|
Contemporary Ethics
Ethics is, in general terms, the study of right and wrong. It can look descriptively at moral behaviour and judgements; it can give practical advice (normative ethics), or it can analyse and theorise about the nature of morality and ethics. Contemporary study of ethics has many links with other disciplines in philosophy itself and other sciences. Normative ethics has declined, while meta-ethics is increasingly followed. Abstract theorizing has in many areas been replaced by experience-based research. Practical and theoretical areas Psychology, sociology, politics, medicine and neurobiology are areas which have helped and been helped in progress in ethics. Within philosophy, epistemology (or the study of how we know) has drawn closer to ethics. This is in part due to the recognition that knowledge, like value and goodness, can be seen as a normative concept. The traditional analyses and definitions of knowledge have been shown to be unsound by the Gettier problem. New interest h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and Business ethics, business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to Duty, duties, like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidegger
Martin Heidegger (; 26 September 1889 – 26 May 1976) was a German philosopher known for contributions to phenomenology, hermeneutics, and existentialism. His work covers a range of topics including metaphysics, art, and language. In April 1933, Heidegger was elected as rector at the University of Freiburg and has been widely criticized for his membership and support for the Nazi Party during his tenure. After World War II he was dismissed from Freiburg and banned from teaching after denazification hearings at Freiburg. There has been controversy about the relationship between his philosophy and Nazism. In Heidegger's first major text, ''Being and Time'' (1927), '' Dasein'' is introduced as a term for the type of being that humans possess. Heidegger believed that Dasein already has a "pre-ontological" and concrete understanding that shapes how it lives, which he analyzed in terms of the unitary structure of "being-in-the-world". Heidegger used this analysis to approach th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (born Emanuel Kant; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German Philosophy, philosopher and one of the central Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and aesthetics have made him one of the most influential and highly discussed figures in modern Western philosophy. In his doctrine of transcendental idealism, Kant argued that space and time are mere "forms of intuition" that structure all experience and that the objects of experience are mere "appearances". The nature of things as they are in themselves is unknowable to us. Nonetheless, in an attempt to counter the philosophical doctrine of Philosophical skepticism, skepticism, he wrote the ''Critique of Pure Reason'' (1781/1787), his best-known work. Kant drew a parallel to the Copernican Revolution#Immanuel Kant, Copernican Revolution in his proposal to think of the objects of experience as confo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic–synthetic Distinction
The analytic–synthetic distinction is a semantic distinction used primarily in philosophy to distinguish between propositions (in particular, statements that are affirmative subject– predicate judgments) that are of two types: analytic propositions and synthetic propositions. Analytic propositions are true or not true solely by virtue of their meaning, whereas synthetic propositions' truth, if any, derives from how their meaning relates to the world. While the distinction was first proposed by Immanuel Kant, it was revised considerably over time, and different philosophers have used the terms in very different ways. Furthermore, some philosophers (starting with Willard Van Orman Quine) have questioned whether there is even a clear distinction to be made between propositions which are analytically true and propositions which are synthetically true. Debates regarding the nature and usefulness of the distinction continue to this day in contemporary philosophy of language. Kant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened to a similar position seeking to remove or to minimize the role of religion in any public sphere. Secularism may encapsulate anti-clericalism, atheism, naturalism, non-sectarianism, neutrality on topics of religion, or antireligion. Secularism is not necessarily antithetical to religion, but may be compatible with it. As a philosophy, secularism seeks to interpret life based on principles derived solely from the material world, without recourse to religion. It shifts the focus from religion towards "temporal" and material concerns. There are distinct traditions of secularism like the French, Turkish, American and Indian models. These differ greatly, from the American emphasis on avoiding an established religion and the freedom of bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Philosophy
Process philosophy (also ontology of becoming or processism) is an approach in philosophy that identifies processes, changes, or shifting relationships as the only real experience of everyday living. In opposition to the classical view of change as illusory (as argued by Parmenides) or accidental (as argued by Aristotle), process philosophy posits transient occasions of change or ''becoming'' as the only fundamental things of the ordinary everyday real world. Since the time of Plato and Aristotle, classical ontology has posited ordinary world reality as constituted of enduring substances, to which transient processes are ontologically subordinate, if they are not denied. If Socrates changes, becomes sick, Socrates is still the same (the substance of Socrates being the same), and change (his sickness) only glides over his substance: change is accidental, and devoid of primary reality, whereas the substance is essential. In physics, Ilya Prigogine distinguishes between the "phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that views language and thought as tools for prediction, problem solving, and action, rather than describing, representing, or mirroring reality. Pragmatists contend that most philosophical topics—such as the nature of knowledge, language, concepts, meaning, belief, and science—are best viewed in terms of their practical uses and successes. Pragmatism began in the United States in the 1870s. Its origins are often attributed to philosophers Charles Sanders Peirce, William James and John Dewey. In 1878, Peirce described it in his pragmatic maxim: "Consider the practical effects of the objects of your conception. Then, your conception of those effects is the whole of your conception of the object."Peirce, C.S. (1878), " How to Make Our Ideas Clear", ''Popular Science Monthly'', v. 12, 286–302. Reprinted often, including ''Collected Papers'' v. 5, paragraphs 388–410 and ''Essential Peirce'' v. 1, 124–141. See end of §II for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Gettier
Edmund Lee Gettier III (; October 31, 1927 – March 23, 2021) was an American philosopher at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. He is best known for his article written in 1963: "Is Justified True Belief Knowledge?", which has generated an extensive philosophical literature trying to respond to what became known as the Gettier problem. Life Edmund Lee Gettier III was born on October 31, 1927, in Baltimore, Maryland. Gettier obtained his B.A. from Johns Hopkins University in 1949. He earned his PhD in philosophy from Cornell University in 1961 with a dissertation on “Bertrand Russell’s Theories of Belief” written under the supervision of Norman Malcolm. Gettier taught philosophy at Wayne State University from 1957 until 1967 initially as an Instructor, then as an assistant professor, and, latterly, as an associate professor. His philosophical colleagues at Wayne State included, among others, Alvin Plantinga and Héctor-Neri Castaneda. In the academic year of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Priori And A Posteriori
('from the earlier') and ('from the later') are Latin phrases used in philosophy to distinguish types of knowledge, justification, or argument by their reliance on experience. knowledge is independent from any experience. Examples include mathematics,Some associationist philosophers have contended that mathematics comes from experience and is not a form of any ''a priori'' knowledge () tautologies and deduction from pure reason. Galen Strawson has stated that an argument is one in which "you can see that it is true just lying on your couch. You don't have to get up off your couch and go outside and examine the way things are in the physical world. You don't have to do any science." () knowledge depends on empirical evidence. Examples include most fields of science and aspects of personal knowledge. The terms originate from the analytic methods found in '' Organon'', a collection of works by Aristotle. Prior analytics () is about deductive logic, which comes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Philosophy
Analytic philosophy is a broad movement within Western philosophy, especially English-speaking world, anglophone philosophy, focused on analysis as a philosophical method; clarity of prose; rigor in arguments; and making use of formal logic, mathematics, and to a lesser degree the natural sciences.Mautner, Thomas (editor) (2005) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy'', entry for "Analytic philosophy", pp. 22–23 It is further characterized by an interest in language, semantics and Meaning (philosophy), meaning, known as the linguistic turn. It has developed several new branches of philosophy and logic, notably philosophy of language, philosophy of mathematics, philosophy of science, modern predicate logic and mathematical logic. The proliferation of analysis in philosophy began around the turn of the 20th century and has been dominant since the latter half of the 20th century. Central figures in its historical development are Gottlob Frege, Bertrand Russell, G. E. Moore, and L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Philosophy
Continental philosophy is a group of philosophies prominent in 20th-century continental Europe that derive from a broadly Kantianism, Kantian tradition.Continental philosophers usually identify such conditions with the transcendental subject or self: , "It is with Kant that philosophical claims about the self attain new and remarkable proportions. The self becomes not just the focus of attention but the entire subject-matter of philosophy. The self is not just another entity in the world, but in an important sense it creates the world, and the reflecting self does not just know itself, but in knowing itself knows all selves, and the structure of any and every possible self." Continental philosophy includes German idealism, Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology, existentialism (and its antecedents, such as the thought of Søren Kierkegaard, Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzsche), hermeneutics, structuralism, post-structuralism, deconstruction, Feminism in France, Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
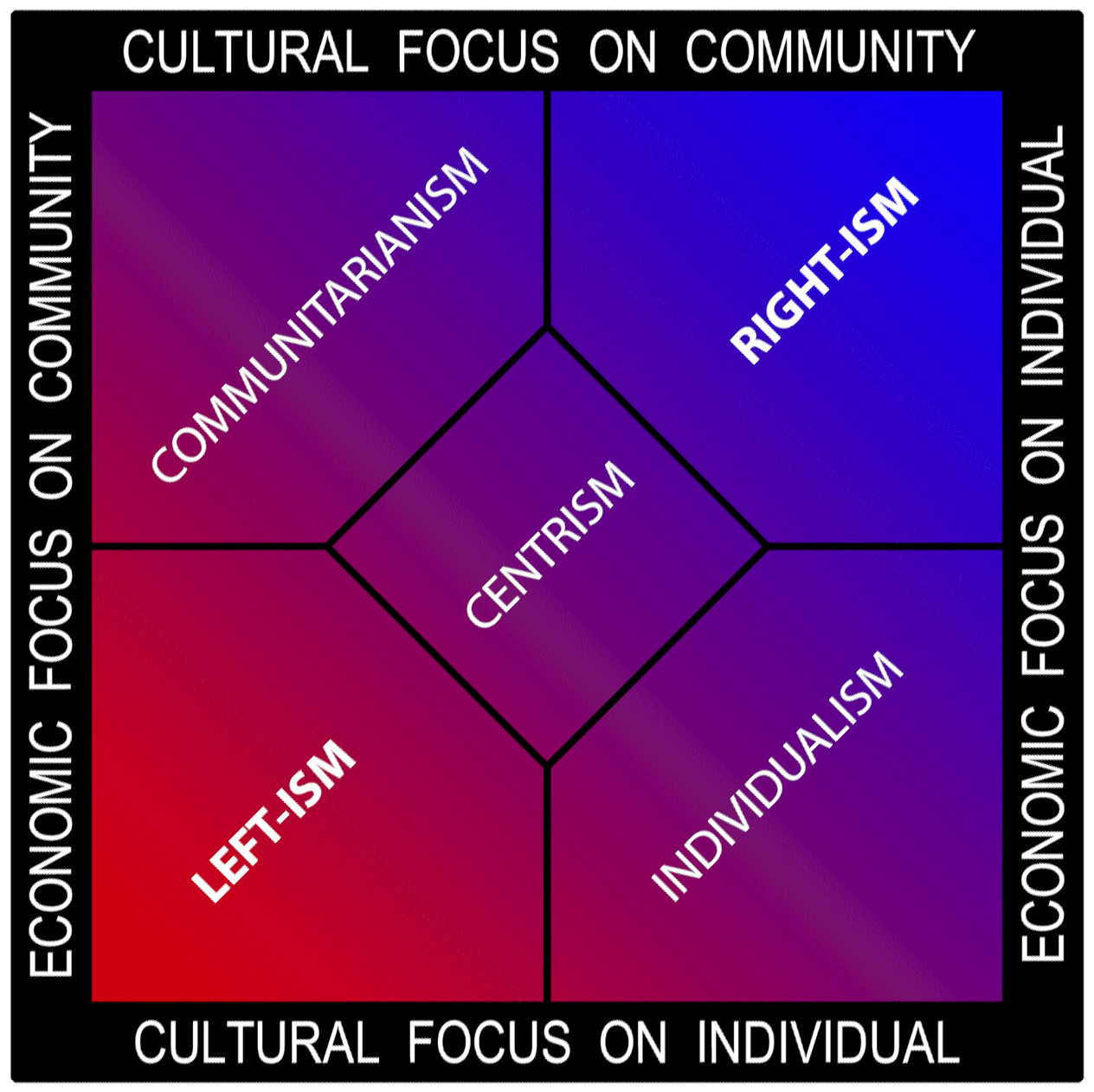
Communitarian
Communitarianism is a philosophy that emphasizes the connection between the individual and the community. Its overriding philosophy is based on the belief that a person's social identity and personality are largely molded by community relationships, with a smaller degree of development being placed on individualism. Although the community might be a family, communitarianism usually is understood, in the wider, philosophical sense, as a collection of interactions, among a community of people in a given place (geographical location), or among a community who share an interest or who share a history. Communitarianism is often contrasted with individualism, and generally opposes ''laissez-faire'' policies that deprioritize the stability of the overall community. Terminology The philosophy of communitarianism originated in the 20th century, but the term "communitarian" was coined in 1841, by John Goodwyn Barmby, a leader of the British Chartist movement, who used it in referrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |