|
Cultural Code
Cultural code refers to several related concepts about the body of shared practices, expectations and conventions specific to a given domain of a culture. Under one interpretation, a cultural code is seen as defining a set of images that are associated with a particular group of stereotypes in our minds. This is sort of cultural unconscious, which is hidden even from our own understanding, but is also seen in our actions. The cultural codes of a nation helps to understand the behavioral responses characteristic of that nation's citizens. The key codes in understanding specific behaviors differentiate between religion, gender, relationships, money, food, health, and cultures.Clotaire R. The Culture Code: An Ingenious Way to Understand Why People Around the World Live and Buy as They Do. New York, 2006. See also * Code (semiotics) * Collective unconscious * Meme References Code In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). ''Primitive Culture''. Vol 1. New York: J. P. Putnam's Son Culture often originates from or is attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculturalism, monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
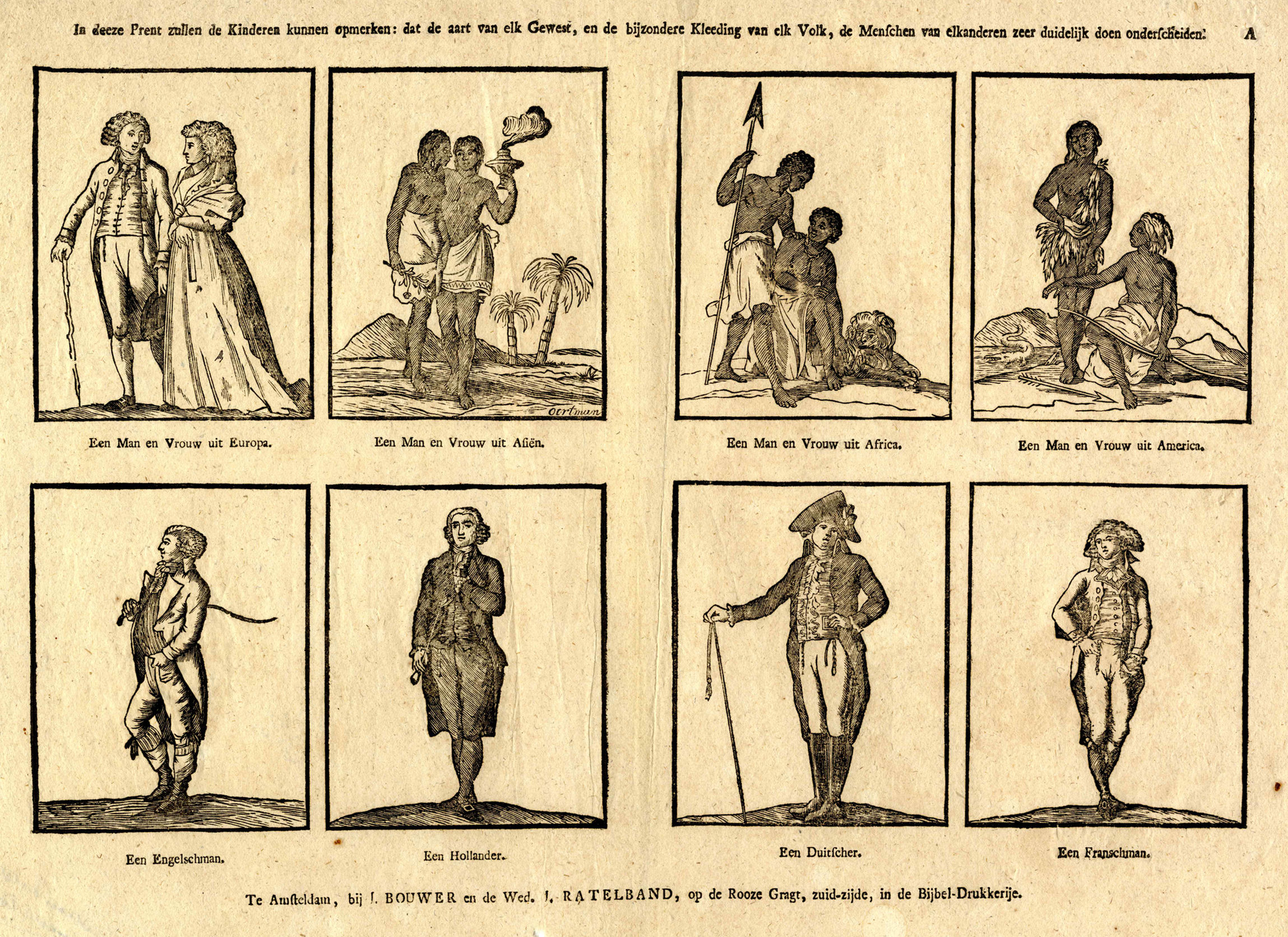
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalization, generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes make information processing easier by allowing the perceiver to rely on previously stored knowledge in place of incoming information. Stereotypes are often faulty generalization, faulty, inaccurate, and Belief perseverance, resistant to new information. Although stereotypes generally have negative implications, they aren't necessarily negative. They may be positive, neutral, or negative. They can be broken down into two categories: explicit stereotypes, which are conscious, and implicit stereotypes, which are subconscious. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype is a belief about a group that a person is consciously aware of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code (semiotics)
In the broadest sense, a code is a (learnt, or arbitrary, or conventional) correspondence or rule between patterns. It can be an arrangement of physical matter, including the electromagnetic spectrum, that stores the potential (when activated) to convey meaning (or a pre-specified result). For instance, the pattern of vibration we call 'sound' when activated within the mind, triggers an image; say the word "cat". Also, seeing the shapes we call 'letters' forming the word makes one think of or visualize a cat. The words upon the screen were conceived in the human mind, and then translated into computer code. A code many are familiar with is our spoken language which is assembled from or built upon phonetic sounds (patterns of vibration in the atmosphere or air). Code can also be used to refer to any physical or electromagnetic quality that human beings (or animals, or electronic devices) can perceive and then link and associate to another set of phenomena such as in a color schem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Unconscious
In psychology, the collective unconsciousness () is a term coined by Carl Jung, which is the belief that the unconscious mind comprises the instincts of Jungian archetypes—innate symbols understood from birth in all humans. Jung considered the collective unconscious to underpin and surround the unconscious mind, distinguishing it from the personal unconscious of Freudian psychoanalysis. He believed that the concept of the collective unconscious helps to explain why similar themes occur in mythologies around the world. He argued that the collective unconscious had a profound influence on the lives of individuals, who lived out its symbols and clothed them in meaning through their experiences. The psychotherapeutic practice of analytical psychology revolves around examining the patient's relationship to the collective unconscious. Psychiatrist and Jungian analyst Lionel Corbett argues that the contemporary terms "autonomous psyche" or "objective psyche" are more commonly used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meme
A meme (; ) is an idea, behavior, or style that Mimesis, spreads by means of imitation from person to person within a culture and often carries symbolic meaning representing a particular phenomenon or theme. A meme acts as a unit for carrying culture, cultural ideas, symbols, or practices, that can be transmitted from one mind to another through writing, speech, gestures, rituals, or other imitable phenomena with a mimicked theme. Supporters of the concept regard memes as cultural analogues to genes in that they Self-replication, self-replicate, mutate, and respond to natural selection, selective pressures. In popular language, a meme may refer to an Internet meme, typically an image, that is remixed, copied, and circulated in a shared cultural experience online. Proponents theorize that memes are a viral phenomenon that may evolve by natural selection in a manner analogous to that of evolution, biological evolution. Memes do this through processes analogous to those of genetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |