|
Colotomic Structure
''Colotomy'' is an Indonesian description of the rhythmic and metric patterns of gamelan music. It refers to the use of specific instruments to mark off nested time intervals, or the process of dividing rhythmic time into such nested cycles. In the gamelan, this is usually done by gongs of various size: the '' kempyang'', '' ketuk'', '' kempul'', ''kenong'', '' gong suwukan'', and ''gong ageng''. The fast-playing instruments, '' kempyang and ketuk'', keep a regular beat. The larger gongs group together these hits into larger groupings, playing once per each grouping. The largest gong, the ''gong ageng'', represents the largest time cycle and generally indicates that that section will be repeated, or the piece will move on to a new section. The details of the rhythmic patterns depend on the colotomic structure (), also known as ''gendhing'' structure. There are a number of different structures, which differ greatly in length and complexity; however, all of them have some coloto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladrang Cycle
''Colotomy'' is an Music of Indonesia, Indonesian description of the rhythmic and meter (music), metric patterns of gamelan music. It refers to the use of specific instruments to mark off nested time intervals, or the process of dividing rhythmic time into such nested cycles. In the gamelan, this is usually done by gongs of various size: the ''kempyang'', ''ketuk'', ''kempul'', ''kenong'', ''gong suwukan'', and ''gong ageng''. The fast-playing instruments, ''kempyang and ketuk'', keep a regular beat (music), beat. The larger gongs group together these hits into larger groupings, playing once per each grouping. The largest gong, the ''gong ageng'', represents the largest time cycle and generally indicates that that section will be repeated, or the piece will move on to a new section. The details of the rhythmic patterns depend on the colotomic structure (), also known as ''gendhing'' structure. There are a number of different structures, which differ greatly in length and complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irama
''Irama'' is the term used for tempo in Indonesian gamelan in Java and Bali. It can be used with elaborating instruments. It is a concept used in Javanese gamelan music, describing melodic tempo and relationships in density between the balungan, elaborating instruments, and gong structure. It is distinct from tempo ( Javanese: ''Laya''), as each ''Irama'' can be played in different tempi. ''Irama'' thus combines "the rate of temporal flow and temporal density"; and the temporal density is the primary factor.Sumarsan, 1996. page 156 One way to think of ''Irama'' is to use the most consistently struck instrument in the gamelan, the '' saron panerus'' (or ''peking''). In some pieces, it plays once per note in the ''balungan'' (such as played by the '' saron barung''). In others, it may play twice as often, or four times, as the notes of the ''balungan'' are more spread out. This corresponds to a slower ''Irama''. In most cases, the more spread out the ''balungan'' is, the longer i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition's character or atmosphere. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often using conventional Italian terms) and, if a specific metrical pace is desired, is usually measured in beat (music), beats per minute (bpm or BPM). In modern classical compositions, a "metronome mark" in beats per minute, indicating only measured speed and not any form of expression, may supplement or replace the normal tempo marking, while in modern genres like electronic dance music, tempo will typically simply be stated in bpm. Tempo (the underlying pulse of the music) is one of the three factors that give a piece of music its texture (music), texture. The others are meter (music), meter, which is indicated by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or musical improvisation, performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such as "the arrangement of musical units of rhythm, melody, and/or harmony that show repetition (music), repetition or variation (music), variation, the arrangement of the instruments (as in the order of solo (music), solos in a jazz or bluegrass performance), or the way a symphonic piece is orchestration, orchestrated", among other factors. It is, "the ways in which a composition is shaped to create a meaningful musical experience for the listener."Kostka, Stefan and Payne, Dorothy (1995). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.152. McGraw-Hill. . These organizational elements may be broken into smaller units called phrases, which express a musical idea but lack sufficient weight to stand alone. Musical form unfolds over time through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleh
The ''sèlèh'' note or ''nada seleh'' is an Indonesian music concept used in Javanese gamelan music. In Javanese gamelan music, the ''sèlèh'' note or ''nada seleh'' is the final note of a '' gatra'', or four- beat melodic unit. As such it is the note which serves as the goal for all the various strands of the musical texture.Brinner, Benjamin (2008). ''Music in Central Java'', p.60. . See also * Gamelan * kotekan * Gatra * Colotomy * Slendro Slendro () is one of the essential tuning systems used in gamelan instruments that have pentatonic scale (music), scale. Based on Javanese people, Javanese mythology, the Slendro Gamelan tuning system is older than the ''pélog'' tuning system. ... * Music of Indonesia * Music of Java Sources Gamelan theory {{Indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gatra (music)
A ''gatra'' ("embryo" or "semantic unit") is a unit of melody in Indonesian Javanese people, Javanese gamelan music, analogous to a bar (music), measure in Western music. It is often considered the smallest unit of a gamelan composition. A ''gatra'' consists of a sequence of four beats (''keteg''), which are filled with notes (or rests, ''pin'') from the ''balungan''. In general, the second and fourth beats of a ''gatra'' are stronger than the first and third, and the final note of a ''gatra'', called the ''seleh'', dominates the ''gatra''. In other words, the ''gatras'' are like Western measures in reverse, with the strongest beat at the end. Important colotomic instruments, most notably the ''gong ageng'', are played on that final beat. If the final beat in a ''gatra'' is a rest, the ''seleh'' is the last note played. It is not uncommon in gamelan repertoire to find entire ''gatras'' of rests. Note that the actual length of time it takes to play a ''gatra'' varies from less than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancaran
''Colotomy'' is an Indonesian description of the rhythmic and metric patterns of gamelan music. It refers to the use of specific instruments to mark off nested time intervals, or the process of dividing rhythmic time into such nested cycles. In the gamelan, this is usually done by gongs of various size: the '' kempyang'', '' ketuk'', '' kempul'', ''kenong'', '' gong suwukan'', and ''gong ageng''. The fast-playing instruments, '' kempyang and ketuk'', keep a regular beat. The larger gongs group together these hits into larger groupings, playing once per each grouping. The largest gong, the ''gong ageng'', represents the largest time cycle and generally indicates that that section will be repeated, or the piece will move on to a new section. The details of the rhythmic patterns depend on the colotomic structure (), also known as ''gendhing'' structure. There are a number of different structures, which differ greatly in length and complexity; however, all of them have some coloto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
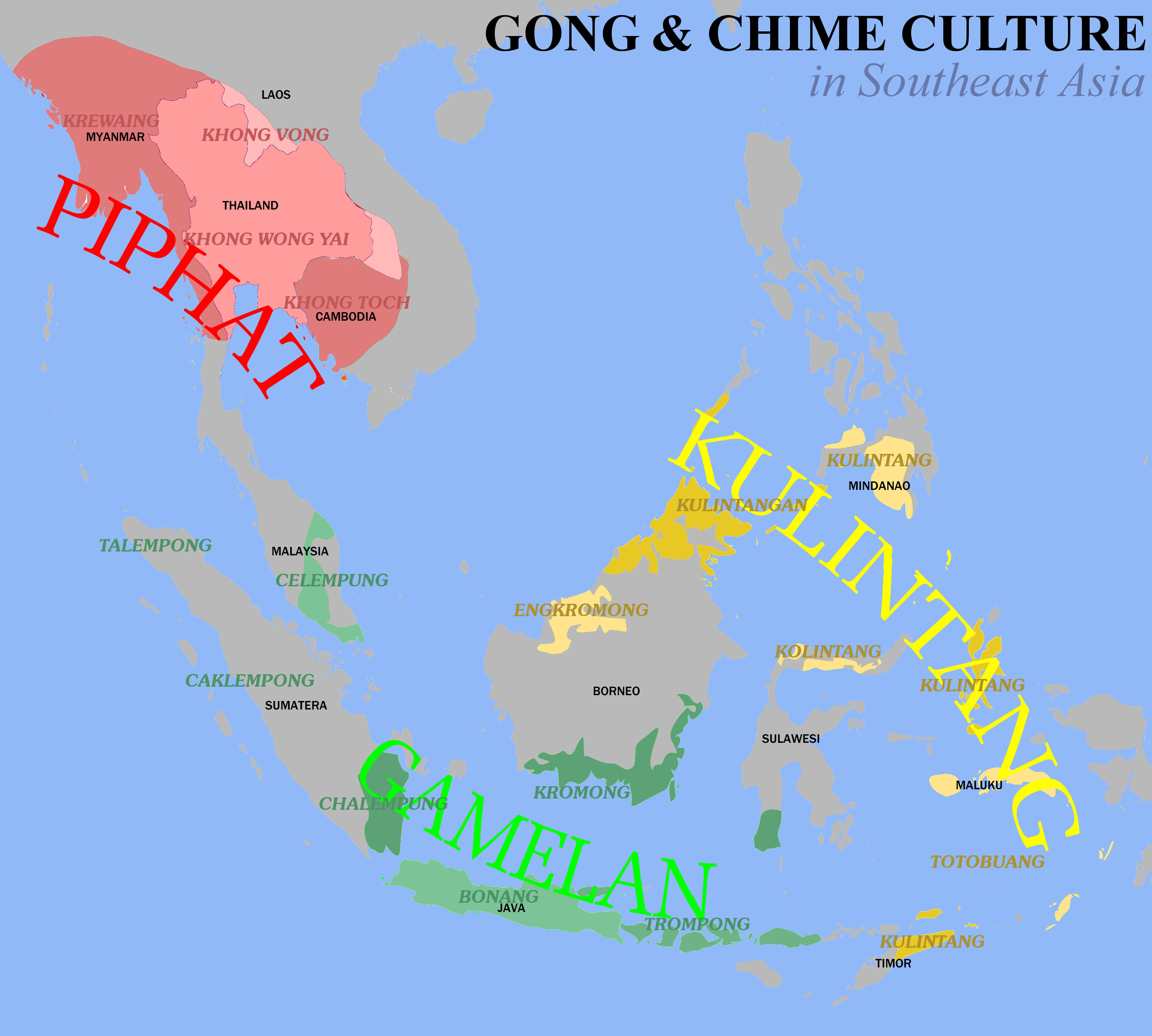
Piphat
A ''piphat'' () is a kind of ensemble in the classical music of Thailand, which features wind and percussion instruments. It is considered the primary form of ensemble for the interpretation of the most sacred and "high-class" compositions of the Thai classical repertoire, including the Buddhist invocation entitled ''sathukan'' () as well as the suites called ''phleng rueang''. It is also used to accompany traditional Thai theatrical and dance forms including '' khon'' () (masked dance-drama), '' lakhon'' (classical dance), and shadow puppet theater. Piphat in the earlier time was called ''phinphat''. It is analogous to its Cambodian musical ensemble of pinpeat and Laotian ensemble of pinphat. Types of ''piphat'' The smallest ''piphat'', called ''piphat khrueang ha'', is composed of six instruments: '' pi nai'' (oboe); ''ranat ek'' (xylophone); '' khong wong yai'' (gong circle); '' taphon'' or other Thai drums; '' glong thad'', a set of two large barrel drums beaten with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gagaku
is a type of Japanese classical music that was historically used for imperial court music and dances. was developed as court music of the Kyoto Imperial Palace, and its near-current form was established in the Heian period (794–1185) around the 10th century.History of gagaku Nihon gagakukai Today, it is performed by the Board of Ceremonies in the . Gagaku consists of three primary repertoires: #Native [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaap Kunst
Jaap Kunst (12 August 1891 – 7 December 1960) was a Dutch musicologist. He is credited with steering the discipline away from exclusively comparative methods and into the direction of historical particularism, coining the term " ethno-musicology" as a more accurate name for the field then known as comparative musicology. Kunst studied the folk music of the Netherlands and his field studies in Indonesia between 1920 and 1934 are seen as fundamental contributions to the knowledge and understanding of Indonesian folk music. His published work totals more than 70 texts. Early life Kunst was born on 12 August 1891 in Groningen. Both of his parents were pianists, and his father was a music-school teacher and music critic. He began to study the violin at only 5 years old, and continued to play the instrument throughout his life. Kunst was drawn toward folk music as a result of vacations to the island of Terschelling. Kunst decided to pursue a career in law. While studying law at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |