|
Croker River
The Croker River is a waterway above the Arctic Circle on the mainland of Northern Canada in the western Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut. It is the largest river between Darnley Bay (in the Northwest Territories) and Coronation Gulf that flows into Amundsen Gulf. The Croker averages in width. It originates at Bluenose Lake then flows northward. It passes through a dolomite box canyon from the coast, before reaching a triangular shaped delta west of Clifton Point , and then entering Amundsen Gulf's Dolphin and Union Strait. Croker River is named after John Wilson Croker, Secretary to the Admiralty. Croker River (PIN 1BG) is a former Distant Early Warning Line and a current North Warning System site. See also *List of rivers of Nunavut This is a list of rivers that are in whole or partly in Nunavut, Canada: By watershed Arctic watershed *Beaufort Sea **Great Bear Lake (Northwest Territories) *** Bloody River ***Dease River ** Horton River *Viscount Melville Sound ** Nanook River . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the '' Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the '' British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluenose Lake
Bluenose Lake is a lake in Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located north of the Arctic Circle within the large, shallow basin of the Melville Hills. It is approximately long, wide, and is situated at above sea level. The Croker River flows north from Bluenose Lake to the Arctic Ocean, entering at Dolphin and Union Strait. It was officially named in 1953 by John Kelsall and James Mitchell subsequent to their biological investigation of the previously unnamed lake. Fauna The area barren-ground caribou are divided, genetically, into two herds, Bluenose-east and Bluenose-west. Other mammals include Arctic fox, Arctic ground squirrel, Arctic hare, Back's lemming, barren-ground grizzly bear, collared lemming, muskox, short-tailed weasel, tundra vole, and wolf. Birds that frequent the area include Arctic loon, Arctic tern, Baird's sandpiper, black-bellied plover, buff-breasted sandpiper, Canada goose, glaucous gull, golden eagle, golden plover, herring gull, king eider, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rivers Of Nunavut
This is a list of rivers that are in whole or partly in Nunavut, Canada: By watershed Arctic watershed *Beaufort Sea **Great Bear Lake (Northwest Territories) *** Bloody River *** Dease River ** Horton River *Viscount Melville Sound **Nanook River (Victoria Island) *Amundsen Gulf **Hornaday River **Roscoe River ** Croker River **Harding River ** Kagloryuak River (Victoria Island) *Dolphin and Union Strait **Hoppner River *Coronation Gulf ** Rae River ** Richardson River **Coppermine River ** Asiak River ** Tree River ** Hood River ** Kugaryuak River ***James River ** Burnside River ***Mara River ** Western River ** Napaaktoktok River *Dease Strait **Ekalluk River ** Hargrave River *Queen Maud Gulf **Ellice River ** Perry River (''Kuukyuak'') ** Armark River ** Simpson River ** McNaughton River ** Kaleet River *Rasmussen Basin ** Back River *** Bullen River *** Consul River *** Baillie River **Castor and Pollux River **Hayes River ** Murchison River *Gulf of Boothia **Arrowsmith Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Warning System
The North Warning System (NWS) is a joint United States and Canadian early-warning radar system for the atmospheric air defense of North America. It provides surveillance of airspace from potential incursions or attacks from across North America's polar region. It replaced the Distant Early Warning Line system in the late 1980s. Overview The NWS consists of both long range AN/FPS-117 and short range AN/FPS-124 surveillance radars, operated and maintained by North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). There are 13 long range sites and 36 short range sites. In Canada, the station sites are owned or leased by the Government of Canada, which also owns most of the infrastructure. The radars and tactical radios are owned by the United States Air Force. The Alaska Regional Operations Control Center (ROCC) at Elmendorf AFB, Alaska controls the stations in Alaska; the Canada East and Canada West Regional Operations Control Centres (ROCCs) at CFB North Bay, Ontario control t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
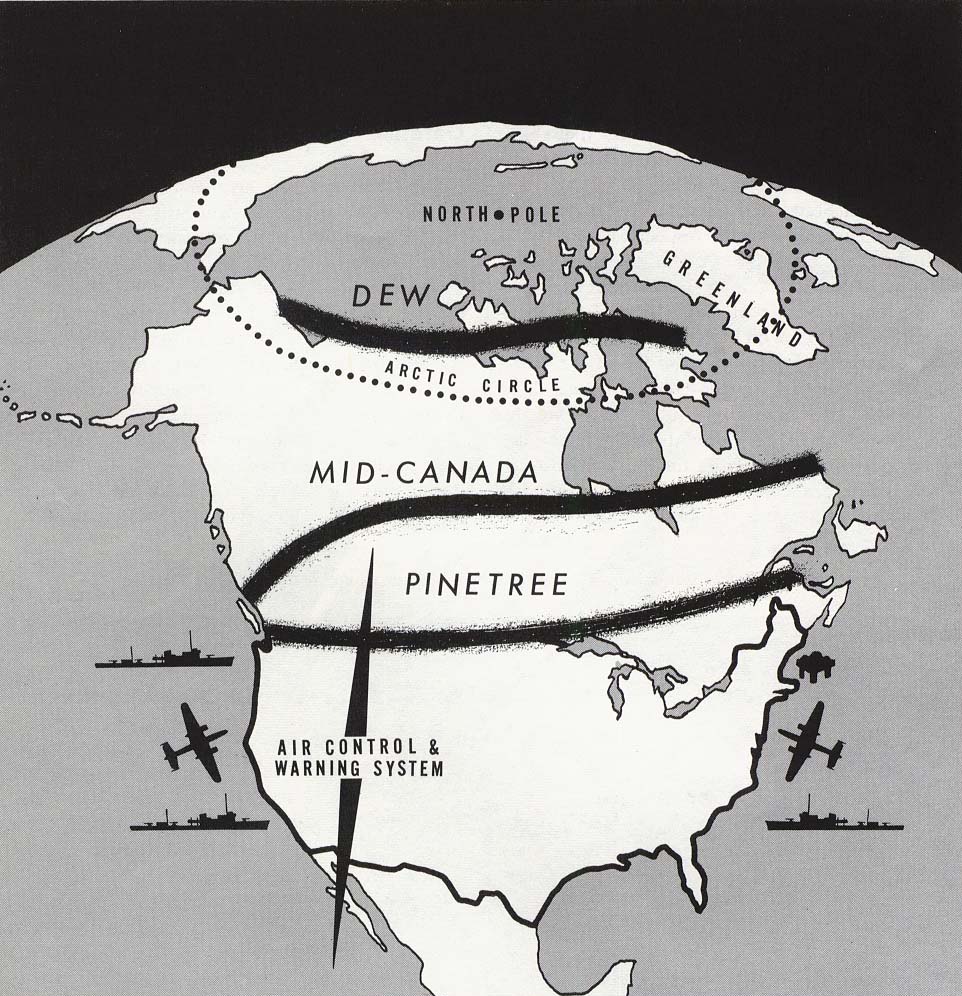
Distant Early Warning Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Project Stretchout and Project Bluegrass), in addition to the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. It was set up to detect incoming bombers of the Soviet Union during the Cold War, and provide early warning of any sea-and-land invasion. The DEW Line was the northernmost and most capable of three radar lines in Canada and Alaska. The first of these was the joint Canadian-United States Pinetree Line, which ran from Newfoundland to Vancouver Island just north of the Canada–United States border, but even while it was being built there were concerns that it would not provide enough warning time to launch an effective counterattack. The Mid-Canada Line (MCL) was proposed as an inexpensive solution using bistatic radar. This provided a "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretary To The Admiralty
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wilson Croker
John Wilson Croker (20 December 178010 August 1857) was an Anglo-Irish statesman and author. Life He was born in Galway, the only son of John Croker, the surveyor-general of customs and excise in Ireland. He was educated at Trinity College Dublin, where he graduated in 1800. Immediately afterwards he entered Lincoln's Inn, and in 1802 he was called to the Irish bar. He married Rosamond Pennell (daughter of William Pennell & Elizabeth Pennell (née Carrington)) on 22 May 1806, in Waterford, Ireland. None of his children with Rosamond Pennell survived past 3 years old. He and Rosamond adopted Rosamond's younger sister (who was the 18th child of Rosamond's parents) and she was also (confusingly) named Rosamond Hester Elizabeth Pennell. The younger Rosamond was born in January 1810 in Waterford, Ireland (christened with the surname Pennell). Sometime between birth and 1814, she became part of the Croker family. The name she was better known by was the nickname "Nony" Croker. Nony' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolphin And Union Strait
Dolphin and Union Strait lies in both the Northwest Territories ( Inuvik Region) and Nunavut (Kitikmeot Region), Canada, between the mainland and Victoria Island. It is part of the Northwest Passage. It links Amundsen Gulf, lying to the northwest, with Coronation Gulf, lying to the southeast. The southeastern end of the strait is marked by Austin Bay. It gets its name from the two boats used by the Scottish naval surgeon and explorer John Richardson, who was the first known European to explore it in 1826. The Inuit who use this area have been variously known as the Copper Inuit, the Copper Eskimos, or the "People at the end of the world," because few other Indigenous groups had continuously used the area before. This is partly why the first Europeans who ventured into this area, were amazed by the "blond" Inuit they had encountered. There are several islands within the strait, including the Liston and Sutton Islands, historically home to the Noahonirmiut band of Copper Inuit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Canyon
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mountain-type ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (rock)
Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). The first geologist to distinguish dolomite rock from limestone was Belsazar Hacquet in 1778. Most dolomite was formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or of lime mud before lithification. The geological process of conversion of calcite to dolomite is known as dolomitization and any intermediate product is known as dolomitic limestone. The "dolomite problem" refers to the vast worldwide depositions of dolomite in the past geologic record in contrast to the limited amounts of dolomite formed in modern times. Recent research has revealed sulfate-reducing bacteria living in anoxic conditions precipitate dolomite whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronation Gulf
Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf. The northwest point is Cape Krusenstern (not the Cape Krusenstern in Alaska). South of that is Richardson Bay and the mouths (from west to east) of the Rae River, Richardson River and the large Coppermine River, Napaaktoktok River, and the Asiak River. The Tree River enters at the south center. At the southeast end is the large Bathurst Inlet. At the northeast end is Cape Flinders on the Kent Peninsula. In the center of the gulf lies the Duke of York Archipelago. The gulf was named by Sir John Franklin in 1821, in honour of the coronation of King George IV. The environment and Native culture of the area were studied by Rudolph Anderson and Diamond Jenness in 1916 as part of the Canadian Arctic Expedition. The mainlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the '' Nunavut Act'' and the '' Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'', which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949. Nunavut comprises a major portion of Northern Canada and most of the Arctic Archipelago. Its vast territory makes it the fifth-largest country subdivision in the world, as well as North America's second-largest (after Greenland). The capital Iqaluit (formerly Frobisher Bay), on Baffin Island in the east, was chosen by a capital plebiscite in 1995. Other major communities include the regional centres of Rankin Inlet and Cambridge Bay. Nunavut also includes Elle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |