|
Cromemco RDOS
The Cromemco 4FDC floppy-disk controller is designed to interface both 5.25- and 8.0-inch floppy disk drives to the S-100 computer bus used in Cromemco and other IEEE 696 computers. It also contains an RS-232 serial I/O channel with software-selectable baud rates from 110 to 76,800. In addition, it has a 1 KB resident 2708 ROM containing Cromemco's RDOS, the resident disk operating system. The 4FDC was designed to drive Persci 277 8-inch single-density floppy drives. These drives were interesting in two respects: * They used a fast voice coil actuator and not a stepper motor to position the drive read write head. * The data separator electronics were on the drive itself. Due to the second fact, an unmodified 4FDC can not be used with 8-inch drives that don't have single-density data separators on the drive electronics. Later Cromemco disk controllers such as the 16FDC and 64FDC contained both single and double density data separators and the 64FDC also supplied write ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromemco 4FDC Color Adjusted
Cromemco, Inc. was a Mountain View, California microcomputer company known for its high-end Z80-based S-100 bus computers and peripherals in the early days of the personal computer revolution. The company began as a partnership in 1974 between Harry Garland and Roger Melen, two Stanford Ph.D. students. The company was named for their residence at Stanford University ( Crothers Memorial, a Stanford dormitory reserved for engineering graduate students). Cromemco was incorporated in 1976 and their first products were the Cromemco Cyclops digital camera, and the Cromemco Dazzler color graphics interface - both groundbreaking at the time - before they moved on to making computer systems. In December 1981, ''Inc.'' magazine named Cromemco in the top ten fastest-growing privately held companies in the U.S. In 1987, it was acquired by Dynatech Corporation of Boston. Early history The collaboration that was to become Cromemco began in 1970 when Harry Garland and Roger Melen, gradua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Read-only Memory
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing software that is rarely changed during the life of the system, also known as firmware. Software applications, such as video games, for programmable devices can be distributed as ROM cartridge, plug-in cartridges containing ROM. Strictly speaking, ''read-only memory'' refers to hard-wired memory, such as diode matrix or a #Solid-state ROM, mask ROM integrated circuit (IC), that cannot be electronically changed after manufacture. Although discrete circuits can be altered in principle, through the addition of Jump wire, bodge wires and the removal or replacement of components, ICs cannot. Correction of errors, or updates to the software, require new devices to be manufactured and to replace the installed device. Floating-gate ROM semiconductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boot Monitor
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via hardware such as a physical button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system. On some systems a power-on reset (POR) does not initiate booting and the operator must initiate booting after POR completes. IBM uses the term Initial Program Load (IPL) on someE.g., System/360 through IBM Z, RS/6000 and System/38 through IBM Power Systems product lines. Restarting a computer also is called ''rebooting'', which can be "hard", e.g. after electrical power to the CPU is switched from off to on, or "soft", where the power is not cut. On some systems, a soft boot may optionally clear RAM to zero. Both hard and soft booting can be initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromemco DOS
Cromemco DOS or CDOS (an abbreviation for Cromemco Disk Operating System) is a CP/M-like operating system by Cromemco designed to allow users of Cromemco microcomputer systems to create and manipulate disk files using symbolic names. Overview CDOS was written in Zilog Z80 machine code. Due to the number of available programs available to run under Digital Research CP/M at that time, CDOS was designed to be upwards CP/M-compatible. Many programs written for CP/M versions up to and including version 1.33 run without modification under CDOS. However, programs written for CDOS generally do not run under CP/M. The Cromemco Z-2 had the ability to run Cromemco DOS. Besides CP/M 2.2 and Cromix, the Cromemco System One can also run Cromemco DOS. The Cromemco C-10 personal computer, introduced in 1982, also ran CDOS. An emulator for a Cromemco CDOS system exists. Commands The following list of commands are supported by Cromemco DOS. Intrinsic commands * BYE * DIR * ERA * REN * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Storage
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and Data storage, recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast technologies are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write Precompensation
Write precompensation (abbreviated WPcom in the literature) is a technical aspect of the design of hard disks, floppy disks and other digital magnetic recording devices. It is the modification of the analog write signal, shifting transitions somewhat in time, in such a way as to ensure that the signal that will later be read back will be as close as possible to the unmodified write signal. It is required because of the non-linear properties of magnetic recording surfaces. A higher amount of precompensation is needed to write data in sector Sector may refer to: Places * Sector, West Virginia, U.S. Geometry * Circular sector, the portion of a disc enclosed by two radii and a circular arc * Hyperbolic sector, a region enclosed by two radii and a hyperbolic arc * Spherical sector, a po ...s that are closer to the center of the disk. In constant angular velocity (CAV) recording, in which the disk spins at a constant speed no matter where the data is written, the sectors closest to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
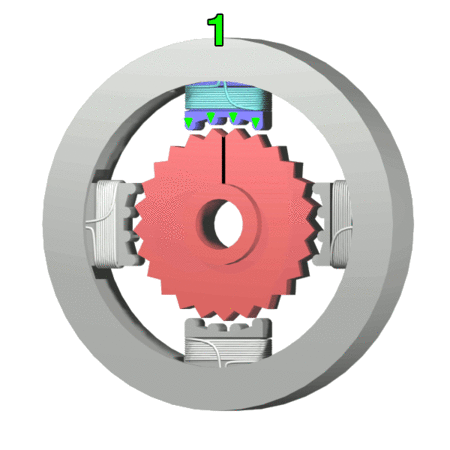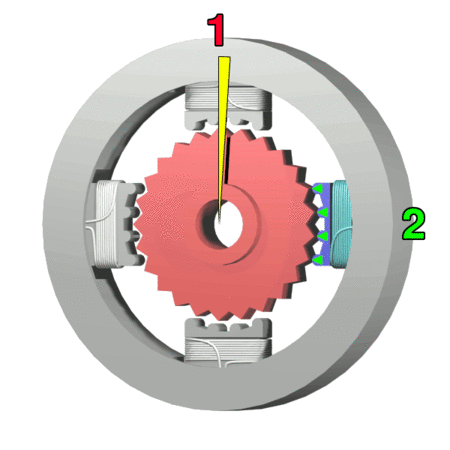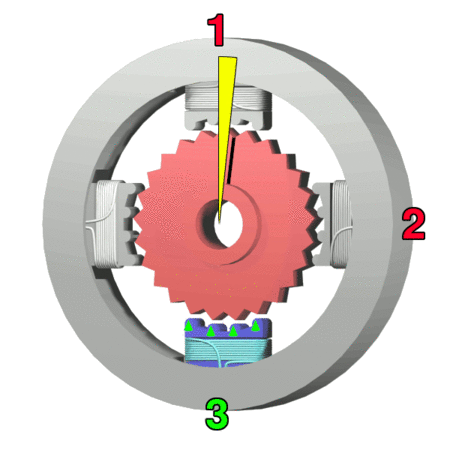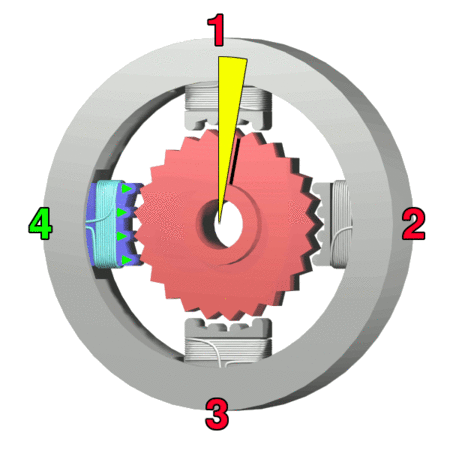
Stepper Motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor,Clarence W. de Silva. Mechatronics: An Integrated Approach (2005). CRC Press. p. 675. "The terms ''stepper motor'', ''stepping motor'', and ''step motor'' are synonymous and are often used interchangeably." is a brushless DC electric motor that rotates in a series of small and discrete angular steps. Stepper motors can be set to any given step position without needing a Rotary encoder, position sensor for feedback. The step position can be rapidly increased or decreased to create continuous rotation, or the motor can be ordered to actively hold its position at one given step. Motors vary in size, speed, step resolution, and torque. Switched reluctance motors are very large stepping motors with a reduced pole count. They generally employ closed-loop commutator (electric), commutators. Mechanism Brushed DC motors rotate continuously when DC voltage is applied to their terminals. The stepper motor is known for its proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Coil
A voice coil (consisting of a former, collar, and winding) is the coil of wire attached to the apex of a loudspeaker cone. It provides the motive force to the cone by the reaction of a magnetic field to the current passing through it. The term is also used for voice coil linear motors such as those used to move the heads inside hard disk drives, which produce a larger force and move a longer distance but work on the same principle. In some applications, such as the operation of servo valves, electronic focus adjustment on digital cameras, these are known as voice coil motors (VCM). Operation By driving a current through the voice coil, a magnetic field is produced. This magnetic field causes the voice coil to react to the magnetic field from a permanent magnet fixed to the speaker's frame, thereby moving the cone of the speaker. By applying an audio waveform to the voice coil, the cone will reproduce the sound pressure waves, corresponding to the original input sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Operating System
A disk operating system (DOS) is a computer operating system that requires a disk or other direct-access storage device as secondary storage. A DOS provides a file system and a means for loading and running computer program, programs stored on the disk. The term is now historical, as most if not all operating systems for general-purpose computers now require direct-access storage devices as secondary storage. History Before modern storage such as the disk drive, floppy disk, and flash storage, early computers used storage such as Analog delay line, delay line, core memory, punched card, punched tape, magnetic tape, and magnetic drum. Early microcomputers and home computers used paper tape, audio cassette tape (such as Kansas City standard), or no permanent storage at all. Without permanent storage, programs and data are input directly into memory using front panel switches, or is input through a computer terminal or keyboard, sometimes controlled by a BASIC interpreter in read-on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resident Operating System
Resident may refer to: People and functions * Resident minister, a representative of a government in a foreign country * Resident (medicine), a stage of postgraduate medical training * Residency (pharmacy), Resident (pharmacy), a stage of postgraduate pharmaceutical training *Resident engineer, an engineer or expert who works at client-side * Resident, a person who maintains Domicile (law), residency in a given place * Resident, a person who has tax residence in a country or jurisdiction * Resident, a patient at a long-term care facility or senior center * Resident minister (also known as "resident"), a rank in the Indian Political Department of British India * Resident (Second Life), Resident (''Second Life''), a member of the Second Life community * Resident DJ, a DJ who performs at a venue on a regular basis or permanently * Resident spy, a spy who operates in a foreign country Culture * Resident (magazine), ''Resident'' (magazine), an Austrian music magazine * The Reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibibyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as the Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words of 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48, or 60 bits, corresponding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floppy-disk Controller
A floppy-disk controller (FDC) is a hardware component that directs and controls reading from and writing to a computer's floppy disk drive (FDD). It has evolved from a discrete set of components on one or more circuit boards to a special-purpose integrated circuit (IC or "chip") or a component thereof. An FDC is responsible for reading data presented from the host computer and converting it to the drive's on-disk format using one of a number of encoding schemes, like FM encoding (single density) or MFM encoding (double density), and reading those formats and returning it to its original binary values. Depending on the platform, data transfers between the controller and host computer would be controlled by the computer's own microprocessor, or an inexpensive dedicated microprocessor like the MOS 6507 or Zilog Z80. Early controllers required additional circuitry to perform specific tasks like providing clock signals and setting various options. Later designs included more of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |