|
CubePort
{{Infobox Software , name = CubePort , logo = , developer = ExoLogic Corporation (2002-current) , latest_release_version = v2.23 , latest_release_date = 03-31-2010 , operating_system = Microsoft Windows , genre = Data transformation , license = Proprietary EULA , website CubePort is a commercial software application that converts from Oracle Essbase to the analogous Microsoft product Microsoft Analysis Services, which is built into Microsoft SQL Server. This application achieves this through various analogy mapping techniques, and is a standard client-server application that runs on a Windows computer but may connect to non-Windows servers. CubePort converts the various OLAP structures and syntaxes in the source through an extraction process, interprets, and recreates in the target. The objective is to simulate exactly the behavior of the original source system to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essbase
Essbase is a multidimensional database management system (MDBMS) that provides a platform upon which to build analytic applications. Essbase began as a product from Arbor Software, which merged with Hyperion Software in 1998. Oracle Corporation acquired Hyperion Solutions Corporation in 2007. Until late 2005 IBM also marketed an OEM version of Essbase as DB2 OLAP Server. The database researcher E. F. Codd coined the term " on-line analytical processing" (OLAP) in a whitepaper that set out twelve rules for analytic systems (an allusion to his earlier famous set of twelve rules defining the relational model). This whitepaper, published by Computerworld, was somewhat explicit in its reference to Essbase features, and when it was later discovered that Codd had been sponsored by Arbor Software, Computerworld withdrew the paper. In contrast to "on-line transaction processing" (OLTP), OLAP defines a database technology optimized for processing human queries rather than transactions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDBMS
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured format using rows and columns. Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and updating the database. History The concept of relational database was defined by E. F. Codd at IBM in 1970. Codd introduced the term ''relational'' in his research paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In this paper and later papers, he defined what he meant by ''relation''. One well-known definition of what constitutes a relational database system is composed of Codd's 12 rules. However, no commercial implementations of the relational model conform to all of Codd's rules, so the term has gradually come to describe a broader class of database systems, which at a minim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidimensional Expressions
Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) is a query language for online analytical processing (OLAP) using a database management system. Much like SQL, it is a query language for OLAP cubes. It is also a calculation language, with syntax similar to spreadsheet formulae. Background The MultiDimensional eXpressions (MDX) language provides a specialized syntax for querying and manipulating the multidimensional data stored in OLAP cubes. While it is possible to translate some of these into traditional SQL, it would frequently require the synthesis of clumsy SQL expressions even for very simple MDX expressions. MDX has been embraced by a wide majority of Comparison of OLAP servers, OLAP vendors and has become the De facto standard, standard for OLAP systems. History MDX was first introduced as part of the OLE DB for OLAP specification in 1997 from Microsoft. It was invented by the group of Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Server engineers including Mosha Pasumansky. The specification was quickly f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
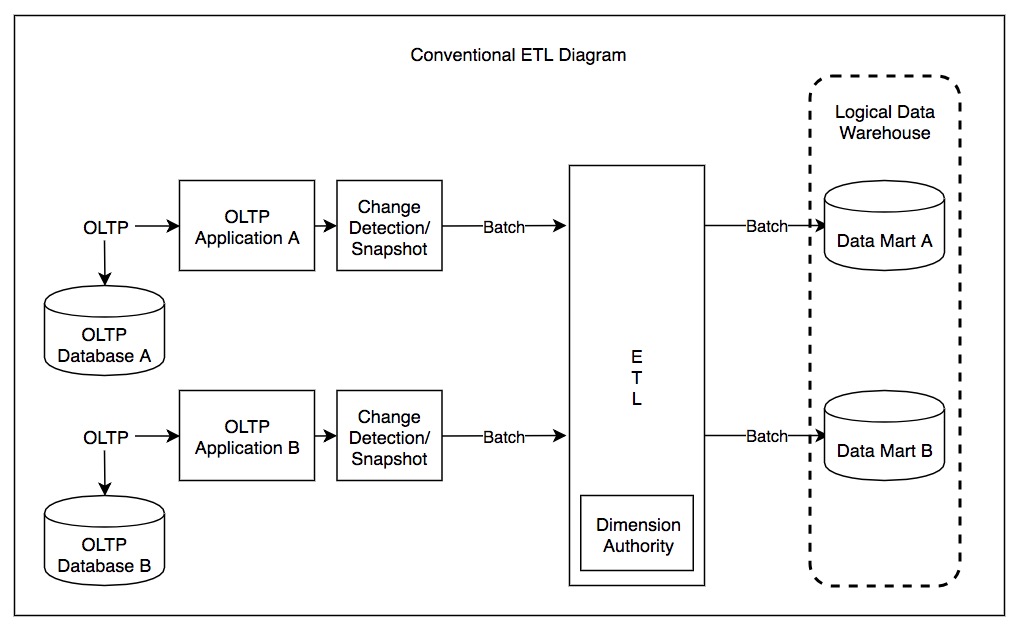
Extract, Transform, Load
Extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase computing process where data is ''extracted'' from an input source, ''transformed'' (including cleaning), and ''loaded'' into an output data container. The data can be collected from one or more sources and it can also be output to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on recurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process is often used in data warehousing. ETL sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OLAP Cube
An OLAP cube is a multi-dimensional array of data. Online analytical processing (OLAP) is a computer-based technique of analyzing data to look for insights. The term ''cube'' here refers to a multi-dimensional dataset, which is also sometimes called a hypercube if the number of dimensions is greater than three. Terminology A cube can be considered a multi-dimensional generalization of a two- or three-dimensional spreadsheet. For example, a company might wish to summarize financial data by product, by time-period, and by city to compare actual and budget expenses. Product, time, city and scenario (actual and budget) are the data's dimensions. ''Cube'' is a shorthand for ''multidimensional dataset'', given that data can have an arbitrary number of ''Dimension (data warehouse), dimensions''. The term hypercube is sometimes used, especially for data with more than three dimensions. A cube is not a "cube" in the strict mathematical sense, as the sides are not all necessarily equal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowflake Schema
In computing, a snowflake schema or snowflake model is a Logical schema, logical arrangement of tables in a multidimensional database such that the Entity-relationship model, entity relationship diagram resembles a snowflake shape. The snowflake schema is represented by centralized fact tables which are connected to multiple Dimension (data warehouse), dimensions. "Snowflaking" is a method of normalizing the dimension tables in a star schema. When it is completely normalized along all the dimension tables, the resultant structure resembles a snowflake with the fact table in the middle. The principle behind snowflaking is normalization of the dimension tables by removing low cardinality attributes and forming separate tables. The snowflake schema is similar to the star schema. However, in the snowflake schema, dimensions are Normalization (database), normalized into multiple related tables, whereas the star schema's dimensions are denormalized with each dimension represented by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Schema
In computing, the star schema or star model is the simplest style of data mart Logical schema, schema and is the approach most widely used to develop data warehouses and dimensional data marts. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of Dimension (data warehouse), dimension tables. The star schema is an important special case of the snowflake schema, and is more effective for handling simpler queries. The star schema gets its name from the Physical data model, physical model'sC J Date, "An Introduction to Database Systems (Eighth Edition)", p. 708 resemblance to a Star polygon, star shape with a fact table at its center and the dimension tables surrounding it representing the star's points. Model The star schema separates business process data into facts, which hold the measurable, quantitative data about a business, and dimensions which are descriptive attributes related to fact data. Examples of fact data include sales price, sale quantity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendor Lock-in
In economics, vendor lock-in, also known as proprietary lock-in or customer lockin, makes a customer dependent on a vendor for products, unable to use another vendor without substantial switching costs. The use of open standards and alternative options makes systems tolerant of change, so that decisions can be postponed until more information is available or unforeseen events are addressed. Vendor lock-in does the opposite: it makes it difficult to move from one solution to another. Lock-in costs that create barriers to market entry may result in antitrust action against a monopoly. Lock-in types ; Monopolistic : Whether a single vendor controls the market for the method or technology being locked in to. Distinguishes between being locked to the mere technology, or specifically the vendor of it. This class of lock-in is potentially technologically hard to overcome if the monopoly is held up by barriers to market that are nontrivial to circumvent, such as patents, secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) consists of strategies, methodologies, and technologies used by enterprises for data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of BI technologies include Financial reporting, reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, Dashboard (business), dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, Predictive Analysis, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI tools can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help organizations identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. They aim to allow for the easy interpretation of these big data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights is assumed to potentially provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability, and help them take strategic decisions. Busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |