|
Communications Receiver
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between verbal and non-verbal communication. Verbal communication involves the exchange of messages in linguistic form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Communication
Human communication, or anthroposemiotics, is a field of study dedicated to understanding how humans Communication, communicate. Humans' ability to communicate with one another would not be possible without an understanding of what we are referencing or thinking about. Because humans are unable to fully understand one another's perspective, there needs to be a creation of commonality through a shared mindset or viewpoint. The field of communication is very diverse, as there are multiple layers of what communication is and how we use its different features as human beings. Humans have communicatory abilities other animals do not. For example, humans are able to communicate about time and place as though they are solid objects. Humans communicate to request help, inform others, and share attitudes for bonding. Communication is a joint activity largely dependent on the ability to maintain common attention. We share relevant background knowledge and joint experience in order to commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
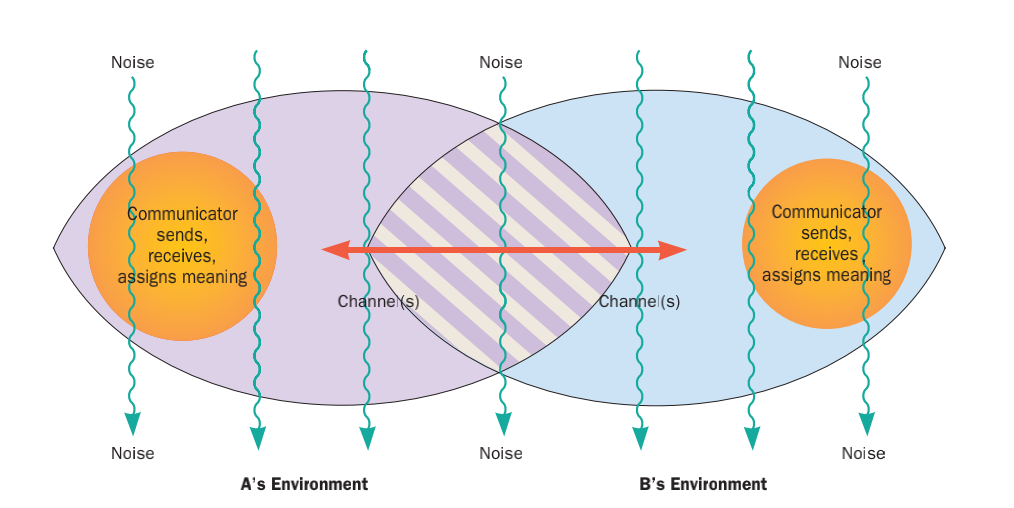
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during Face-to-face interaction, face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) Interpersonal deception theory, deceptive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Technology
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Other early pioneers in electrical and electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Communication
The history of communication technologies (media and appropriate inscription tools) have evolved in tandem with shifts in political and economic systems, and by extension, systems of power. Communication can range from very subtle processes of exchange to full conversations and mass communication. The history of communication itself can be traced back since the origin of speech circa 100,000 Common Era, BCE. The use of technology in communication may be considered since the first use of symbols about 30,000 years BCE. Among the symbols used, there are cave paintings, petroglyphs, pictograms and ideograms. History of writing, Writing was a major innovation, as well as History of printing, printing technology and, more recently, History of telecommunication, telecommunications and the History of the Internet, Internet. Primitive times Human communication was initiated with the origin of speech approximately 100,000 BCE. Symbols were developed about 30,000 years ago. The imperfection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for transportation (e.g. riding horses and camels), while others are service animals trained to execute certain specialized tasks (e.g. hunting and guide dogs, messenger pigeons, and fishing cormorants). They may also be used for milking or herding. Some, at the end of their working lives, may also be used for meat or leather. The history of working animals may predate agriculture as dogs were used by hunter-gatherer ancestors; around the world, millions of animals work in relationship with their owners. Domesticated species are often bred for different uses and conditions, especially horses and working dogs. Working animals are usually raised on farms, though some are still captured from the wild, such as dolphins and some Asian elephants. People have found uses for a wide variety of abili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by Plant, plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollination, pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal Mutualism (biology), mutualists, which in turn provide plant defense against herbivory#Indirect defenses, herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverfly, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterfly, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and Bat#Fruit and nectar, bats. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of predacious or Parasitoid wasp, parasitoid wasps (e.g., the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely on nectar as a primary food source. In turn, these wasps then hunt agricultural pest insects as food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interspecies Communication
Interspecies communication is communication between different species of animals, plants, or microorganisms. Although researchers have explored the topic for many years, only recently has interspecies communication been recognized as an established field of inquiry. Mutualism Cooperative interspecies communication implies sharing and understanding information between two or more species that work towards the benefit of both species ( mutualism). Since the 1970s, primatologist Sue Savage-Rumbaugh has been working with primates at Georgia State University's Language Research Center (LRC), and more recently, the Iowa Primate Learning Sanctuary. In 1985, using lexigram symbols, a keyboard and monitor, and other computer technology, Savage-Rumbaugh began her groundbreaking work with Kanzi, a male bonobo (P. paniscus). Her research has made significant contributions to a growing body of work in sociobiology studying language learning in non-human primates and exploring the role of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat non-vascular autotrophs such as mosses, algae and lichens, but do not include those feeding on decomposed plant matters (i.e. detritivores) or macrofungi (i.e. fungivores). As a result of their plant-based diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouth structures ( jaws or mouthparts) well adapted to mechanically break down plant materials, and their digestive systems have special enzymes (e.g. amylase and cellulase) to digest polysaccharides. Grazing herbivores such as horses and cattles have wide flat- crowned teeth that are better adapted for grinding grass, tree bark and other tougher lignin-containing materials, and many of them evolved rumination or cecotropic behaviors to better extract nutrients from plants. A larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Organic Compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furniture, Handicraft, arts and crafts supplies, Dry cleaning, dry cleaned clothing, and Cleaning agent, cleaning supplies. VOCs are responsible for the odor of scents and perfumes as well as pollutants. They play an important role in communication between animals and plants, such as attractants for pollinators, protection from predation, and even inter-plant interactions. Some VOCs are dangerous to human health or cause harm to the natural environment, environment, often despite the odor being perceived as pleasant, such as "new car smell". Human impact on the environment, Anthropogenic VOCs are regulated by law, especially indoors, where concentrations are the highest. Most VOCs are not acutely toxic, but may have long-term chronic health effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/. There are approximately 132 species, most of which are native to Asia, with a number also appearing in Europe, northern Africa, and North America. Only one species, '' Acer laurinum'', extends to the Southern Hemisphere.Gibbs, D. & Chen, Y. (2009The Red List of Maples Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) The type species of the genus is the sycamore maple ''Acer pseudoplatanus'', one of the most common maple species in Europe.van Gelderen, C. J. & van Gelderen, D. M. (1999). '' Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia'' Most maples usually have easily identifiable palmate leaves (with a few exceptions, such as '' Acer carpinifolium'', '' Acer laurinum'', and '' Acer negundo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtship Display
A courtship display is a set of display behaviors in which an animal, usually a male, attempts to attract a mate; the mate exercises choice, so sexual selection acts on the display. These behaviors often include ritualized movement ("dances"), vocalizations, mechanical sound production, or displays of beauty, strength, or agonistic ability. Male display In some species, males will perform ritualized movements to attract females. The male six-plumed bird-of-paradise ( ''Parotia lawesii'') exemplifies male courtship display with its ritualized " ballerina dance" and unique occipital and breast feathers that serve to stimulate the female visual system. In '' Drosophila subobscura,'' male courtship display is seen through the male's intricate wing scissoring patterns and rapid sidestepping. These stimulations, along with many other factors, result in subsequent copulation or rejection. In other species, males may exhibit courtship displays that serve as both visual and auditor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |