|
Crisp Glacier
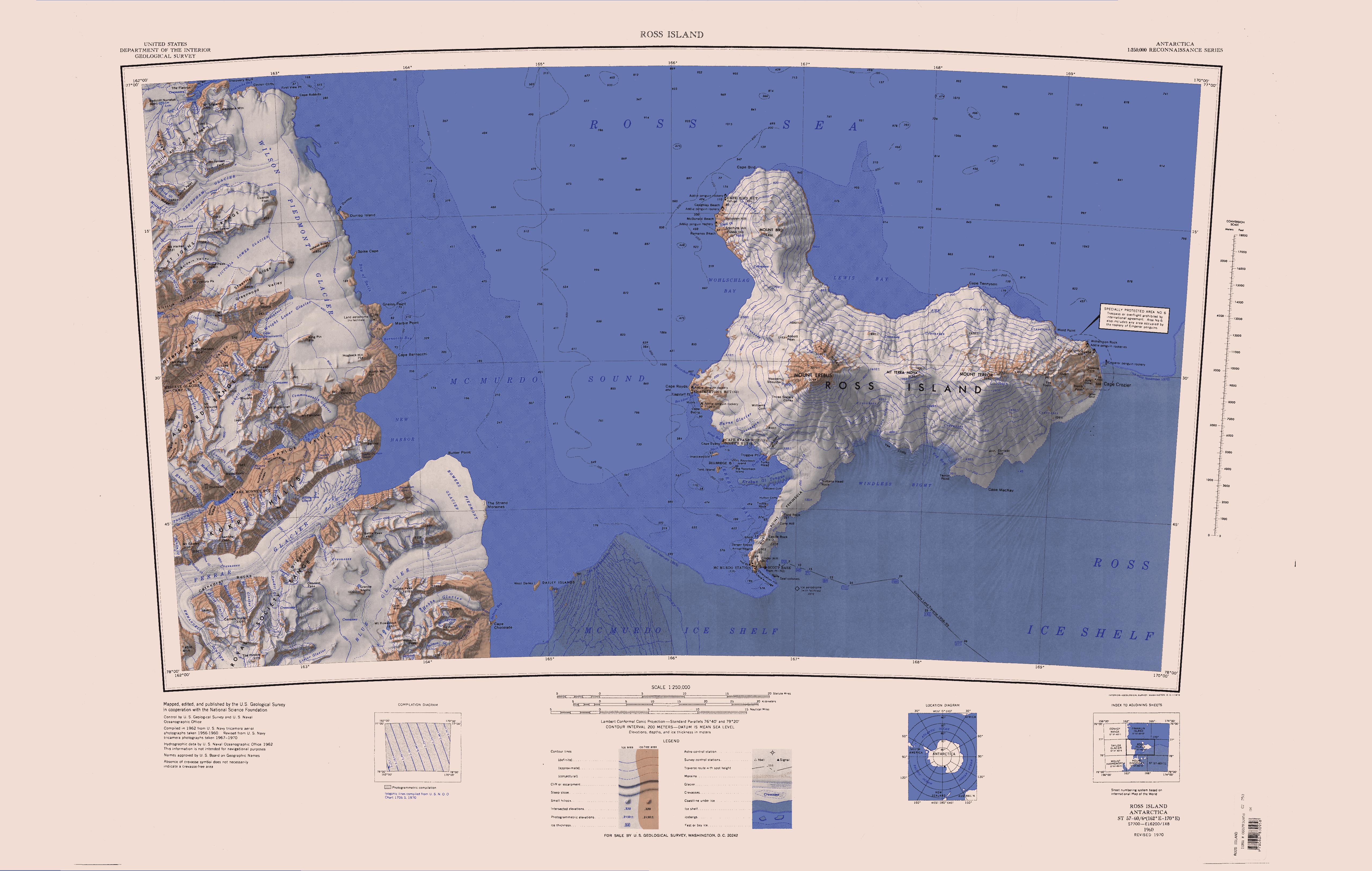
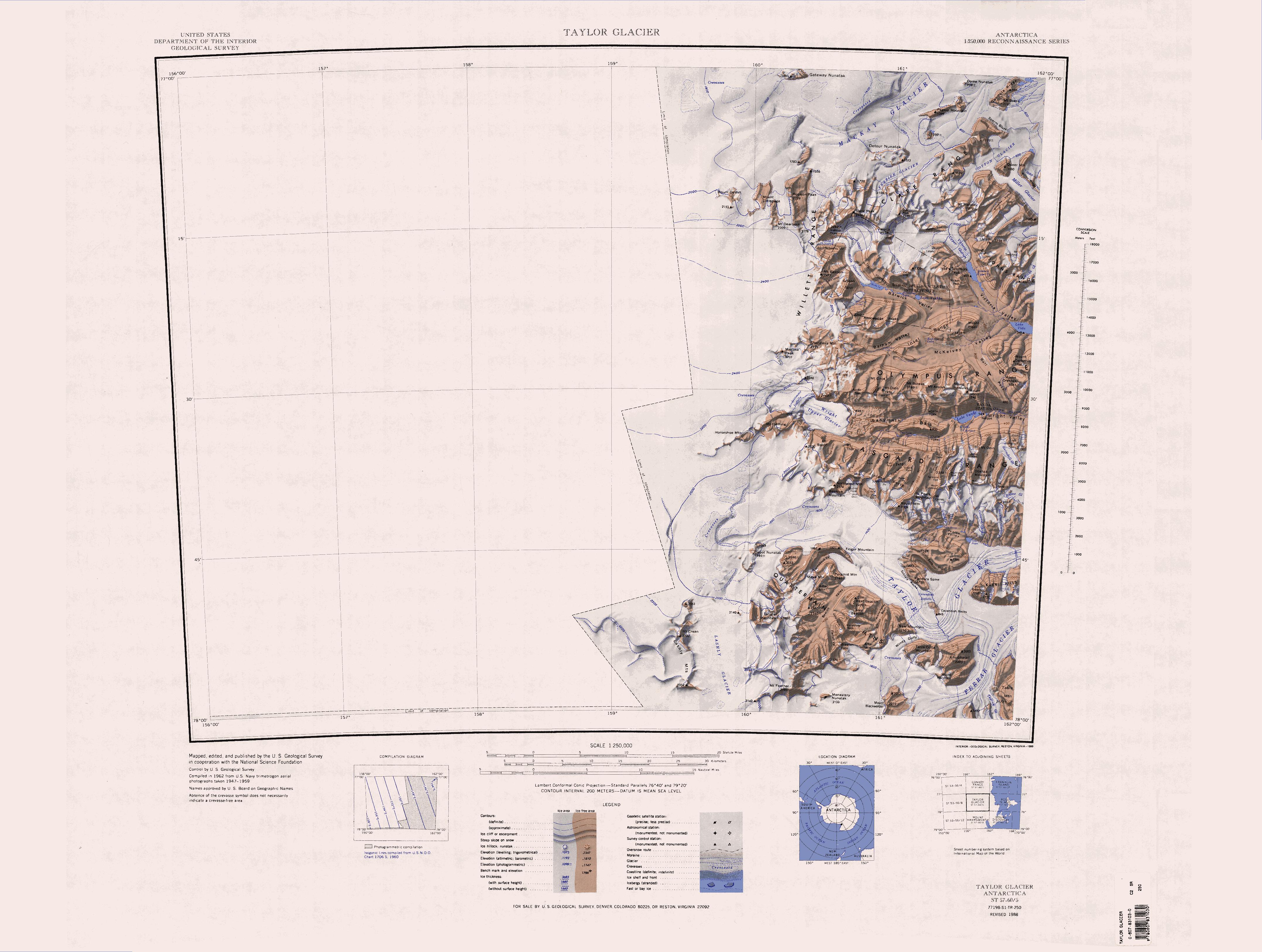
The Gonville and Caius Range () is a range of peaks, high, between Mackay Glacier and Debenham Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Gonville and Caius Range was first mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, under Robert Falcon Scott, and was named for Gonville and Caius College, of Cambridge University, the alma mater of several members of the expedition. Location The Clare Range is to the west of the Gonville and Caius Range, and Saint Johns Range to the south. Wilson Piedmont Glacier is to the east, along the coast of the Ross Sea. Mackay Glacier defines the north limit of the range. Killer Ridge, Second Facet and First Facet are to the north of Debenham Glacier and its tributary Miller Glacier. Queer Mountain is just west of Killer Ridge. The Crisp Glacier flows between the Killer Ridge and Second Facet. To the north are Mount Jensen, Red Ridge, Robson Glacier, Haystack Mountain and Mount England. Glaciers Crisp Glacier . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount England And The New Glacier
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Books * ''Mount!'', a 2016 novel by Jilly Cooper Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To prepare dead an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killer Whale
The orca (''Orcinus orca''), or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. The only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'', it is recognizable by its black-and-white-patterned body. A cosmopolitan species, it inhabits a wide range of marine environments, from Arctic to Antarctic regions to tropical seas. Orcas are apex predators with a diverse diet. Individual populations often specialize in particular types of prey, including fish, sharks, rays, and marine mammals such as seals, dolphins, and whales. They are highly social, with some populations forming stable matrilineal family groups (pods). Their sophisticated hunting techniques and vocal behaviors, often unique to specific groups and passed down from generation to generation, are considered to be manifestations of animal culture. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists the orca's conservation status as data deficient as multiple orca types may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit language, Inuit ) is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They often form natural pyramidal peaks. Isolated nunataks are also called glacial islands, and smaller nunataks rounded by glacial action may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic language, Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term ''nunatak'' is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the ridge protrudes above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some are isolated, they can also form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, hampering the formation of glacial ice on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Glacier
Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Discovery and name The Wilson Piedmont Glacier was discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition, 1901–1904. The British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–1913, named the feature for Dr. Edward A. Wilson, surgeon and artist with Scott's first expedition and chief of the scientific staff with the second. Wilson lost his life on the way back from the South Pole with Scott. Glaciology The Wilson Piedmont Glacier extends along the coastal plain of the west coast of the Ross Sea from Granite Harbor south to McMurdo Sound. Most of its input is from direct precipitation, but it receives some inflows from alpine glaciers. It has a broad dome with a divide near the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Most ice flows east to the Ross Sea, where the glacier terminates and comes afloat in the sea along its eastern margin. Some ice flows west and contributes to the Wright Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Flatiron
Granite Harbour () is a bay in the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about long, entered between Cape Archer and Cape Roberts. It was discovered and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) of 1901–04 in the ''RRS Discovery, Discovery'' in January 1902, while searching for safe winter quarters for the ship. The name derives from the great granite boulders found on its shores. Features Granite Harbor extends from Cape Archer at the south tip of Evans Piedmont Glacier to Cape Roberts on the north of Wilson Piedmont Glacier. Its main inflow is Mackay Glacier, which terminates in Mackay Glacier Tongue, extending into the bay. Features to the north of this glacier include Tiger Island, Benson Glacier, Lion Island, Hunt Glacier, Dreikanter Head, Marston Glacier, Kar Plateau and Point Retreat. Features to the south include Cuff Cape, The Flatiron, Devils Punchbowl, Finger Point, New Glacier, Discovery Bluff, Avalanche Bay, Couloir Cliffs, First View Point and Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are fewer than two hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three non-seasonal United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim (though the right is not forfeited); they are dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Glacier
Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Discovery and name The Wilson Piedmont Glacier was discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition, 1901–1904. The British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–1913, named the feature for Dr. Edward A. Wilson, surgeon and artist with Scott's first expedition and chief of the scientific staff with the second. Wilson lost his life on the way back from the South Pole with Scott. Glaciology The Wilson Piedmont Glacier extends along the coastal plain of the west coast of the Ross Sea from Granite Harbor south to McMurdo Sound. Most of its input is from direct precipitation, but it receives some inflows from alpine glaciers. It has a broad dome with a divide near the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Most ice flows east to the Ross Sea, where the glacier terminates and comes afloat in the sea along its eastern margin. Some ice flows west and contributes to the Wright Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackay Glacier
Mackay Glacier () is a large glacier in Victoria Land, descending eastward from the Antarctic Plateau, between the Convoy Range and Clare Range, into the southern part of Granite Harbour. It was discovered by the South magnetic pole party of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, and named for Alistair Mackay, a member of the party. The glacier's glacier tongue, tongue is called Mackay Glacier Tongue. First mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 and named for Alistair F. Mackay, a member of the party. Its mouth is south of the Evans Piedmont Glacier and the Mawson Glacier. It is north of the Wilson Piedmont Glacier and the Ferrar Glacier. Course The Mackay Glacier forms on the Antarctic Plateau to the south of Gateway Nunatak and the north of Willett Range. It flows east to the north of Detour Nunatak and Pegtop Mountain, which separate it from Frazier Glacier to the south, which flows past the Clare Range further to the south. It is joined by Frazier Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Piedmont Glacier
Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Discovery and name The Wilson Piedmont Glacier was discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition, 1901–1904. The British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–1913, named the feature for Dr. Edward A. Wilson, surgeon and artist with Scott's first expedition and chief of the scientific staff with the second. Wilson lost his life on the way back from the South Pole with Scott. Glaciology The Wilson Piedmont Glacier extends along the coastal plain of the west coast of the Ross Sea from Granite Harbor south to McMurdo Sound. Most of its input is from direct precipitation, but it receives some inflows from alpine glaciers. It has a broad dome with a divide near the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Most ice flows east to the Ross Sea, where the glacier terminates and comes afloat in the sea along its eastern margin. Some ice flows west and contributes to the Wright Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |