|
Climate Change In Puerto Rico
Climate change in Puerto Rico encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico. The United States Environmental Protection Agency reports: "Puerto Rico's climate is changing. The Commonwealth has warmed by more than one degree (F) since the mid 20th century, and the surrounding waters have warmed by nearly two degrees since 1901. The sea is rising about an inch every 15 years, and heavy rainstorms are becoming more severe. In the coming decades, rising temperatures are likely to increase storm damages, significantly harm coral reefs, and increase the frequency of unpleasantly hot days". A 2019 report stated that Puerto Rico "is affected by climate change more than anywhere else in the world". Rising seas and retreating shores "Sea level has risen by about four inches relative to Puerto Rico’s shoreline since 1960. As the oceans and atmosphere continue to warm, sea level around Pue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico Köppen
Puerto, a Spanish word meaning ''seaport'', may refer to: Places *El Puerto de Santa María, Andalusia, Spain *Puerto, a seaport town in Cagayan de Oro City, Philippines *Puerto Colombia, Colombia *Puerto Cumarebo, Venezuela *Puerto Galera, Oriental Mindoro, Philippines *Puerto La Cruz, Venezuela *Puerto Píritu, Venezuela *Puerto Princesa, Palawan, Philippines *Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States *Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Others *Puerto Rico (board game), ''Puerto Rico'' (board game) *Operación Puerto doping case See also * * Puerta (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral. The leading cause of coral bleaching is rising ocean temperature due to climate change. A temperature about 1 °C (or 2 °F) above average can cause bleaching. According to the United Nations Environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
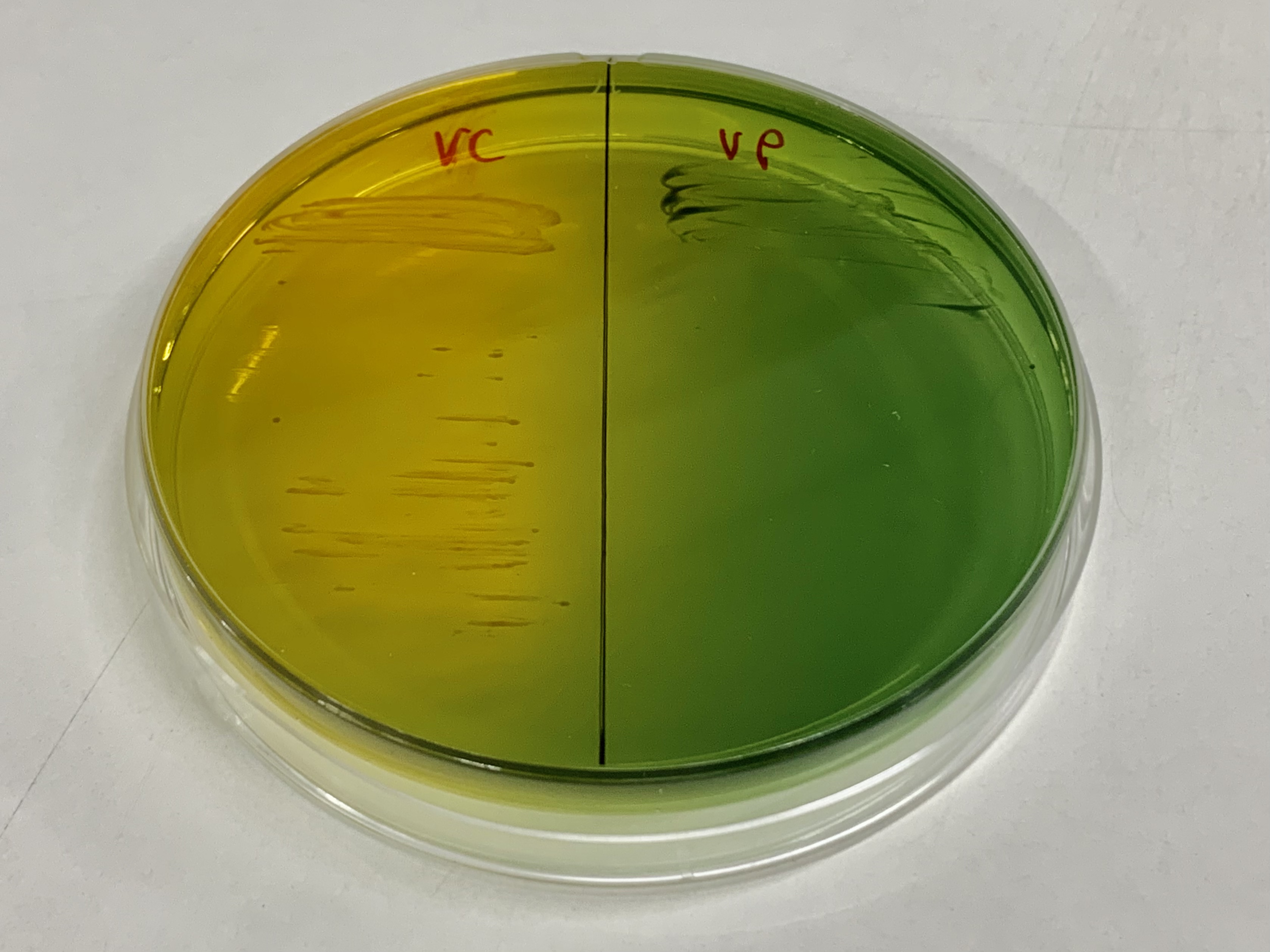
Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive in fresh water, ''Vibrio'' spp. are commonly found in various salt water environments. ''Vibrio'' spp. are facultative anaerobes that test positive for oxidase and do not form spores. All members of the genus are motile. They are able to have polar or lateral flagellum with or without sheaths. ''Vibrio'' species typically possess two chromosomes, which is unusual for bacteria. Each chromosome has a distinct and independent origin of replication, and are conserved together over time in the genus. Recent phylogenies have been constructed based on a suite of genes (multilocus sequence analysis). O. F. Müller (1773, 1786) described eight species of the genus ''Vibrio'' (included in Infusoria), three of which were spirilliforms. Some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world. Seeds of the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The beans are roasted and then ground into fine particles that are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out, producing a cup of coffee. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often used to mask the bitter taste or enhance the flavor. Though coffee is now a global commodity, it has a long history tied closely to food traditions around the Red Sea. The earliest credible evidence of coffee drinking in the form of the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry (botany), berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa''. In some countries, Cooking banana, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguishing them from dessert bananas. The fruit is variable in size, color, and firmness, but is usually elongated and curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a rind, which may be green, yellow, red, purple, or brown when ripe. The fruits grow upward in clusters near the top of the plant. Almost all modern edible seedless (Parthenocarpy, parthenocarp) bananas come from two wild species – ''Musa acuminata'' and ''Musa balbisiana''. The Binomial nomenclature, scientific names of most cultivated bananas are ''Musa acuminata'', ''Musa balbisiana'', and Musa × paradisiaca, ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca'' for the hybrid ''Musa acuminata'' × ''M. balbisiana'', depending on their genome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooking Banana
Cooking bananas are banana cultivars in the genus '' Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking. They may be eaten ripe or unripe and are generally starchy. Many cooking bananas are referred to as plantains (/ˈplæntɪn/, /plænˈteɪn/, /ˈplɑːntɪn/) or green bananas. In botanical usage, the term "plantain" is used only for true plantains, while other starchy cultivars used for cooking are called "cooking bananas". True plantains are cultivars belonging to the AAB group, while cooking bananas are any cultivars belonging to AAB, AAA, ABB, or BBB groups. The currently accepted scientific name for all such cultivars in these groups is ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca''. Fe'i bananas (''Musa'' × ''troglodytarum'') from the Pacific Islands are often eaten roasted or boiled, and are thus informally referred to as "mountain plantains," but they do not belong to any of the species from which all modern banana cultivars are descended. Cooking bananas are a major food staple in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosses
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta ('' sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromeliads
The Bromeliaceae (the bromeliads) are a family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, '' Pitcairnia feliciana''. It is among the basal families within the Poales and is the only family within the order that has septal nectaries and inferior ovaries.Judd, Walter S. Plant systematics a phylogenetic approach. 3rd ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc., 2007. These inferior ovaries characterize the Bromelioideae, a subfamily of the Bromeliaceae. The family includes both epiphytes, such as Spanish moss ('' Tillandsia usneoides''), and terrestrial species, such as the pineapple ('' Ananas comosus''). Many bromeliads are able to store water in a structure formed by their tightly overlapping leaf bases. However, the family is diverse enough to include the tank bromeliads, grey-leaved epiphyte ''Tillandsia'' species tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Flooding
Coastal flooding normally occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged by seawater. The range of a coastal flooding is a result of the elevation of floodwater that penetrates the inland which is controlled by the topography of the coastal land exposed to flooding. Flood damage modelling was limited to local, regional or national scales. However, with the presence of climate change and an increase in the population rates, flood events have intensified and called for a global interest in finding out different methods with both spatial and temporal dynamics. The seawater can flood the land via several different paths: direct flooding, overtopping of a barrier, breaching of a barrier. Coastal flooding is largely a natural event, however human influence on the coastal environment can exacerbate coastal flooding. Extraction of water from groundwater reservoirs in the coastal zone can instigate subsidence of the land, thus increasing the risk of flooding. Engineered protection struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_and_one_loose_plantain.jpg)


.jpg)
