|
Cubed Sphere
In Cartography, mapmaking, a quadrilateralized spherical cube, or quad sphere for short, is an equal-area projection, equal-area polyhedral map projection, polyhedral map projection and discrete global grid scheme for data collected on a Sphere, spherical surface (either that of the Earth or the celestial sphere). It was first proposed in 1975 by Chan and O'Neill for the Naval Research Laboratory, Naval Environmental Prediction Research Facility. This scheme is also often called the COBE sky cube, because it was designed to hold data from the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) project. Elements The quad sphere has two principal characteristic features. The first is that the mapping consists of projecting the sphere onto the faces of an inscribed cube using a Curvilinear perspective, curvilinear projection that preserves area. The sphere is divided into six equal regions, which correspond to the faces of the cube. The vertex (geometry), vertices of the cube correspond to the Cartesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Cube Map Development
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Of Two
A power of two is a number of the form where is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number 2, two as the Base (exponentiation), base and integer as the exponent. In the fast-growing hierarchy, is exactly equal to f_1^n(1). In the Hardy hierarchy, is exactly equal to H_(1). Powers of two with Sign (mathematics)#Terminology for signs, non-negative exponents are integers: , , and is two multiplication, multiplied by itself times. The first ten powers of 2 for non-negative values of are: :1, 2, 4, 8, 16 (number), 16, 32 (number), 32, 64 (number), 64, 128 (number), 128, 256 (number), 256, 512 (number), 512, ... By comparison, powers of two with negative exponents are fractions: for positive integer , is one half multiplied by itself times. Thus the first few negative powers of 2 are , , , , etc. Sometimes these are called ''inverse powers of two'' because each is the multiplicative inverse of a positive power of two. Base of the binary numeral sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Map Projections
This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise WP:NOTABLE, notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections, there can be no comprehensive list. Table of projections *The first known popularizer/user and not necessarily the creator. Key Type of projection surface ; Cylindrical: In normal aspect, these map regularly-spaced meridians to equally spaced vertical lines, and parallels to horizontal lines. ; Pseudocylindrical: In normal aspect, these map the central meridian and parallels as straight lines. Other meridians are curves (or possibly straight from pole to equator), regularly spaced along parallels. ; Conic: In normal aspect, conic (or conical) projections map meridians as straight lines, and parallels as arcs of circles. ; Pseudoconical: In normal aspect, pseudoconical projections represent the central meridian as a straight line, other meridians as complex curves, and parallels as ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial intelligence (AI). It has been referred to as "the most powerful company in the world" by the BBC and is one of the world's List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands. Google's parent company, Alphabet Inc., is one of the five Big Tech companies alongside Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, Meta Platforms, Meta, and Microsoft. Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by American computer scientists Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Together, they own about 14% of its publicly listed shares and control 56% of its stockholder voting power through super-voting stock. The company went public company, public via an initial public offering (IPO) in 2004. In 2015, Google was reorganized as a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEALPix
HEALPix (sometimes written as Healpix), an acronym for Hierarchical Equal Area isoLatitude Pixelisation of a 2-sphere, is an algorithm for pixelisation of the 2-sphere based on subdivision of a distorted rhombic dodecahedron, and the associated class of map projections. The pixelisation algorithm was devised in 1997 by Krzysztof M. Górski at the Theoretical Astrophysics Center in Copenhagen, Denmark, and first published as a preprint in 1998. Projection and pixelisation The HEALPix projection is a general class of spherical projections, sharing several key properties, which map the 2-sphere to the Euclidean plane. Any of these can be followed by partitioning (pixelising) the resulting region of the 2-plane. In particular, when one of these projections (the H=4, K=3 HEALPix projection) is followed by a pixelisation of the 2-plane, the result is generally known as the HEALPix pixelisation, which is widely used in physical cosmology for maps of the cosmic microwave background. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
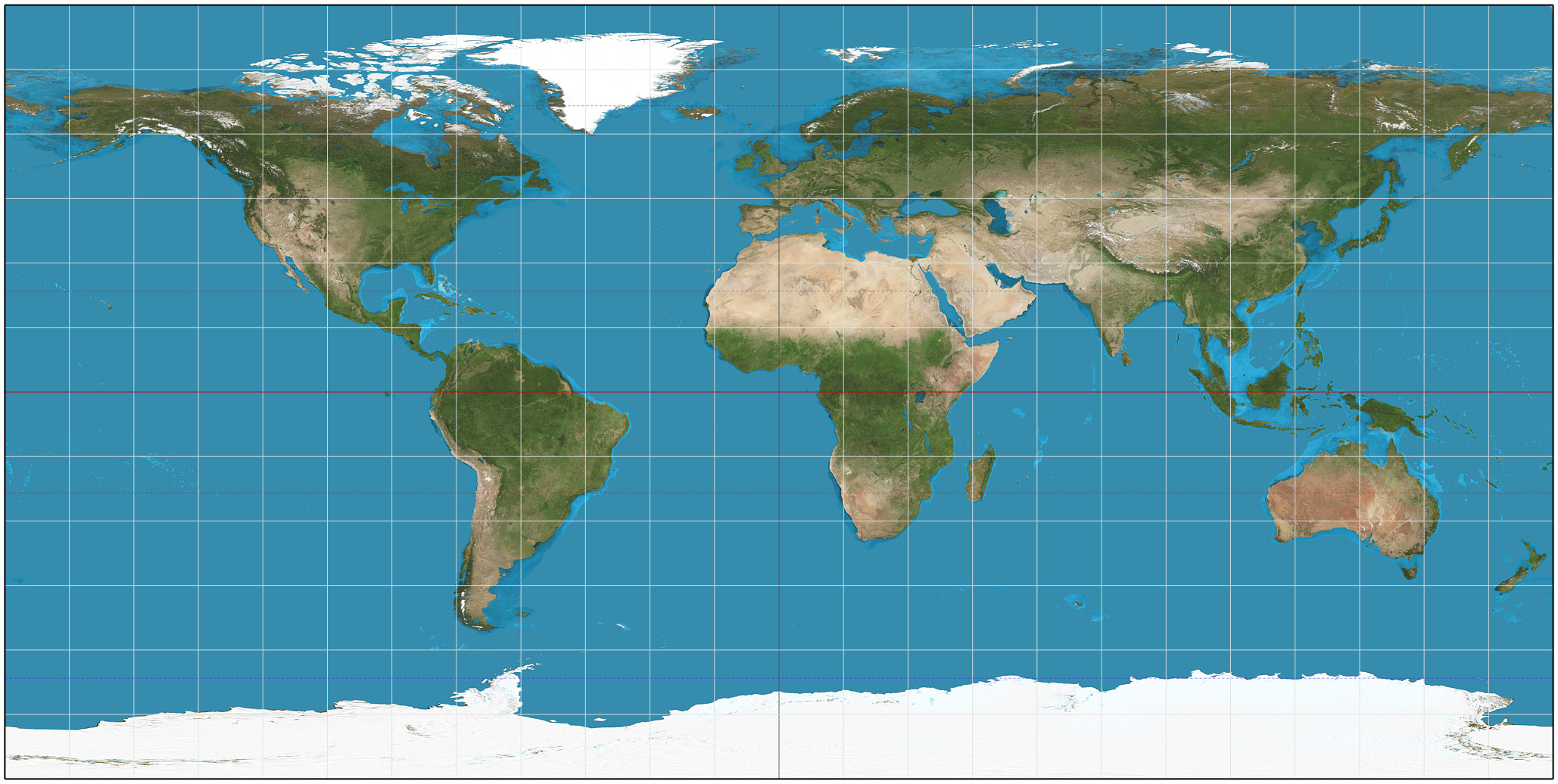
Earth Cube Map
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large sheets of ice at Earth's polar deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a magnetosphere capable of deflecting most of the destructive solar winds and cosmic radiation. Earth has a dynamic atmosphere, which sustains Earth' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Singularity
In mathematics, a singularity is a point at which a given mathematical object is not defined, or a point where the mathematical object ceases to be well-behaved in some particular way, such as by lacking differentiability or analyticity. For example, the reciprocal function f(x) = 1/x has a singularity at x = 0, where the value of the function is not defined, as involving a division by zero. The absolute value function g(x) = , x, also has a singularity at x = 0, since it is not differentiable there. The algebraic curve In mathematics, an affine algebraic plane curve is the zero set of a polynomial in two variables. A projective algebraic plane curve is the zero set in a projective plane of a homogeneous polynomial in three variables. An affine algebraic plane cu ... defined by \left\ in the (x, y) coordinate system has a singularity (called a cusp (singularity), cusp) at (0, 0). For singularities in algebraic geometry, see singular point of an algebraic variety. For singul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of A Set
In mathematics, a partition of a set is a grouping of its elements into Empty set, non-empty subsets, in such a way that every element is included in exactly one subset. Every equivalence relation on a Set (mathematics), set defines a partition of this set, and every partition defines an equivalence relation. A set equipped with an equivalence relation or a partition is sometimes called a setoid, typically in type theory and proof theory. Definition and notation A partition of a set ''X'' is a set of non-empty subsets of ''X'' such that every element ''x'' in ''X'' is in exactly one of these subsets (i.e., the subsets are nonempty mutually disjoint sets). Equivalently, a family of sets ''P'' is a partition of ''X'' if and only if all of the following conditions hold: *The family ''P'' does not contain the empty set (that is \emptyset \notin P). *The union (set theory), union of the sets in ''P'' is equal to ''X'' (that is \textstyle\bigcup_ A = X). The sets in ''P'' are said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numbering Scheme
There are many different numbering schemes for assigning nominal numbers to entities. These generally require an agreed set of rules, or a central coordinator. The schemes can be considered to be examples of a primary key of a database management system table, whose table definitions require a database design. In computability theory, the simplest numbering scheme is the assignment of natural numbers to a set of objects such as functions, rational numbers, graphs, or words in some formal language. A numbering can be used to transfer the idea of computability and related concepts, which are originally defined on the natural numbers using computable functions, to these different types of objects. A simple extension is to assign cardinal numbers to physical objects according to the choice of some base of reference and of measurement units for counting or measuring these objects within a given precision. In such case, numbering is a kind of classification, i.e. assigning a num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quad-tree
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are the two-dimensional analog of octrees and are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions. The data associated with a leaf cell varies by application, but the leaf cell represents a "unit of interesting spatial information". The subdivided regions may be square or rectangular, or may have arbitrary shapes. This data structure was named a quadtree by Raphael Finkel and J.L. Bentley in 1974. A similar partitioning is also known as a ''Q-tree''. All forms of quadtrees share some common features: * They decompose space into adaptable cells. * Each cell (or bucket) has a maximum capacity. When maximum capacity is reached, the bucket splits. * The tree directory follows the spatial decomposition of the quadtree. A tree-pyramid (T-pyramid) is a "complete" tree; every node of the T-pyramid has four child nodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Tree
In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the ''left child'' and the ''right child''. That is, it is a ''k''-ary tree with . A recursive definition using set theory is that a binary tree is a triple , where ''L'' and ''R'' are binary trees or the empty set and ''S'' is a singleton (a single–element set) containing the root. From a graph theory perspective, binary trees as defined here are arborescences. A binary tree may thus be also called a bifurcating arborescence, a term which appears in some early programming books before the modern computer science terminology prevailed. It is also possible to interpret a binary tree as an undirected, rather than directed graph, in which case a binary tree is an ordered, rooted tree. Some authors use rooted binary tree instead of ''binary tree'' to emphasize the fact that the tree is rooted, but as defined above, a binary tree is always rooted. In ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasterisation
In computer graphics, rasterisation (British English) or rasterization (American English) is the task of taking an image described in a vector graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes). The rasterized image may then be displayed on a computer display, video display or printer, or stored in a bitmap file format. Rasterization may refer to the technique of drawing 3D models, or to the conversion of 2D rendering primitives, such as polygons and line segments, into a rasterized format. Etymology The term "rasterisation" comes . 2D images Line primitives Bresenham's line algorithm is an example of an algorithm used to rasterize lines. Circle primitives Algorithms such as the midpoint circle algorithm are used to render circles onto a pixelated canvas. 3D images Rasterization is one of the typical techniques of rendering 3D models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |