|
Cloning Vector
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use. There are many types of cloning vectors, but the most commonly used ones are genetically engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PBR322 Color
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula Phosphorus, PBromine, Br3. The liquid fumes in moist air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is used in the laboratory for the conversion of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols to Organobromine compound, alkyl bromides. Preparation PBr3 is prepared by treating red phosphorus with bromine. An excess of phosphorus is used in order to prevent formation of PBr5: :P4 + 6 Br2 → 4 PBr3 Because the reaction is highly exothermic, it is often conducted in the presence of a diluent such as PBr3. Phosphorus tribromide is also generated in situ from red phosphorus and bromine. Reactions Phosphorus tribromide, like Phosphorus trichloride, PCl3 and Phosphorus trifluoride, PF3, has both properties of a Lewis base and a Lewis acid. For example, with a Lewis acid such as boron tribromide it forms stable 1 :1 adducts such as Br3B · PBr3. At the same time PBr3 can react as an electrophile or Lewis acid in many of its rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
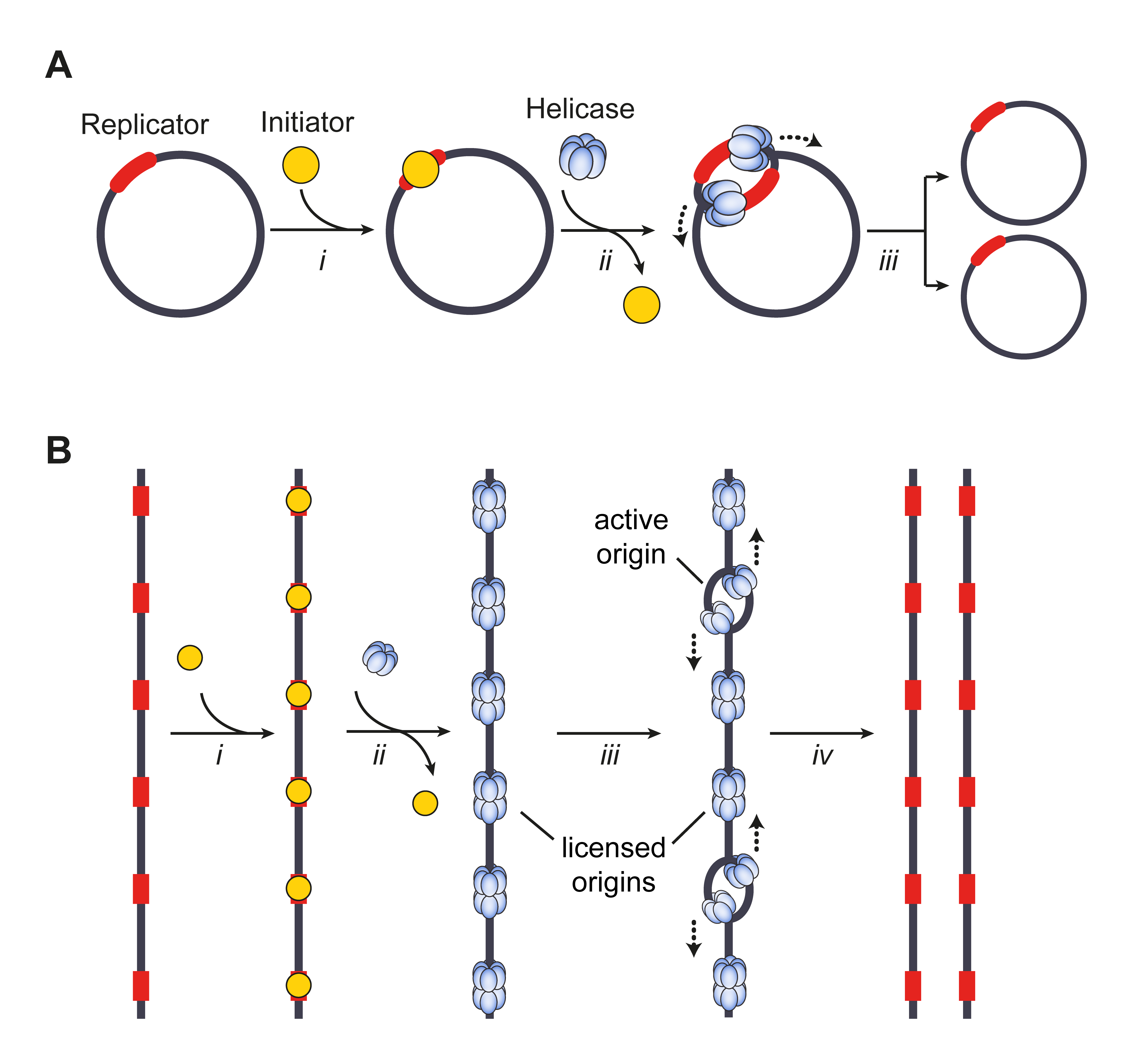
Origin Of Replication
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License This can either involve the DNA replication, replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA virus, DNA or RNA virus, RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory. Transformation is one of three processes that lead to horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from one bacterium to another, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium. As of 2014 about 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selectable Marker
A selectable marker is a gene introduced into cell (biology), cells, especially bacteria or cells in cell culture, culture, which confers one or more traits suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and genetic engineering to indicate the success of a transfection or genetic transformation, transformation or other procedure meant to introduce foreign DNA into a cell. Selectable markers are often antibiotic resistance genes: bacteria subjected to a procedure by which exogenous DNA containing an antibiotic resistance gene (usually alongside other genes of interest) has been introduced are grown on a medium containing an antibiotic, such that only those bacterial cells which have successfully taken up and gene expression, expressed the introduced genetic material, including the gene which confers antibiotic resistance, can survive and produce colony (biology), colonies. The genes encoding resistance to antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateway Technology
The Gateway cloning method is a method of molecular cloning invented and commercialized by Invitrogen since the late 1990s, which makes use of the integration and excision recombination reactions that take place when bacteriophage lambda infects bacteria. This technology provides a fast and highly efficient way to transport DNA sequences into multi-vector systems for functional analysis and protein expression using Gateway att sites and two proprietary enzyme mixes called BP Clonase and LR Clonase. ''In vivo'', these recombination reactions are facilitated by the recombination of attachment sites from the lambda/phage chromosome (attP) and the bacteria (attB). As a result of recombination between the attP and attB sites, the phage integrates into the bacterial genome flanked by two new recombination sites (attLeft and attRight). The removal of the phage from the bacterial chromosome and the regeneration of attP and attB sites can both result from the attL and attR sites recombining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site-specific Recombination
Site-specific recombination, also known as conservative site-specific recombination, is a type of genetic recombination in which DNA strand exchange takes place between segments possessing at least a certain degree of sequence homology. Enzymes known as site-specific recombinases (SSRs) perform rearrangements of DNA segments by recognizing and binding to short, specific DNA sequences (sites), at which they cleave the DNA backbone, exchange the two DNA helices involved, and rejoin the DNA strands. In some cases the presence of a recombinase enzyme and the recombination sites is sufficient for the reaction to proceed; in other systems a number of accessory proteins and/or accessory sites are required. Many different site-specific recombinase technology, genome modification strategies, among these recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE), an advanced approach for the targeted introduction of transcription units into predetermined genomic loci, rely on SSRs. Site-specific recombinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOPO Cloning
Topoisomerase-based cloning (TOPO cloning) is a molecular biology technique in which DNA fragments are cloned into specific vectors without the requirement for DNA ligases. Taq polymerase has a nontemplate-dependent terminal transferase activity that adds a single deoxyadenosine (A) to the 3'-end of the PCR products. This characteristic is exploited in "sticky end" TOPO TA cloning. For "blunt end" TOPO cloning, the recipient vector does not have overhangs and blunt-ended DNA fragments can be cloned. Principle The technique utilizes the inherent biological activity of DNA topoisomerase I. The biological role of topoisomerase is to cleave and rejoin supercoiled DNA ends to facilitate replication. Vaccinia virus topoisomerase I specifically recognize DNA sequence 5´-(C/T)CCTT-3'. During replication, the enzyme digests DNA specifically at this sequence, unwinds the DNA and, re-ligates it again at the 3' phosphate group of the thymidine Thymidine (nucleoside#List of nucleos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues in DNA arise due to the intertwined nature of its double-helical structure, which, for example, can lead to overwinding of the DNA duplex during DNA replication and transcription. If left unchanged, this torsion would eventually stop the DNA or RNA polymerases involved in these processes from continuing along the DNA helix. A second topological challenge results from the linking or tangling of DNA during replication. Left unresolved, links between replicated DNA will impede cell division. The DNA topoisomerases prevent and correct these types of topological problems. They do this by binding to DNA and cutting the sugar-phosphate backbone of either one (type I topoisomerases) or both (type II topoisomerases) of the DNA strands. This transien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-cloning
In molecular biology, subcloning is a technique used to move a particular DNA sequence from a ''parent vector'' to a ''destination vector''. Subcloning is not to be confused with molecular cloning Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their DNA replication, replication within Host (biology), host organisms. The use of the word ''cloning'' re ..., a related technique. Procedure Restriction enzymes are used to excise the gene of interest (the ''insert'') from the parent. The insert is purified in order to isolate it from other DNA molecules. A common purification method is gel isolation. The number of copies of the gene is then amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Simultaneously, the same restriction enzymes are used to digest (cut) the destination. The idea behind using the same restriction enzymes is to create Complementary DNA, complementary sticky ends, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two covalent phosphodiester bonds between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |