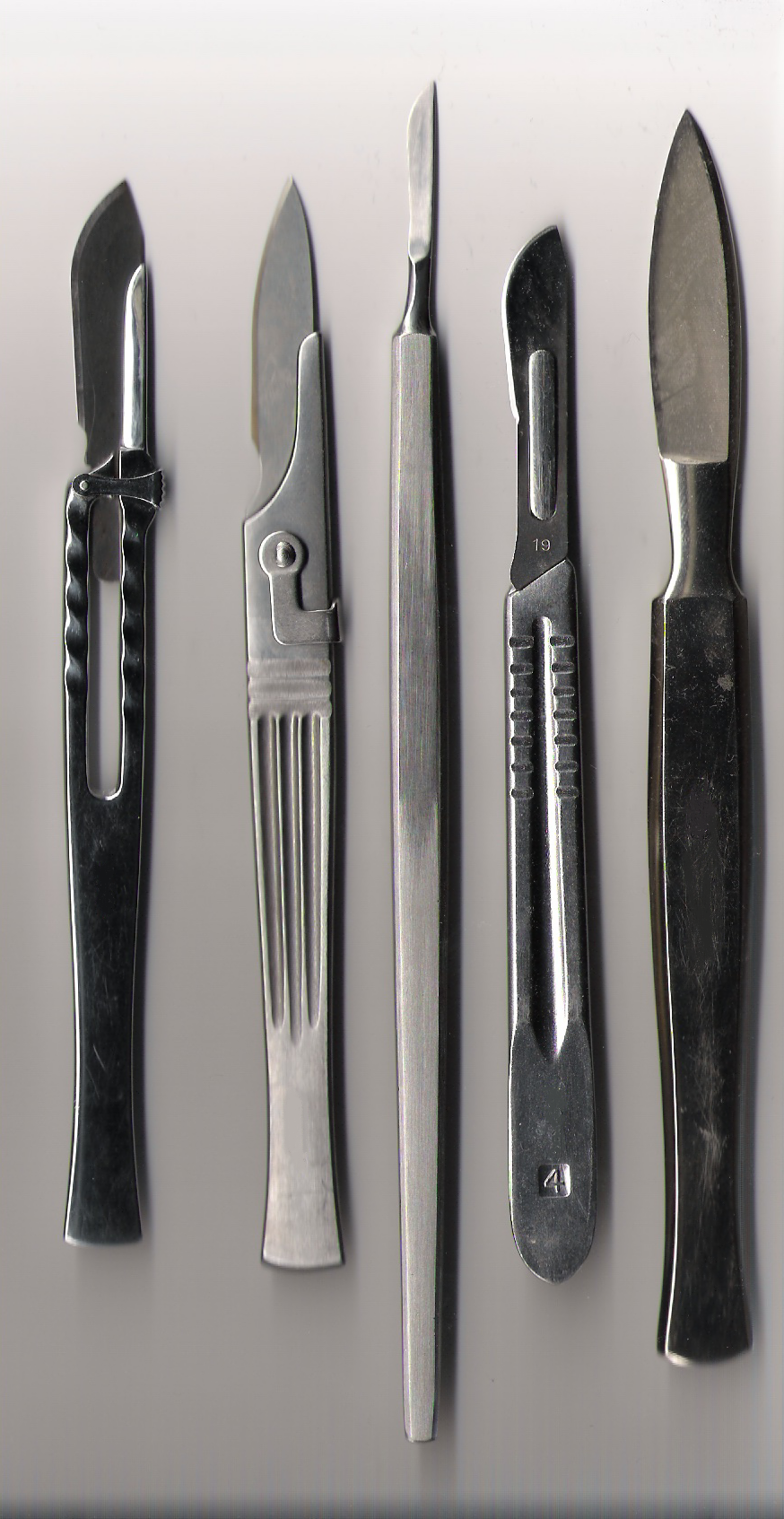
A curette is a surgical instrument designed for scraping or debridement, debriding biological tissue or debris in a biopsy, :wikt:excision, excision, or cleaning procedure. In form, the curette is a small hand tool, often similar in shape to a stylus; at the tip of the curette is a small scoop, hook, or Chisel#Gouge, gouge. The verb ''to curette'' means "to scrape with a curette", and curettage ( or ) is treatment that involves such scraping. Uses Some examples of medical use of a curette include: * the removal of impacted ear wax; * dilation and curettage of the uterus, a gynaecology, gynecologic procedure; *excision of many Benign tumor, benign tumors and some Cancer, malignant tumors; * excision of the adenoids (adenoidectomy) by an otolaryngologist; * to scrape dental tartar, tartar deposits from tooth enamel with a periodontal curette. See also *Ear pick References External links Curette images from the Waring Historical Library at the Medical University of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Curette
The periodontal curette is a type of hand-activated instrument used in dentistry and dental hygiene for the purpose of scaling and root planing.Darby ML, Walsh MM, editors. ''Dental Hygiene: Theory and Practice.'' 4th ed. St. Louis: Saunders/Elsevier; 2015. The periodontal curette is considered a treatment instrument and is classified into two main categories: universal curettes and Gracey curettes. Periodontal curettes have one face, one or two cutting edges and a rounded back and rounded toe. They are typically the instrument of choice for subgingival Calculus (dental), calculus removal. Universal and Gracey curettes are typically used during nonsurgical periodontal therapy of a patient's dental hygiene care.Gehrig JS, Willmann DE. ''Foundations of Periodontics for the Dental Hygienist.'' 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2016. The goal of nonsurgical periodontal therapy is to eliminate inflammation and return the patient's periodontium back to health.Newman MG, Takei HH, Klok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curette In Sterile Packaging
A curette is a surgical instrument designed for scraping or debriding biological tissue or debris in a biopsy, excision, or cleaning procedure. In form, the curette is a small hand tool, often similar in shape to a stylus; at the tip of the curette is a small scoop, hook, or gouge. The verb ''to curette'' means "to scrape with a curette", and curettage ( or ) is treatment that involves such scraping. Uses Some examples of medical use of a curette include: * the removal of impacted ear wax; * dilation and curettage of the uterus, a gynecologic procedure; *excision of many benign tumors and some malignant tumors; * excision of the adenoids ( adenoidectomy) by an otolaryngologist; * to scrape tartar deposits from tooth enamel Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Tartar
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by precipitation of minerals from saliva and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in plaque on the teeth. This process of precipitation kills the bacterial cells within dental plaque, but the rough and hardened surface that is formed provides an ideal surface for further plaque formation. This leads to calculus buildup, which compromises the health of the gingiva (gums). Calculus can form both along the gumline, where it is referred to as supragingival (), and within the narrow sulcus that exists between the teeth and the gingiva, where it is referred to as subgingival (). Calculus formation is associated with a number of clinical manifestations, including bad breath, receding gums and chronically inflamed gingiva. Brushing and flossing can remove plaque from which calculus forms; however, once formed, calculus is too hard (firmly attached) to be removed with a toothbrush. Calculus buildup can be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Pick
Ear picks, also called ear scoops, or ear spoons, or earpicks, are a type of curette used to clean the ear canal of earwax (cerumen). They are preferred and are commonly used in East Asia, South Asia and Southeast Asia because Asians tend to develop dry ear wax. In Asia, these are traditionally made from bamboo or precious metals such as silver or gold, but more commonly now, from stainless steel or plastic. European ear scoops produced up to the early 19th century were made from either bronze or precious metals such as silver. Use of ear picks to remove wax is discouraged by some health professionals for fear of damaging the ear and causing infections. Types Other than the wide variety of materials used to make them, ear picks vary widely in their tips and embellishments. Disposable plastic ear picks with a cotton swab at one end are increasingly popular. Tips *''Ladle'': The traditional and most commonly seen type of tip for the ear pick. They comprise a spoon or spatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoids
In anatomy, the pharyngeal tonsil, also known as the nasopharyngeal tonsil or adenoid, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. In children, it normally forms a soft mound in the roof and back wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula. The term ''adenoid'' is also used to represent adenoid hypertrophy, the abnormal growth of the pharyngeal tonsils. Structure The adenoid is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. The adenoid, unlike the palatine tonsils, has pseudostratified epithelium. The adenoids are part of the so-called Waldeyer ring of lymphoid tissue which also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils and the tubal tonsils. Development Adenoids develop from a subepithelial inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Tissue
In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of Cell (biology), cells (tumor) that does not Cancer invasion, invade neighboring tissue or Metastasis, metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to Cancer, malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower Cell growth, growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well Cell differentiation, differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface (fibrous sheath of connective tissue) or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include Melanocytic nevus, moles and uterine fibroids. Some forms of benign tumors may be harmful to health. Benign tumor growth causes a Mass effect (medicine), mass effect that can compress neighboring tissues. This can lead to nerve damage, blood flow reduction (Ischaemia, ischemia), tissue death (necrosis), or organ damage. The health effects of benign tumor growth may be more prominent if the tumor is contained within an enclosed space such as the cranium, respir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Instrument
A surgical instrument is a medical device for performing specific actions or carrying out desired effects during a surgery or operation, such as modifying biological tissue, or to provide access for viewing it. Over time, many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented. Some surgical instruments are designed for general use in all sorts of surgeries, while others are designed for only certain specialties or specific procedures. Classification of surgical instruments helps surgeons to understand the functions and purposes of the instruments. With the goal of optimizing surgical results and performing more difficult operations, more instruments continue to be invented in the modern era. History Many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented and some have been repurposed as medical knowledge and surgical practices have developed. As surgery practice diversified, some tools are advanced for higher accuracy and stability while so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
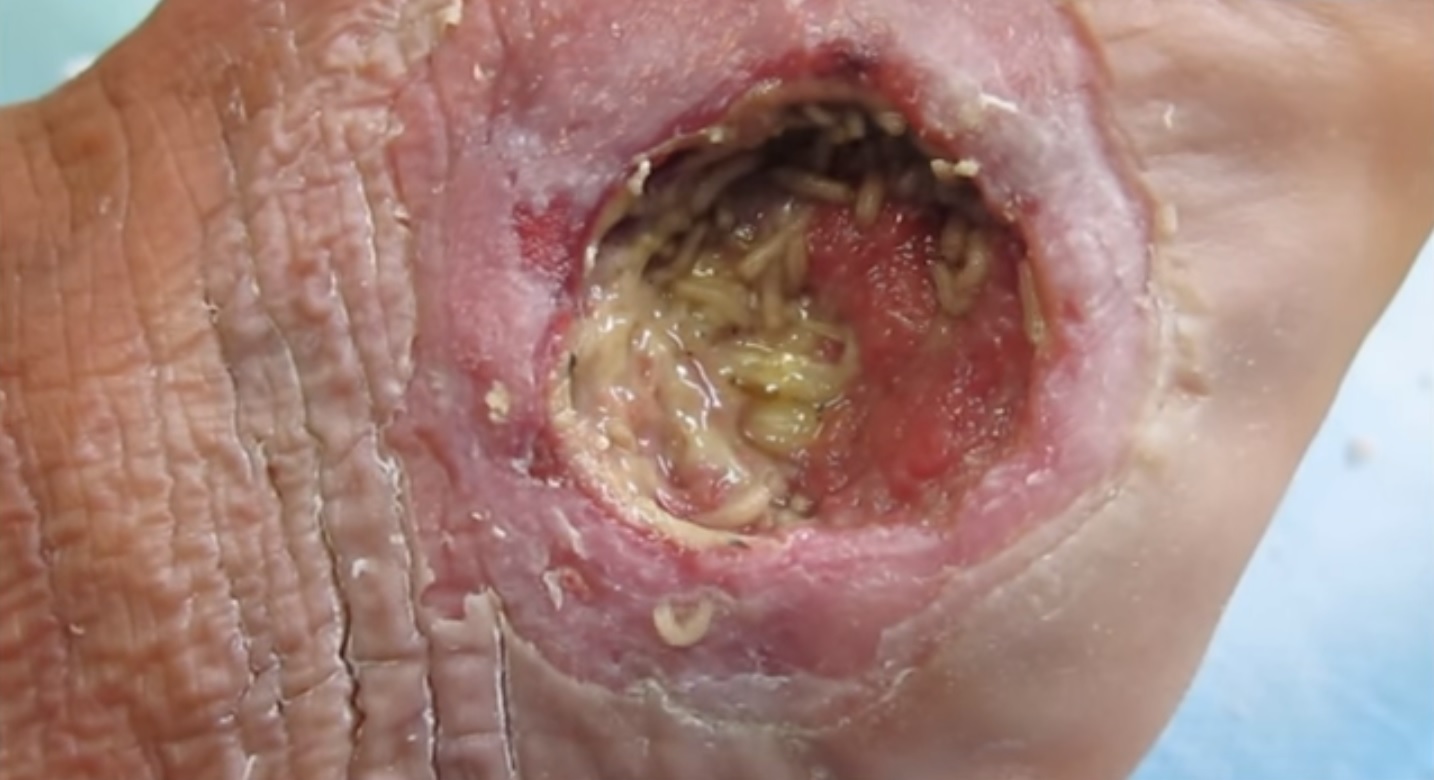
Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), or by maggot therapy. In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas. Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites. Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed. Types There is a lack of high-quality evidence to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face, scalp, and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of Neo-Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoid for reasons which include impaired breathing through the nose, chronic infections, or recurrent earaches. The effectiveness of removing the adenoids in children to improve recurrent nasal symptoms and/or nasal obstruction has not been well studied. The surgery is less commonly performed in adults in whom the adenoid is much smaller and less active than it is in children. It is most often done on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia. Post-operative pain is generally minimal and reduced by icy or cold foods. The procedure is often combined with tonsillectomy (this combination is usually called an "adenotonsillectomy" or "T&A"), for which the recovery time is an estimated 10–14 days, sometimes longer, mostly dependent on age. Adenoidectomy is not often performed under one year of age as adenoid function is part of the body's immune system, but its contribution to this decreases progressively beyond this age. Medical uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |