|
Coorg Province
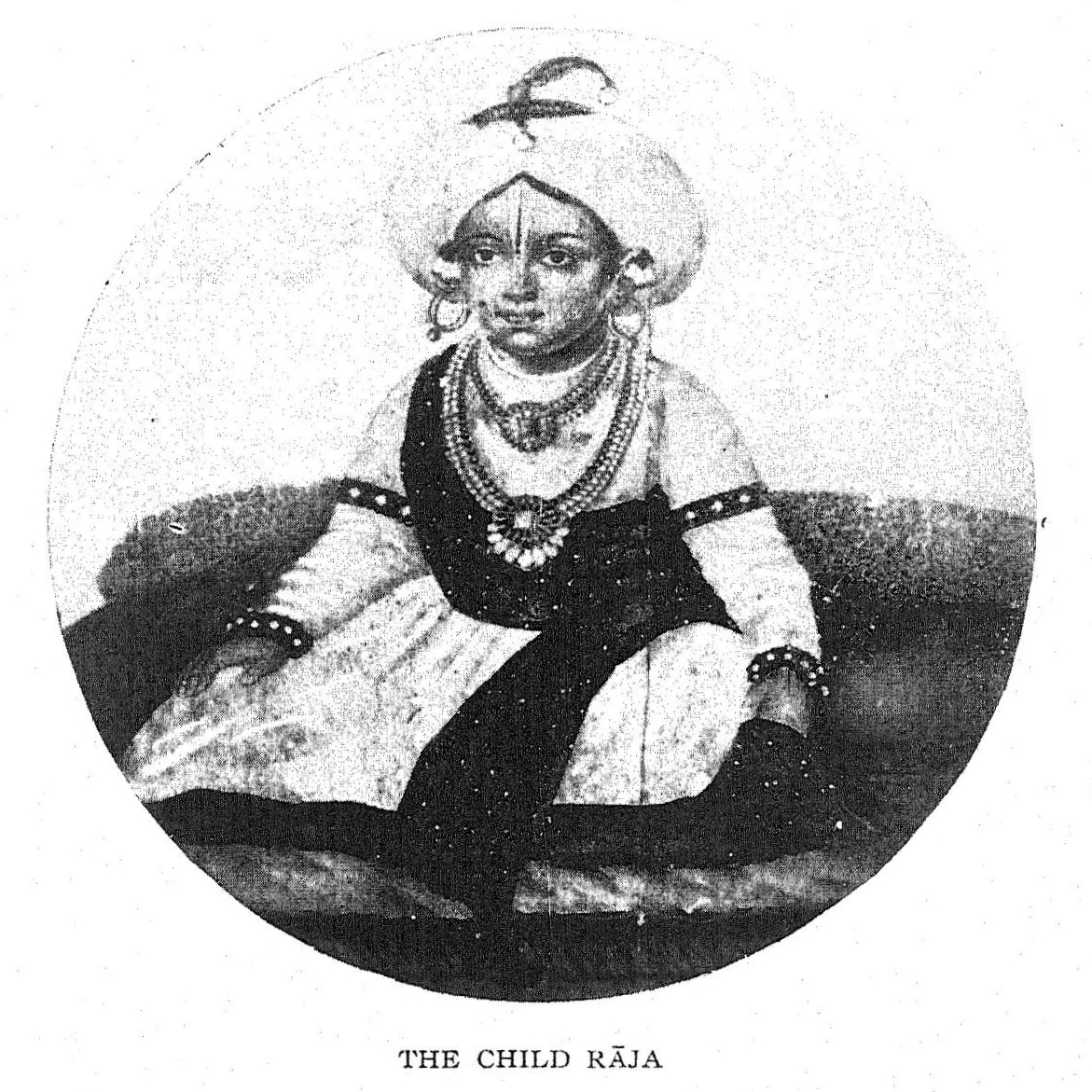
Coorg Province was a province of British India from 1834 to 1947 and the Dominion of India from 1947 to 1950. Mercara was the capital of the province. It was administered by a Commissioner and later, Chief Commissioner appointed by the Government of India. The Chief Commissioner, was usually based in Bangalore. From 1834 to 1881, the Chief Commissioner, was also the Commissioner of Mysore. From 1881 to 1940, the Chief Commissioner was usually the British Resident to the princely state of Mysore. The province of Coorg was established in May 1834, when the Kingdom of Coorg was abolished and its territories annexed to British India in the aftermath of the Coorg War. Coorg Province was largely inhabited by the Kodava people who spoke the Kodava language. During the 19th century, a number of coffee plantations were established in Coorg with the result that Coorg became one of the largest producers of coffee in the British Empire. The Kodava people of Coorg were renowned for their b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Reorganisation Act, 1956
The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines. Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the most extensive change in state boundaries after the independence of India. The Act came into effect at the same time as the Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956, which (among other things) restructured the constitutional framework for India's existing states and the requirements to pass the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 under the provisions of Part I of the Constitution of India, Article 3. Political integration after independence and the Constitution of 1950 British India, which included present-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar, was divided into two types of territories: the Provinces of British India, which were governed directly by British officials responsible to the Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virajpet
The town of Virajpet also spelled as Virajapete () is township of the district of Kodagu, in India's southern States and union territories of India, State of Karnataka. It is the main town of the ''Virajpet taluka'', south of the district, and borders Kerala State. The name of the town is derived from its founder, Dodda Vira Rajendra. History The name Virajpet is a shorter version of its previous name Virarajendrapet, named after the Kingdom of Coorg, Haleri King Dodda Vira Rajendra, who founded the town in 1792. He founded the town to commemorate his meeting with General (United Kingdom), General Robert Abercromby of Airthrey, Robert Abercromby, his ally against Tipu Sultan, the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, in 1791. Virajpet was the headquarters of Yedenalknad taluk. The first population comprised people who Vira Rajendra had in his predatory excursions swept away from Mysore. But, the people that fled to Virajpet were principally the inhabitants of Periyapatna, who were look ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraserpet
Kushalanagar or Kushalanagara is a city located in the Kodagu district of the Indian state of Karnataka. Surrounded by Kaveri river, it is the gateway to Kodagu district. It also serves as the headquarters of Kushalanagar Taluk. By population, Kushalanagar is the second largest town in Kodagu district after Madikeri and the fastest developing town in the district. Kushalnagar is an important commercial centre in Kodagu. Etymology According to popular myth, the name was given by Hyder Ali who was camped there when he received news of the birth of his son Tipu and called it as ''Kushyal nagar'' (="town of gladness") But in reality, Tipu was born around 1750 while Hyder Ali entered Kodagu for the first time in the 1760s. After the British conquest of Coorg it was known as Fraserpet after Colonel James Stuart Fraser who was the Political Agent in Coorg around 1834. Geography Kushalanagar is located at . It has an average elevation of 844 metres (2726 feet). Kushalanag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanara
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karāvali, is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern Konkan coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka. The subregion comprises three civil districts, namely: Uttara Kannada, Udupi district, Udupi, and Dakshina Kannada. Kasaragod was included prior to the States Reorganisation Act. Etymology According to historian Severino da Silva, the ancient name for this region is ''Parashurama Srushti'' (creation of Parashurama). According to him and Stephen Fuchs, the name ''Canara'' is the invention of Portuguese people, Portuguese, Dutch people, Dutch, and English people, English people who visited the area for trade from the early sixteenth century onwards. The Bednore Dynasty, under whose rule this tract was at that time, was known to them as the Kannada Dynasty, i.e., the dynasty speaking the Kannada language. "Karāvalli", the Kannada word for 'coast', is the term used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puttur Taluk
Puttur Taluk is a taluka in Dakshina Kannada district of the Indian state of Karnataka. The headquarters is the town of Puttur, Karnataka, Puttur. There are thirty-seven Panchayat villages in Puttur Taluka. * Ariyadka * Aryapu * Badagannuru * Bajathuru * Balnadu * Bannuru * Belanduru * Bettampady * Hirebandady * Kabaka Puttur, Kabaka * Kaniyuru * Kedambady * Kodimbady * Koila * Kolthige * Munduru * Narimogaru * Nettanige Mudnuru * Panaje * Savanuru * Uppinangady * Volamogaru Languages (1951) Notes External links * Taluks of Karnataka Geography of Dakshina Kannada district {{DakshinaKannada-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sullia Taluk
Sullia taluk is a taluk of the Dakshina Kannada district of the Indian state of Karnataka. The headquarters is the town of Sullia. In 2012, the government of Karnataka has planned to set up a rubber factory in Sullia taluk. Village #Aletty Aletty is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India.Village code= 2723700 Aletty, Dakshina Kannada, Karnataka It is located in the Sullia taluk of Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka. Demographics * India census, Aletty had a p .... #Ajjavara #Aranthodu. References Taluks of Karnataka Geography of Dakshina Kannada district {{DakshinaKannada-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketoli Chengappa
Dewan Bahadur Ketolira Chengappa, C.I.E. (1878–1963) was an Indian civil servant and administrator who served as the Chief Commissioner of Coorg Province from 1943 to 1949. Early life and education Chengappa was born on 3 March 1878 to Ketolira Muddaiah (worked as a village official) & Bolliavva from Yavakapadi Village, Kabinakad, Napoklu. He completed his matriculation in the year 1893. Thereafter, he went on graduate from University of Madras. Later on he cleared the Indian Civil Service (ICS), the elite higher civil service of the British Empire in British India. Career Chengappa joined the services as a parpathigar in 1909 and rose to become the Assistant Commissioner in 1916. He became the first Indian to be appointed as a District Magistrate by the British in 1921. After his tenure as Commissioner of Coorg in 1935, he was appointed by the British as the Chief of National War Front in Coorg in 1942. Subsequently, he was elevated to the position of Chief Commissioner of Coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
The Tulu language (, Tigalari script: , Kannada script: , Malayalam script: ; ) is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and in the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and also in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of Tulu are referred to as Tuluva or Tulu people and the geographical area is unofficially called Tulu Nadu. The Indian census report of 2011 reported a total of 1,846,427 native Tulu speakers in India. The 2001 census had reported a total of 1,722,768 native speakers. There is some difficulty in counting Tulu speakers who have migrated from their native region as they are often counted as Kannada speakers in Indian census reports. Separated early from Proto-South Dravidian, Tulu has several features not found in Tamil–Kannada. For example, it has the pluperfect and the future perfect, like French or Spanish, but formed without an auxiliary ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnaraja Wadiyar III
Krishnaraja Wodeyar III (14 July 1794 – 27 March 1868) was an Indian king who was the twenty-second Maharaja of Mysore. He ruled the kingdom for nearly seventy years, from 30 June 1799 to 27 March 1868, for a good portion of the latter period of which he was merely a nominal ruler. He is known for his contribution and patronage to different arts and music during his reign. He was succeeded by his biological grandson and adopted son, Chamarajendra Wadiyar X. Early years Krishnaraja Wodeyar III was born at Srirangapatna to Maharaja Chamaraja Wadiyar IX and his first wife, Maharani Kempananjammani Devi.Annals of The Mysore Royal Family Part-1: A publication by the Royal Family of Mysore: 1916 Maharani Lakshmi Devi, his adoptive grandmother, played a major role in the education and upbringing of her adopted grandson, Krishnaraja Wodeyar III, and was instrumental in his ascent to the throne.Rajakaryaprasakta Rao Bahadur (1936), p265 Since the insurrection of Mysore and stormi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Cubbon (army Officer)
Lieutenant-General (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Sir Mark Cubbon Order of the Bath, KCB (23 August 1775 – 23 April 1861) was a United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British army officer with the Honourable East India Company, East India Company who was the Mysore Commission, Chief Commissioner of Mysore 1834 to 1861. During his tenure, he established a Law and order (politics), law and order system, introduced judicial and economic reforms and through action in all spheres of governance helped develop the economy of Mysore. He resigned from his office in 1860 due to ill-health and left for England for the first time since his arrival in India as a cadet in 1800. The administration of the kingdom of Mysore under his leadership ensured that the Indian Rebellion of 1857, 1857 rebellion had almost no impact in the region. He died in 1861 on board ship at Suez. Cubbon Road and Cubbon Park in Bengaluru, Bangalore are named after him. Early life Cubbon was born at the vica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |