
A lichen ( , ) is a composite
organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
that arises from
algae or
cyanobacteria living among
filaments of multiple
fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
species
in a
mutualistic relationship.
[Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms]
. University of California Museum of Paleontology.[ Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not ]plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclu ...
s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (fruticose
A fruticose lichen is a form of lichen fungi that is characterized by a coral-like shrubby or bushy growth structure. It is formed from a symbiotic relationship of a photobiont such as green algae or less commonly cyanobacteria and one, two or ...
); flat leaf-like structures (foliose
Foliose lichen is one of the morphological classes of lichens, which are complex organisms that arise from the symbiotic relationship between fungi and a photosynthetic partner, typically algae. This partnership allows lichen to live in diverse ...
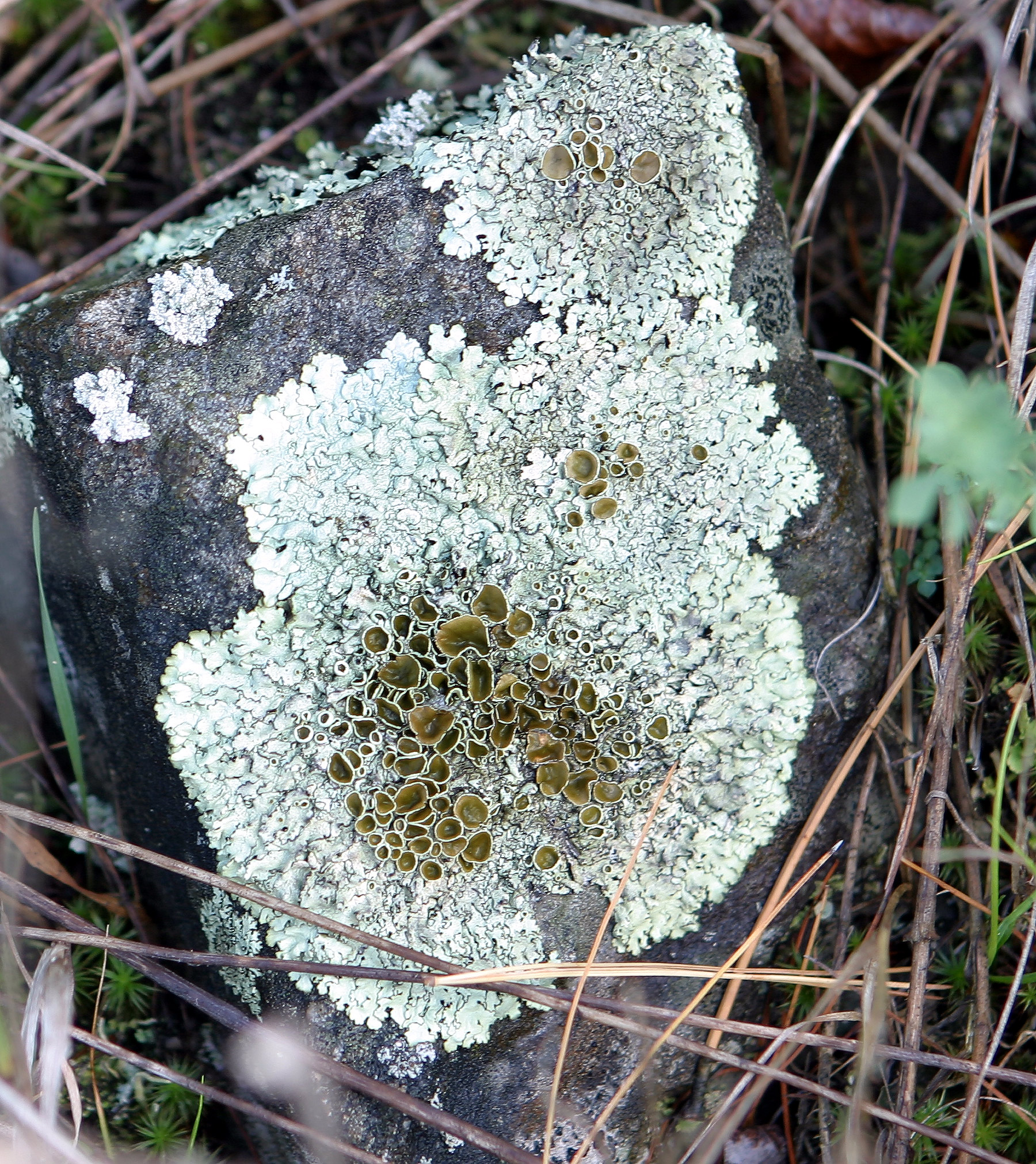
); grow crust-like, adhering tightly to a surface (substrate) like a thick coat of paint (crustose
Crustose is a habit of some types of algae and lichens in which the organism grows tightly appressed to a substrate, forming a biological layer. ''Crustose'' adheres very closely to the substrates at all points. ''Crustose'' is found on rocks ...
);[ have a powder-like appearance ( leprose); or other growth forms.][ Here, "macro" and "micro" do not refer to size, but to the growth form.][ Common names for lichens may contain the word '' moss'' (e.g., "]reindeer moss
''Cladonia rangiferina'', also known as reindeer cup lichen, reindeer lichen (cf. Sw. ''renlav'') or grey reindeer lichen, is a light-colored fruticose, cup lichen species in the family Cladoniaceae. It grows in both hot and cold climates in w ...
", "Iceland moss
''Cetraria islandica'', also known as true Iceland lichen or Iceland moss, is an Arctic-alpine lichen whose erect or upright, leaflike habit gives it the appearance of a moss, where its name likely comes from.
Description
It is often of a pale ...
"), and lichens may superficially look like and grow with mosses, but they are not closely related to mosses or any plant.[Brodo, Irwin M. and Duran Sharnoff, Sylvia (2001) ''Lichens of North America''. .] Lichens do not have roots that absorb water and nutrients as plants do,[Sharnoff, Stephen (2014) ''Field Guide to California Lichens'', Yale University Press. ] but like plants, they produce their own nutrition by photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
.[ When they grow on plants, they do not live as ]parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s, but instead use the plant's surface as a substrate.
Lichens occur from sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
to high alpine elevations, in many environmental conditions, and can grow on almost any surface.[ They are abundant growing on bark, leaves, mosses, or other lichens]gravestones
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, da ...
, roof
A roof ( : roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of te ...
s, exposed soil surfaces, rubber, bones, and in the soil as part of biological soil crusts. Various lichens have adapted to survive in some of the most extreme environments on Earth: arctic tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
, hot dry deserts, rocky coast
A cliffed coast, also called an abrasion coast, is a form of coast where the action of marine waves has formed steep cliffs that may or may not be precipitous. It contrasts with a flat or alluvial coast.
Formation
In coastal areas in whic ...
s, and toxic slag heaps. They can even live inside solid rock, growing between the grains.
It is estimated that 6–8% of Earth's land surface is covered by lichens. There are about 20,000 known species.[ Some lichens have lost the ability to reproduce sexually, yet continue to ]speciate
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
.microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s in a functioning system that may evolve as an even more complex composite organism.[ Lichens may be long-lived, with some considered to be among the oldest living things.]lichenometry
In archaeology, palaeontology, and geomorphology, lichenometry is a geomorphic method of geochronologic dating that uses lichen growth to determine the age of exposed rock, based on a presumed specific rate of increase in radial size over time. ...
).
Etymology and pronunciation
The English word ''lichen'' derives from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
("tree moss, lichen, lichen-like eruption on skin") via Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
. The Greek noun, which literally means "licker", derives from the verb , "to lick".
Anatomy and morphology
Growth forms
Lichens grow in a wide range of shapes and forms ( morphologies). The shape of a lichen is usually determined by the organization of the fungal filaments.[ The nonreproductive tissues, or vegetative body parts, are called the ''thallus''. Lichens are grouped by thallus type, since the thallus is usually the most visually prominent part of the lichen. Thallus growth forms typically correspond to a few basic internal structure types. Common names for lichens often come from a growth form or color that is typical of a lichen ]genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
.
Common groupings of lichen thallus growth forms are:
# fruticose
A fruticose lichen is a form of lichen fungi that is characterized by a coral-like shrubby or bushy growth structure. It is formed from a symbiotic relationship of a photobiont such as green algae or less commonly cyanobacteria and one, two or ...
[ – growing like a tuft or multiple-branched leafless mini-shrub, upright or hanging down, 3-dimensional branches with nearly round cross section (]terete
Terete is a term in botany used to describe a cross section that is circular, or like a distorted circle, with a single surface wrapping around it.Lichen Vocabulary, Lichens of North America Information, Sylvia and Stephen Sharnoff/ref> This is u ...
) or flattened
# foliose
Foliose lichen is one of the morphological classes of lichens, which are complex organisms that arise from the symbiotic relationship between fungi and a photosynthetic partner, typically algae. This partnership allows lichen to live in diverse ...
[ – growing in 2-dimensional, flat, leaf-like lobes
# ]crustose
Crustose is a habit of some types of algae and lichens in which the organism grows tightly appressed to a substrate, forming a biological layer. ''Crustose'' adheres very closely to the substrates at all points. ''Crustose'' is found on rocks ...
[ – crust-like, adhering tightly to a surface ( substrate) like a thick coat of paint
# squamulose][ – formed of small leaf-like scales crustose below but free at the tips
# leprose][ – powdery
# ]gelatinous
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also ...
– jelly-like
# filamentous – stringy or like matted hair
# byssoid – wispy, like teased wool
Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving surfaces covered wit ...
# structureless
There are variations in growth types in a single lichen species, grey areas between the growth type descriptions, and overlapping between growth types, so some authors might describe lichens using different growth type descriptions.
When a crustose lichen gets old, the center may start to crack up like old-dried paint, old-broken asphalt paving, or like the polygonal "islands" of cracked-up mud in a dried lakebed. This is called being rimose or areolate
Lichens are composite organisms made up of multiple species: a fungal partner, one or more photosynthetic partners, and sometimes a basidiomycete yeast. They are regularly grouped by their external appearance – a characteristic known as their ...
, and the "island" pieces separated by the cracks are called areolas.prothallus
A prothallus, or prothallium, (from Latin ''pro'' = forwards and Greek ''θαλλος'' (''thallos'') = twig) is usually the gametophyte stage in the life of a fern or other pteridophyte. Occasionally the term is also used to describe the young ...
or hypothallus.[ When a crustose lichen grows from a center and appears to radiate out, it is called crustose placodioid. When the edges of the areolas lift up from the substrate, it is called squamulose.][
These growth form groups are not precisely defined. Foliose lichens may sometimes branch and appear to be fruticose. Fruticose lichens may have flattened branching parts and appear leafy. Squamulose lichens may appear where the edges lift up. Gelatinous lichens may appear leafy when dry.][ Means of telling them apart in these cases are in the sections below.
Structures involved in reproduction often appear as discs, bumps, or squiggly lines on the surface of the thallus.][ The thallus is not always the part of the lichen that is most visually noticeable. Some lichens can grow ''inside'' solid rock between the grains ( endolithic lichens), with only the sexual fruiting part visible growing outside the rock.][Lichen Vocabulary, Lichens of North America Information, Sylvia and Stephen Sharnoff]
The most visually noticeable reproductive parts are often circular, raised, plate-like or disc-like outgrowths, with crinkly edges, and are described in sections below.
Color
Lichens come in many colors.[ Coloration is usually determined by the photosynthetic component.][ This is because moisture causes the surface skin (]cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
) to become more transparent, exposing the green photobiont layer.[ Different colored lichens covering large areas of exposed rock surfaces, or lichens covering or hanging from bark can be a spectacular display when the patches of diverse colors "come to life" or "glow" in brilliant displays following rain.
Different colored lichens may inhabit different adjacent sections of a rock face, depending on the angle of exposure to light.][ Colonies of lichens may be spectacular in appearance, dominating much of the surface of the visual landscape in forests and natural places, such as the vertical "paint" covering the vast rock faces of ]Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park ( ) is an American national park in California, surrounded on the southeast by Sierra National Forest and on the northwest by Stanislaus National Forest. The park is managed by the National Park Service and covers an ...
.[Michigan Lichens, Julie Jones Medlin, B. Jain Publishers, 1996, , 9780877370390]
The color of a lichen changes depending on whether the lichen is wet or dry.[ Color descriptions used for identification are based on the color that shows when the lichen is dry.][ Dry lichens with a cyanobacterium as the photosynthetic partner tend to be dark grey, brown, or black.][
The underside of the leaf-like lobes of foliose lichens is a different color from the top side (]dorsiventral A dorsiventral (Lat. ''dorsum'', "the back", ''venter'', "the belly") organ is one that has two surfaces differing from each other in appearance and structure, as an ordinary leaf. This term has also been used as a synonym for dorsoventral organs, ...
), often brown or black, sometimes white. A fruticose lichen may have flattened "branches", appearing similar to a foliose lichen, but the underside of a leaf-like structure on a fruticose lichen is the ''same'' color as the top side. The leaf-like lobes of a foliose lichen may branch, giving the appearance of a fruticose lichen, but the underside will be a ''different'' color from the top side.[
The sheen on some jelly-like gelatinous lichens is created by ]mucilaginous
Mucilage is a thick, gluey substance produced by nearly all plants and some microorganisms. These microorganisms include protists which use it for their locomotion. The direction of their movement is always opposite to that of the secretion of ...
secretions.[
]
Internal structure
 A lichen consists of a simple photosynthesizing organism, usually a green alga or
A lichen consists of a simple photosynthesizing organism, usually a green alga or cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, surrounded by filaments of a fungus. Generally, most of a lichen's bulk is made of interwoven fungal filaments,[Lichens: More on Morphology, University of California Museum of Paleontology]
but this is reversed in filamentous and gelatinous lichens.[ The fungus is called a ''mycobiont''. The photosynthesizing organism is called a ''photobiont''. Algal photobionts are called ''phycobionts''.][
The part of a lichen that is not involved in reproduction, the "body" or "vegetative tissue" of a lichen, is called the ''thallus''. The thallus form is very different from any form where the fungus or alga are growing separately. The thallus is made up of filaments of the fungus called '' hyphae''. The filaments grow by branching then rejoining to create a mesh, which is called being " anastomosed". The mesh of fungal filaments may be dense or loose.
Generally, the fungal mesh surrounds the algal or ]cyanobacterial
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue ...
cells, often enclosing them within complex fungal tissues that are unique to lichen associations. The thallus may or may not have a protective "skin" of densely packed fungal filaments, often containing a second fungal species,[ gelatinous, and other lichens do not have a cortex, which is called being ecorticate.][
] Fruticose, foliose, crustose, and squamulose lichens generally have up to three different types of tissue, differentiated by having different densities of fungal filaments.
Fruticose, foliose, crustose, and squamulose lichens generally have up to three different types of tissue, differentiated by having different densities of fungal filaments.[ The top layer, where the lichen contacts the environment, is called a ''cortex''.][ The cortex is made of densely tightly woven, packed, and glued together ( agglutinated) fungal filaments.][ The dense packing makes the cortex act like a protective "skin", keeping other organisms out, and reducing the intensity of sunlight on the layers below.][ The cortex layer can be up to several hundred micrometers (μm) in thickness (less than a millimeter).][ The cortex may be further topped by an epicortex of secretions, not cells, 0.6–1 μm thick in some lichens.][ This secretion layer may or may not have pores.][
Below the cortex layer is a layer called the ''photobiontic layer'' or ''symbiont layer''.][ The symbiont layer has less densely packed fungal filaments, with the photosynthetic partner embedded in them.][ The less dense packing allows air circulation during photosynthesis, similar to the anatomy of a leaf.][ Each cell or group of cells of the photobiont is usually individually wrapped by hyphae, and in some cases penetrated by a ]haustorium
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates th ...
.[ In crustose and foliose lichens, algae in the photobiontic layer are diffuse among the fungal filaments, decreasing in gradation into the layer below. In fruticose lichens, the photobiontic layer is sharply distinct from the layer below.][
The layer beneath the symbiont layer called is called the '']medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
''. The medulla is less densely packed with fungal filaments than the layers above. In foliose lichens, there is usually, as in '' Peltigera'',[ another densely packed layer of fungal filaments called the lower cortex.][ Root-like fungal structures called ''rhizines'' ( usually)][ grow from the lower cortex to attach or anchor the lichen to the substrate.][ Fruticose lichens have a single cortex wrapping all the way around the "stems" and "branches".][ The medulla is the lowest layer, and may form a cottony white inner core for the branchlike thallus, or it may be hollow.][ Crustose and squamulose lichens lack a lower cortex, and the medulla is in direct contact with the substrate that the lichen grows on.
In crustose areolate lichens, the edges of the areolas peel up from the substrate and appear leafy. In squamulose lichens the part of the lichen thallus that is not attached to the substrate may also appear leafy. But these leafy parts lack a lower cortex, which distinguishes crustose and squamulose lichens from foliose lichens.][ Conversely, foliose lichens may appear flattened against the substrate like a crustose lichen, but most of the leaf-like lobes can be lifted up from the substrate because it is separated from it by a tightly packed lower cortex.][ byssoid, and leprose lichens lack a cortex (are ecorticate), and generally have only undifferentiated tissue, similar to only having a symbiont layer.
In lichens that include both green algal ''and'' cyanobacterial symbionts, the cyanobacteria may be held on the upper or lower surface in small pustules called '' cephalodia''.
'' Pruinia'' is a whitish coating on top of an upper surface.][ An '' epinecral layer'' is "a layer of horny dead fungal hyphae with indistinct ]lumina
Lumina may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Lumina'', a literary journal published by Sarah Lawrence College
* ''World of Lumina'' or ''Lumina'', a graphic novel by Emanuele Tenderini and Linda Cavallini
Music
* "Lumina", ...
in or near the cortex above the algal layer".
Physiology
Symbiotic relation
A lichen is a composite organism that emerges from algae or cyanobacteria living among the filaments ( hyphae) of the fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
in a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship. The fungi benefit from the carbohydrates produced by the algae or cyanobacteria via photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
. The algae or cyanobacteria benefit by being protected from the environment by the filaments of the fungi, which also gather moisture and nutrients from the environment, and (usually) provide an anchor to it. Although some photosynthetic partners in a lichen can survive outside the lichen, the lichen symbiotic association extends the ecological range of both partners, whereby most descriptions of lichen associations describe them as symbiotic. Both partners gain water and mineral nutrients mainly from the atmosphere, through rain and dust. The fungal partner protects the alga by retaining water, serving as a larger capture area for mineral nutrients and, in some cases, provides minerals obtained from the substrate. If a cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
is present, as a primary partner or another symbiont in addition to a green alga as in certain tripartite lichens, they can fix atmospheric nitrogen, complementing the activities of the green alga.
In three different lineages the fungal partner has independently lost the mitochondrial gene atp9, which has key functions in mitochondrial energy production. The loss makes the fungi completely dependent on their symbionts.
The algal or cyanobacterial cells are photosynthetic and, as in plants, they reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
into organic carbon sugars to feed both symbionts. Phycobionts (algae) produce sugar alcohols
Sugar alcohols (also called polyhydric alcohols, polyalcohols, alditols or glycitols) are organic compounds, typically derived from sugars, containing one hydroxyl group (–OH) attached to each carbon atom. They are white, water-soluble soli ...
( ribitol, sorbitol, and erythritol
Erythritol is an organic compound, a four-carbon sugar alcohol (or polyol) with no optical activity, used as a food additive and sugar substitute. It is naturally occurring. It can be made from corn using enzymes and fermentation. Its formula is ...
), which are absorbed by the mycobiont (fungus).[ Cyanobionts produce ]glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
.[ Lichenized fungal cells can make the photobiont "leak" out the products of photosynthesis, where they can then be absorbed by the fungus.][
It appears many, probably the majority, of lichen also live in a symbiotic relationship with an order of basidiomycete yeasts called Cyphobasidiales. The absence of this third partner could explain why growing lichen in the laboratory is difficult. The yeast cells are responsible for the formation of the characteristic cortex of the lichen thallus, and could also be important for its shape.
The lichen combination of alga or cyanobacterium with a fungus has a very different form (morphology), physiology, and biochemistry than the component fungus, alga, or cyanobacterium growing by itself, naturally or in culture. The body (]thallus
Thallus (plural: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. Many of these organisms ...
) of most lichens is different from those of either the fungus or alga growing separately. When grown in the laboratory in the absence of its photobiont, a lichen fungus develops as a structureless, undifferentiated mass of fungal filaments ( hyphae). If combined with its photobiont under appropriate conditions, its characteristic form associated with the photobiont emerges, in the process called morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
.[ In a few remarkable cases, a single lichen fungus can develop into two very different lichen forms when associating with either a green algal or a cyanobacterial symbiont. Quite naturally, these alternative forms were at first considered to be different species, until they were found growing in a conjoined manner.
Evidence that lichens are examples of successful symbiosis is the fact that lichens can be found in almost every habitat and geographic area on the planet.][ Two species in two genera of green algae are found in over 35% of all lichens, but can only rarely be found living on their own outside of a lichen.
In a case where one fungal partner simultaneously had two green algae partners that outperform each other in different climates, this might indicate having more than one photosynthetic partner at the same time might enable the lichen to exist in a wider range of habitats and geographic locations.][
At least one form of lichen, the North American beard-like lichens, are constituted of not two but three symbiotic partners: an ascomycetous fungus, a photosynthetic alga, and, unexpectedly, a basidiomycetous yeast.
Phycobionts can have a net output of sugars with only water vapor.][ The thallus must be saturated with liquid water for cyanobionts to photosynthesize.][
Algae produce sugars that are absorbed by the fungus by diffusion into special fungal hyphae called appressoria or ]haustoria
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates th ...
in contact with the wall of the algal cells.[ The algae may contribute up to 80% of their sugar production to the fungus.][
]
Ecology
Lichen associations may be examples of mutualism or commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction ( symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fr ...
, but the lichen relationship can be considered parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
[ The ]fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from t ...
surrounds the algal cells,[ often enclosing them within complex fungal tissues unique to lichen associations. In many species the fungus penetrates the algal cell wall,][ forming penetration pegs (]haustoria
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates th ...
) similar to those produced by pathogenic fungi Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. Approximately 300 fungi are known to be pathogenic to humans. Markedly more fungi are known to be pathogenic to plant life than those of the animal kingdom. The study of ...
that feed on a host.[ Cyanobacteria in laboratory settings can grow faster when they are alone rather than when they are part of a lichen.
]
Miniature ecosystem and holobiont theory
Symbiosis in lichens is so well-balanced that lichens have been considered to be relatively self-contained miniature ecosystems in and of themselves.[
][ Honegger, R. (1991) ''Fungal evolution: symbiosis and morphogenesis, Symbiosis as a Source of Evolutionary Innovation'', Margulis, L., and Fester, R. (eds). Cambridge, MA, USA: The MIT Press, pp. 319–340.] It is thought that lichens may be even more complex symbiotic systems that include non-photosynthetic bacterial communities performing other functions as partners in a holobiont
A holobiont is an assemblage of a host and the many other species living in or around it, which together form a discrete ecological unit through symbiosis, though there is controversy over this discreteness. The components of a holobiont are i ...
.[Barreno, E., Herrera-Campos, M., García-Breijo, F., Gasulla, F., and Reig-Armiñana, J. (2008]
"Non photosynthetic bacteria associated to cortical structures on Ramalina and ''Usnea'' thalli from Mexico"
Asilomar, Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Abstracts IAL 6- ABLS Joint Meeting.
Many lichens are very sensitive to environmental disturbances and can be used to cheaplyair pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
,[ ]ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
depletion, and metal contamination. Lichens have been used in making dyes, perfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Th ...
s,traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
s. A few lichen species are eaten by insects[ or larger animals, such as reindeer. Lichens are widely used as environmental indicators or bio-indicators. When air is very badly polluted with sulphur dioxide, there may be no lichens present; only some green algae can tolerate those conditions. If the air is clean, then shrubby, hairy and leafy lichens become abundant. A few lichen species can tolerate fairly high levels of pollution, and are commonly found in urban areas, on pavements, walls and tree bark. The most sensitive lichens are shrubby and leafy, while the most tolerant lichens are all crusty in appearance. Since industrialisation, many of the shrubby and leafy lichens such as '' Ramalina'', '' Usnea'' and '' Lobaria'' species have very limited ranges, often being confined to the areas which have the cleanest air.
]
Lichenicolous fungi
Some fungi can only be found living ''on'' lichens as obligate parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s. These are referred to as lichenicolous fungi, and are a different species from the fungus living inside the lichen; thus they are not considered to be part of the lichen.
Reaction to water
Moisture makes the cortex become more transparent.[ This way, the algae can conduct photosynthesis when moisture is available, and is protected at other times. When the cortex is more transparent, the algae show more clearly and the lichen looks greener.
]
Metabolites, metabolite structures and bioactivity
Lichens can show intense antioxidant activity. Secondary metabolites
Secondary metabolites, also called specialised metabolites, toxins, secondary products, or natural products, are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the nor ...
are often deposited as crystals in the apoplast
Inside a plant, the apoplast can mean the space outside of cell membranes, where material can diffuse freely; that is, the extracellular spaces.
''Apoplast '' can also refer especially to the continuum of cell walls of adjacent cells; fluid and ...
.[
Sometimes lichens contain structures made from fungal metabolites, for example crustose lichens sometimes have a polysaccharide layer in the cortex.
]
Growth rate
Lichens often have a regular but very slow growth rate of less than a millimeter per year.
In crustose lichens, the area along the margin is where the most active growth is taking place.[ Most crustose lichens grow only 1–2 mm in diameter per year.
]
Life span
Lichens may be long-lived, with some considered to be among the oldest living organisms.[ An ]Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
species called "map lichen" (''Rhizocarpon geographicum
''Rhizocarpon geographicum'' (the map lichen) is a species of lichen, which grows on rocks in mountainous areas of low air pollution. Each lichen is a flat patch bordered by a black line of fungal hyphae. These patches grow adjacent to each other ...
'') has been dated at 8,600 years, apparently the world's oldest living organism.
Response to environmental stress
Unlike simple dehydration in plants and animals, lichens may experience a ''complete'' loss of body water in dry periods.[ Lichens are capable of surviving extremely low levels of ]water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
content (poikilohydric
Poikilohydry is the lack of ability (structural or functional mechanism) to maintain and/or regulate water content to achieve homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis ( British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady i ...
).[
In tests, lichen survived and showed remarkable results on the adaptation capacity of photosynthetic activity within the simulation time of 34 days under Martian conditions in the Mars Simulation Laboratory (MSL) maintained by the ]German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany ...
(DLR).Rhizocarpon geographicum
''Rhizocarpon geographicum'' (the map lichen) is a species of lichen, which grows on rocks in mountainous areas of low air pollution. Each lichen is a flat patch bordered by a black line of fungal hyphae. These patches grow adjacent to each other ...
'' and '' Xanthoria elegans''—were sealed in a capsule and launched on a Russian Soyuz rocket 31 May 2005. Once in orbit, the capsules were opened and the lichens were directly exposed to the vacuum of space with its widely fluctuating temperatures and cosmic radiation. After 15 days, the lichens were brought back to earth and were found to be unchanged in their ability to photosynthesize.[
]
Reproduction and dispersal
Vegetative reproduction
 Many lichens reproduce asexually, either by a piece breaking off and growing on its own (
Many lichens reproduce asexually, either by a piece breaking off and growing on its own (vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or spec ...
) or through the dispersal of diaspores containing a few algal cells surrounded by fungal cells.[ Because of the relative lack of differentiation in the thallus, the line between diaspore formation and vegetative reproduction is often blurred. Fruticose lichens can easily fragment, and new lichens can grow from the fragment (]vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or spec ...
). Many lichens break up into fragments when they dry, dispersing themselves by wind action, to resume growth when moisture returns.[ ''Soredia'' (singular: "soredium") are small groups of algal cells surrounded by fungal filaments that form in structures called soralia, from which the soredia can be dispersed by wind.][ ''Isidia'' (singular: "isidium") are branched, spiny, elongated, outgrowths from the thallus that break off for mechanical dispersal.][ Lichen propagules ( diaspores) typically contain cells from both partners, although the fungal components of so-called "fringe species" rely instead on algal cells dispersed by the "core species".]
Sexual reproduction
 Structures involved in reproduction often appear as discs, bumps, or squiggly lines on the surface of the thallus.
Structures involved in reproduction often appear as discs, bumps, or squiggly lines on the surface of the thallus.[ Though it has been argued that sexual reproduction in photobionts is selected against, there is strong evidence that suggests meiotic activities (sexual reproduction) in ''Trebouxia''. Many lichen fungi reproduce sexually like other fungi, producing spores formed by ]meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately r ...
and fusion of gametes. Following dispersal, such fungal spores must meet with a compatible algal partner before a functional lichen can form.
Some lichen fungi belong to the phylum Basidiomycota (''basidiolichens'') and produce mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is ...
-like reproductive structures resembling those of their nonlichenized relatives.
Most lichen fungi belong to Ascomycetes (''ascolichens''). Among the ascolichens, spores are produced in spore-producing structures called ''ascomata
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
''.[ The most common types of ascomata are the '']apothecium
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
'' (plural: apothecia) and ''perithecium
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
'' (plural: perithecia).[ Apothecia are usually cups or plate-like discs located on the top surface of the lichen thallus. When apothecia are shaped like squiggly line segments instead of like discs, they are called ''lirellae''.][ Perithecia are shaped like flasks that are immersed in the lichen thallus tissue, which has a small hole for the spores to escape the flask, and appear like black dots on the lichen surface.][
The three most common spore body types are raised discs called '']apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
'' (singular: apothecium), bottle-like cups with a small hole at the top called ''perithecia'' (singular: perithecium), and ''pycnidia'' (singular: pycnidium), shaped like perithecia but without asci (an ascus is the structure that contains and releases the sexual spores in fungi of the Ascomycota).
The apothecium has a layer of exposed spore-producing cells called '' asci'' (singular: ascus), and is usually a different color from the thallus tissue.[ When the apothecium has an outer margin, the margin is called the ''exciple''.][ When the exciple has a color similar to colored thallus tissue the apothecium or lichen is called ''lecanorine'', meaning similar to members of the genus '' Lecanora''.][ When the exciple is blackened like carbon it is called ''lecideine'' meaning similar to members of the genus '']Lecidea
''Lecidea'' is a genus of crustose lichens with a carbon black ring or outer margin ( exciple) around the fruiting body disc (apothecium), usually (or always) found growing on (saxicolous) or in (endolithic
An endolith or endolithic is an or ...
''.[ When the margin is pale or colorless it is called ''biatorine''.][
] A "
A "podetium
A podetium (plural: podetia) is the upright secondary thallus in '' Cladonia'' lichens. It is a hollow stalk extending from the primary thallus. Podetia can be pointed stalks, club like, cupped, or branched in shape and may or may not contain the ...
" (plural: podetia
A podetium (plural: podetia) is the upright secondary thallus in ''Cladonia'' lichens. It is a hollow stalk extending from the primary thallus. Podetia can be pointed stalks, club like, cupped, or branched in shape and may or may not contain the ...
) is a lichenized stalk-like structure of the fruiting body rising from the thallus, associated with some fungi that produce a fungal apothecium
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
.[ Since it is part of the reproductive tissue, podetia are not considered part of the main body (thallus), but may be visually prominent.][ The podetium may be branched, and sometimes cup-like. They usually bear the fungal ]pycnidia
A pycnidium (plural pycnidia) is an asexual fruiting body produced by mitosporic fungi, for instance in the order Sphaeropsidales ( Deuteromycota, Coelomycetes) or order Pleosporales (Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes). It is often spherical or inverse ...
or apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
or both.[ Many lichens have ]apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos ...
that are visible to the naked eye.[
Most lichens produce abundant sexual structures.][ Many species appear to disperse only by sexual spores.]homothallic Homothallic refers to the possession, within a single organism, of the resources to reproduce sexually; i.e., having male and female reproductive structures on the same thallus. The opposite sexual functions are performed by different cells of a si ...
). This breeding system may enable successful reproduction in harsh environments.[
''Mazaedia'' (singular: mazaedium) are apothecia shaped like a dressmaker's pin in pin lichens, where the fruiting body is a brown or black mass of loose ascospores enclosed by a cup-shaped exciple, which sits on top of a tiny stalk.][
]
Taxonomy and classification
Lichens are classified by the fungal component. Lichen species are given the same scientific name ( binomial name) as the fungus species in the lichen. Lichens are being integrated into the classification schemes for fungi. The alga bears its own scientific name, which bears no relationship to that of the lichen or fungus.[ Nearly 20% of known fungal species are associated with lichens.][
"''Lichenized fungus''" may refer to the entire lichen, or to just the fungus. This may cause confusion without context. A particular fungus species may form lichens with different algae species, giving rise to what appear to be different lichen species, but which are still classified (as of 2014) as the same lichen species.][ Even more unusual than basidiolichens is the fungus '' Geosiphon pyriforme'', a member of the Glomeromycota that is unique in that it encloses a cyanobacterial symbiont inside its cells. '' Geosiphon'' is not usually considered to be a lichen, and its peculiar symbiosis was not recognized for many years. The genus is more closely allied to endomycorrhizal genera. Fungi from ]Verrucariales
Verrucariales is an order of ascomycetous fungi within the subclass Chaetothyriomycetidae of the class Eurotiomycetes. Although most of the Verrucariales are lichenised, the family Sarcopyreniaceae consists of 11 species of lichenicolous (lichen ...
also form marine lichens with the brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and p ...
''Petroderma maculiforme'', and have a symbiotic relationship with seaweed (such as rockweed) and '' Blidingia minima'', where the algae are the dominant components. The fungi is thought to help the rockweeds to resist desiccation when exposed to air. In addition, lichens can also use yellow-green algae ('' Heterococcus'') as their symbiotic partner.
Lichens independently emerged from fungi associating with algae and cyanobacteria multiple times throughout history.
Fungi
The fungal component of a lichen is called the ''mycobiont''. The mycobiont may be an Ascomycete or Basidiomycete.[ The associated lichens are called either ascolichens or ]basidiolichen
Basidiolichens are lichenized members of the Basidiomycota, a much smaller group of lichens than the far more common ascolichens in the Ascomycota. In arctic, alpine, and temperate forests, the most common basidiolichens are in the agaric genus ...
s, respectively. Living as a symbiont
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasi ...
in a lichen appears to be a successful way for a fungus to derive essential nutrients, since about 20% of all fungal species have acquired this mode of life.[
Thalli produced by a given fungal symbiont with its differing partners may be similar, and the secondary metabolites identical, indicating that the fungus has the dominant role in determining the morphology of the lichen. But the same mycobiont with different photobionts may also produce very different growth forms.][ Lichens are known in which there is one fungus associated with two or even three algal species.
Although each lichen thallus generally appears homogeneous, some evidence seems to suggest that the fungal component may consist of more than one genetic individual of that species.
Two or more fungal species can interact to form the same lichen.][
The following table lists the orders and ]families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
of fungi that include lichen-forming species.
Photobionts
The photosynthetic partner in a lichen is called a ''photobiont''. The photobionts in lichens come from a variety of simple prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
and eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
organisms. In the majority of lichens the photobiont is a green alga (Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta or Prasinophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it refers to a ...
) or a cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
. In some lichens both types are present; in such cases, the alga is typically the primary partner, with the cyanobacteria being located in cryptic pockets. Algal photobionts are called ''phycobionts'', while cyanobacterial photobionts are called ''cyanobionts''.[ According to one source, about 90% of all known lichens have phycobionts, and about 10% have cyanobionts,][ while another source states that two thirds of lichens have green algae as phycobiont, and about one third have a cyanobiont.][ Approximately 100 species of photosynthetic partners from 40][ genera and five distinct classes (prokaryotic: Cyanophyceae; eukaryotic: ]Trebouxiophyceae
The Trebouxiophyceae are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Their circumscription within the green algae is not well established due to the need for more genetic studies at higher levels within the group.
Genera without interve ...
, Phaeophyceae, Chlorophyceae) have been found to associate with the lichen-forming fungi.[
Common algal photobionts are from the genera '' Trebouxia'', '' Trentepohlia'', '' Pseudotrebouxia'', or '' Myrmecia''. ''Trebouxia'' is the most common genus of green algae in lichens, occurring in about 40% of all lichens. "Trebouxioid" means either a photobiont that is in the genus ''Trebouxia'', or resembles a member of that genus, and is therefore presumably a member of the class ]Trebouxiophyceae
The Trebouxiophyceae are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Their circumscription within the green algae is not well established due to the need for more genetic studies at higher levels within the group.
Genera without interve ...
.[ Overall, about 100 species of eukaryotes are known to occur as photobionts in lichens. All the algae are probably able to exist independently in nature as well as in the lichen.][
A "]cyanolichen
Cyanolichens are lichens that apart from the basic fungal component ("mycobiont"), contain cyanobacteria, otherwise known as blue-green algae, as the photosynthesizing component ("photobiont"). Overall, about a third of lichen photobionts are cyan ...
" is a lichen with a cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
as its main photosynthetic component (photobiont).genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
is '' Nostoc''.[ Other][ common ]cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
photobionts are from ''Scytonema
''Scytonema'' is a genus of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that contains over 100 species. It grows in filaments that form dark mats. Many species are aquatic and are either free-floating or grow attached to a submerged substrate, while others s ...
''.[ Many cyanolichens are small and black, and have ]limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
as the substrate. Another cyanolichen group, the jelly lichens of the genera ''Collema
''Collema'' (jelly lichen) is a genus of lichens in the family Collemataceae. The photobiont is the cyanobacterium genus ''Nostoc''.Dobson, F.S. (2000) Lichens, an illustrated guide to the British and Irish species. 4th edition. Richmond publish ...
'' or '' Leptogium'' are gelatinous and live on moist soils. Another group of large and foliose
Foliose lichen is one of the morphological classes of lichens, which are complex organisms that arise from the symbiotic relationship between fungi and a photosynthetic partner, typically algae. This partnership allows lichen to live in diverse ...
species including '' Peltigera'', '' Lobaria'', and '' Degelia'' are grey-blue, especially when dampened or wet. Many of these characterize the Lobarion communities of higher rainfall areas in western Britain, e.g., in the Celtic rain forest. Strains of cyanobacteria found in various cyanolichens are often closely related to one another.[ They differ from the most closely related free-living strains.][ More than one phycobiont may be present in a single thallus.][
A single lichen may contain several algal genotypes. These multiple genotypes may better enable response to adaptation to environmental changes, and enable the lichen to inhabit a wider range of environments.
]
Controversy over classification method and species names
There are about 20,000 known lichen species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
.[ Because lichens are combinations of members of two or even three different biological ]kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
s, these components ''must'' have a ''different'' ancestral lineage from each other. By convention, lichens are still called "species" anyway, and are classified according to the species of their fungus, not the species of the algae or cyanobacteria. Lichens are given the same scientific name ( binomial name) as the fungus in them, which may cause some confusion. The alga bears its own scientific name, which has no relationship to the name of the lichen or fungus.
Diversity
The largest number of lichenized fungi occur in the Ascomycota, with about 40% of species forming such an association.saprotroph
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi ( ...
s or plant parasites (for example, the Leotiales, Dothideales
Dothideales are an order of bitunicate fungi consisting mainly of saprobic or plant parasitic species.
Description
Taxa in this order are characterized by the absence of a hamathecium (defined as hyphae or other tissues between asci) in a l ...
, and Pezizales). Other lichen fungi occur in only five orders in which all members are engaged in this habit (Orders Graphidales, Gyalectales, Peltigerales
Peltigerales is an order of lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. The taxonomy of the group has seen numerous changes; it was formerly often treated as a suborder of the order Lecanorales. It co ...
, Pertusariales, and Teloschistales
The Teloschistales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. According to one 2008 estimate, the order contains 5 families, 66 genera, and 1954 species. The predominant photobi ...
). Overall, about 98% of lichens have an ascomycetous mycobiont.fungi imperfecti
The fungi imperfecti or imperfect fungi, are fungi which do not fit into the commonly established taxonomic classifications of fungi that are based on biological species concepts or morphological characteristics of sexual structures because the ...
, a catch-all category for fungi whose sexual form of reproduction has never been observed. Comparatively few basidiomycetes are lichenized, but these include agarics
An agaric () is a type of fungus fruiting body characterized by the presence of a pileus (cap) that is clearly differentiated from the stipe (stalk), with lamellae (gills) on the underside of the pileus. In the UK, agarics are called "mushrooms ...
, such as species of ''Lichenomphalia
''Lichenomphalia'' is both a basidiolichen and an agaric genus. Most of the species have inconspicuous lichenized thalli that consist of scattered, small, loose, nearly microscopic green balls or foliose small flakes containing single-celled gr ...
'', clavarioid fungi
The clavarioid fungi are a group of fungi in the ''Basidiomycota'' typically having erect, simple or branched basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that are formed on the ground, on decaying vegetation, or on dead wood. They are colloquially called club fun ...
, such as species of ''Multiclavula
''Multiclavula'' is a genus of basidiolichens in the family Hydnaceae. The widespread genus contains 14 species.Reschke, K., Lotz-Winter, H., Fischer, C.W., Hofmann, T.A., Piepenbring, M., 2021. New and interesting species of Agaricomycetes from ...
'', and corticioid fungi
The corticioid fungi are a group of fungi in the Basidiomycota typically having effused, smooth basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that are formed on the undersides of dead tree trunks or branches. They are sometimes colloquially called crust fungi or pa ...
, such as species of '' Dictyonema''.
Identification methods
Lichen identification uses growth form, microscopy and reactions to chemical tests.
The outcome of the "Pd test" is called "Pd", which is also used as an abbreviation for the chemical used in the test, para-phenylenediamine.[ If putting a drop on a lichen turns an area bright yellow to orange, this helps identify it as belonging to either the genus '']Cladonia
''Cladonia'' is a genus of moss-like lichens in the family Cladoniaceae. They are the primary food source for reindeer/caribou. ''Cladonia'' species are of economic importance to reindeer-herders, such as the Sami in Scandinavia or the Nenets ...
'' or '' Lecanora''.[
]
Evolution and paleontology
The fossil record for lichens is poor.["Lichens: Fossil Record"]
, University of California Museum of Paleontology. The extreme habitats that lichens dominate, such as tundra, mountains, and deserts, are not ordinarily conducive to producing fossils.[ Lichen fragments are also found in fossil leaf beds, such as '' Lobaria'' from Trinity County in northern California, USA, dating back to the early to middle ]Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
.[
The oldest fossil lichen in which both symbiotic partners have been recovered is '' Winfrenatia'', an early zygomycetous ( Glomeromycotan) lichen symbiosis that may have involved controlled parasitism, is permineralized in the ]Rhynie Chert
The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness (a Lagerstätte). It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is locate ...
of Scotland, dating from early Early Devonian
The Early Devonian is the first of three epochs comprising the Devonian period, corresponding to the Lower Devonian series. It lasted from and began with the Lochkovian Stage , which was followed by the Pragian from and then by the Emsian, ...
, about 400 million years ago.[ The slightly older fossil '' Spongiophyton'' has also been interpreted as a lichen on morphological][ and isotopic][ grounds, although the isotopic basis is decidedly shaky.][ It has been demonstrated that Silurian- Devonian fossils '' Nematothallus'' and '' Prototaxites'' were lichenized. Thus lichenized Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were a component of Early Silurian- Devonian terrestrial ecosystems.][ Newer research suggests that lichen evolved after the evolution of land plants.
The ancestral ecological state of both Ascomycota and Basidiomycota was probably saprobism, and independent lichenization events may have occurred multiple times.][ In 1995, Gargas and colleagues proposed that there were at least five independent origins of lichenization; three in the basidiomycetes and at least two in the Ascomycetes.][ Lutzoni et al. (2001) suggest lichenization probably evolved earlier and was followed by multiple independent losses. Some non-lichen-forming fungi may have secondarily lost the ability to form a lichen association. As a result, lichenization has been viewed as a highly successful nutritional strategy.][
Lichenized Glomeromycota may extend well back into the Precambrian. Lichen-like fossils consisting of coccoid cells ( cyanobacteria?) and thin filaments (mucoromycotinan Glomeromycota?) are permineralized in marine phosphorite of the ]Doushantuo Formation
The Doushantuo Formation (formerly transcribed as Toushantuo or Toushantou, from ) is a geological formation in western Hubei, eastern Guizhou, southern Shaanxi, central Jiangxi, and other localities in China. It is known for the fossil Lagerst ...
in southern China. These fossils are thought to be 551 to 635 million years old or Ediacaran.[ Ediacaran ]acritarchs
Acritarchs are organic microfossils, known from approximately 1800 million years ago to the present. The classification is a catch all term used to refer to any organic microfossils that cannot be assigned to other groups. Their diversity refle ...
also have many similarities with Glomeromycotan vesicles and spores. It has also been claimed that Ediacaran fossils including '' Dickinsonia'',[ were lichens,][ although this claim is controversial.][ Endosymbiotic Glomeromycota comparable with living '' Geosiphon'' may extend back into the Proterozoic in the form of 1500 million year old '']Horodyskia
''Horodyskia'' is a fossilised organism found in rocks dated from to . Its shape has been described as a "string of beads" connected by a very fine thread. It is considered one of the oldest known eukaryotes.
Biology
Comparisons of differe ...
'' and 2200 million year old '' Diskagma''.
Ecology and interactions with environment
Substrates and habitats
 Lichens cover about 7% of the planet's surface and grow on and in a wide range of substrates and habitats, including some of the most extreme conditions on earth. They are abundant growing on bark, leaves, and hanging from epiphyte branches in
Lichens cover about 7% of the planet's surface and grow on and in a wide range of substrates and habitats, including some of the most extreme conditions on earth. They are abundant growing on bark, leaves, and hanging from epiphyte branches in rain forest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest ...
s and in temperate woodland. They grow on bare rock, walls, gravestones, roofs, and exposed soil surfaces. They can survive in some of the most extreme environments on Earth: arctic tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
, hot dry deserts, rocky coasts, and toxic slag heap
A spoil tip (also called a boney pile, culm bank, gob pile, waste tip or bing) is a pile built of accumulated ''spoil'' – waste material removed during mining. These waste materials are typically composed of shale, as well as smaller quan ...
s. They can live inside solid rock, growing between the grains, and in the soil as part of a biological soil crust in arid habitats such as deserts. Some lichens do not grow on anything, living out their lives blowing about the environment.[
When growing on mineral surfaces, some lichens slowly decompose their substrate by chemically degrading and physically disrupting the minerals, contributing to the process of ]weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement) ...
by which rocks are gradually turned into soil. While this contribution to weathering is usually benign, it can cause problems for artificial stone structures. For example, there is an ongoing lichen growth problem on Mount Rushmore National Memorial that requires the employment of mountain-climbing conservators to clean the monument.parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
on the plants they grow on, but only use them as a substrate. The fungi of some lichen species may "take over" the algae of other lichen species.[ Lichens growing on leaves may have the appearance of being parasites on the leaves, but they are not. Some lichens in ''Diploschistes'' parasitise other lichens. ''Diploschistes muscorum'' starts its development in the tissue of a host ''Cladonia'' species.][
In the arctic tundra, lichens, together with mosses and liverworts, make up the majority of the ]ground cover
Groundcover or ground cover is any plant that grows over an area of ground. Groundcover provides protection of the topsoil from erosion and drought.
In an ecosystem, the ground cover forms the layer of vegetation below the shrub layer known as ...
, which helps insulate the ground and may provide forage for grazing animals. An example is "Reindeer moss
''Cladonia rangiferina'', also known as reindeer cup lichen, reindeer lichen (cf. Sw. ''renlav'') or grey reindeer lichen, is a light-colored fruticose, cup lichen species in the family Cladoniaceae. It grows in both hot and cold climates in w ...
", which is a lichen, not a moss.[
There are only two species of known permanently submerged lichens; '' Hydrothyria venosa'' is found in fresh water environments, and '' Verrucaria serpuloides'' is found in marine environments.
A crustose lichen that grows on rock is called a '']saxicolous lichen
A saxicolous lichen is a lichen that grows on rock. The prefix "sax" from the Latin means "rock" or "stone".
Characteristics
Saxicolous lichens exhibit very slow growth rates. They may develop on rock substrates for long periods of time, give ...
''.[''Mosses Lichens & Ferns of Northwest North America'', Dale H. Vitt, Janet E. Marsh, Robin B. Bovey, Lone Pine Publishing Company, ] Crustose lichens that grow on the rock are epilithic, and those that grow immersed inside rock, growing between the crystals with only their fruiting bodies exposed to the air, are called '' endolithic lichens''.[ A crustose lichen that grows on bark is called a '' corticolous lichen''.][ A lichen that grows on wood from which the bark has been stripped is called a '' lignicolous lichen''.][ Lichens that use leaves as substrates, whether the leaf is still on the tree or on the ground, are called '' epiphyllous'' or '' foliicolous''.][ A '' terricolous lichen'' grows on the soil as a substrate. Many squamulous lichens are terricolous.][ '' Umbilicate lichens'' are foliose lichens that are attached to the substrate at only one point.]
Lichens and soils
In addition to distinct physical mechanisms by which lichens break down raw stone, recent studies indicate lichens attack stone chemically, entering newly chelated minerals into the ecology.The lichen exudates, which have powerful chelating capacity, the widespread occurrence of mineral neoformation, particularly metal oxalates, together with the characteristics of weathered substrates, all confirm the significance of lichens as chemical weathering agents.
Over time, this activity creates new fertile soil from lifeless stone.
Lichens may be important in contributing nitrogen to soils in some deserts through being eaten, along with their rock substrate, by snails, which then defecate, putting the nitrogen into the soils. Lichens help bind and stabilize soil sand in dunes.
Ecological interactions
Lichens are pioneer species
Pioneer species are hardy species that are the first to colonize barren environments or previously biodiverse steady-state ecosystems that have been disrupted, such as by wildfire.
Pioneer flora
Some lichens grow on rocks without soil, so ...
, among the first living things to grow on bare rock or areas denuded of life by a disaster.[ Lichens may have to compete with plants for access to sunlight, but because of their small size and slow growth, they thrive in places where higher plants have difficulty growing. Lichens are often the first to settle in places lacking soil, constituting the sole vegetation in some extreme environments such as those found at high mountain elevations and at high latitudes. Some survive in the tough conditions of deserts, and others on frozen soil of the Arctic regions.][
A major ecophysiological advantage of lichens is that they are ]poikilohydric
Poikilohydry is the lack of ability (structural or functional mechanism) to maintain and/or regulate water content to achieve homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis ( British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady i ...
(''poikilo''- variable, ''hydric''- relating to water), meaning that though they have little control over the status of their hydration, they can tolerate irregular and extended periods of severe desiccation. Like some mosses, liverworts, fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s and a few resurrection plants, upon desiccation, lichens enter a metabolic suspension or stasis (known as cryptobiosis) in which the cells of the lichen symbionts are dehydrated to a degree that halts most biochemical activity. In this cryptobiotic state, lichens can survive wider extremes of temperature, radiation and drought in the harsh environments they often inhabit.
 Lichens do not have roots and do not need to tap continuous reservoirs of water like most higher plants, thus they can grow in locations impossible for most plants, such as bare rock, sterile soil or sand, and various artificial structures such as walls, roofs, and monuments. Many lichens also grow as epiphytes (''epi''- on the surface, ''phyte''- plant) on plants, particularly on the trunks and branches of trees. When growing on plants, lichens are not
Lichens do not have roots and do not need to tap continuous reservoirs of water like most higher plants, thus they can grow in locations impossible for most plants, such as bare rock, sterile soil or sand, and various artificial structures such as walls, roofs, and monuments. Many lichens also grow as epiphytes (''epi''- on the surface, ''phyte''- plant) on plants, particularly on the trunks and branches of trees. When growing on plants, lichens are not parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s; they do not consume any part of the plant nor poison it. Lichens produce allelopathic chemicals that inhibit the growth of mosses. Some ground-dwelling lichens, such as members of the subgenus '' Cladina'' (reindeer lichens), produce allelopathic chemicals that leach into the soil and inhibit the germination of seeds, spruce and other plants. Stability (that is, longevity) of their substrate is a major factor of lichen habitats. Most lichens grow on stable rock surfaces or the bark of old trees, but many others grow on soil and sand. In these latter cases, lichens are often an important part of soil stabilization; indeed, in some desert ecosystems, vascular (higher) plant seeds cannot become established except in places where lichen crusts stabilize the sand and help retain water.
Lichens may be eaten by some animals, such as reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 sub ...
, living in arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
regions. The larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e of a number of Lepidoptera species feed exclusively on lichens. These include common footman and marbled beauty. They are very low in protein and high in carbohydrates, making them unsuitable for some animals. The Northern flying squirrel
The northern flying squirrel (''Glaucomys sabrinus'') is one of three species of the genus '' Glaucomys'', the only flying squirrels found in North America.Walker EP, Paradiso JL. 1975. ''Mammals of the World''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Universit ...
uses it for nesting, food and winter water.
Effects of air pollution
 If lichens are exposed to air pollutants at all times, without any
If lichens are exposed to air pollutants at all times, without any deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
parts, they are unable to avoid the accumulation of pollutants. Also lacking stomata and a cuticle, lichens may absorb aerosols and gases over the entire thallus surface from which they may readily diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
to the photobiont layer.[ Because lichens do not possess roots, their primary source of most elements is the air, and therefore elemental levels in lichens often reflect the accumulated composition of ambient air. The processes by which atmospheric deposition occurs include fog and dew, gaseous absorption, and dry deposition.][ Consequently, many environmental studies with lichens emphasize their feasibility as effective biomonitors of atmospheric quality.][
Not all lichens are equally sensitive to air pollutants, so different lichen species show different levels of sensitivity to specific atmospheric pollutants.][ Upon exposure to air pollution, the photobiont may use metabolic energy for repair of its cellular structures that would otherwise be used for maintenance of its photosynthetic activity, therefore leaving less metabolic energy available for the mycobiont. The alteration of the balance between the photobiont and mycobiont can lead to the breakdown of the symbiotic association. Therefore, lichen decline may result not only from the accumulation of toxic substances, but also from altered nutrient supplies that favor one symbiont over the other.][
This interaction between lichens and air pollution has been used as a means of monitoring air quality since 1859, with more systematic methods developed by ]William Nylander
William Andrew Michael Junior Nylander Altelius (born 1 May 1996) is a Canadian-born Swedish professional ice hockey right winger for the Toronto Maple Leafs of the National Hockey League (NHL). Nylander was selected by the Maple Leafs in th ...
in 1866.[
]
Human use

Food
Lichens are eaten by many different cultures across the world. Although some lichens are only eaten in times of famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
, others are a staple food or even a delicacy
A delicacy is usually a rare and expensive food item that is considered highly desirable, sophisticated, or peculiarly distinctive within a given culture. Irrespective of local preferences, such a label is typically pervasive throughout a r ...
. Two obstacles are often encountered when eating lichens: lichen polysaccharides are generally indigestible to humans, and lichens usually contain mildly toxic secondary compounds that should be removed before eating. Very few lichens are poisonous, but those high in vulpinic acid or usnic acid are toxic.Iceland moss
''Cetraria islandica'', also known as true Iceland lichen or Iceland moss, is an Arctic-alpine lichen whose erect or upright, leaflike habit gives it the appearance of a moss, where its name likely comes from.
Description
It is often of a pale ...
(''Cetraria islandica'') was an important source of food for humans in northern Europe, and was cooked as a bread, porridge, pudding, soup, or salad. '' Bryoria fremontii'' (edible horsehair lichen) was an important food in parts of North America, where it was usually pitcooked. Northern peoples in North America and Siberia traditionally eat the partially digested reindeer lichen (''Cladina'' spp.) after they remove it from the rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment al ...
of caribou or reindeer that have been killed. Rock tripe
Rock tripe is the common name for various lichens of the genus ''Umbilicaria'' that grow on rocks. They are widely distributed, including on bare rock in Antarctica, and throughout northern parts of North America such as New England and the Ro ...
(''Umbilicaria'' spp. and ''Lasalia'' spp.) is a lichen that has frequently been used as an emergency food in North America, and one species, ''Umbilicaria esculenta
''Umbilicaria esculenta'' is a lichen of the genus ''Umbilicaria'' that grows on rocks, also known as rock tripe. It can be found in East Asia including in China, Japan, and Korea. It is edible when properly prepared and has been used as a fo ...
'', (''iwatake'' in Japanese) is used in a variety of traditional Korean and Japanese foods.
Lichenometry

 Lichenometry is a technique used to determine the age of exposed rock surfaces based on the size of lichen thalli. Introduced by Beschel in the 1950s,
Lichenometry is a technique used to determine the age of exposed rock surfaces based on the size of lichen thalli. Introduced by Beschel in the 1950s,[ the technique has found many applications. it is used in ]archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsca ...
, palaeontology, and geomorphology. It uses the presumed regular but slow rate of lichen growth to determine the age of exposed rock.[ Measuring the diameter (or other size measurement) of the largest lichen of a species on a rock surface indicates the length of time since the rock surface was first exposed. Lichen can be preserved on old rock faces for up to 10,000 years, providing the maximum age limit of the technique, though it is most accurate (within 10% error) when applied to surfaces that have been exposed for less than 1,000 years. Lichenometry is especially useful for dating surfaces less than 500 years old, as radiocarbon dating techniques are less accurate over this period.]Rhizocarpon
''Rhizocarpon'' is a genus of crustose, saxicolous (or sometimes lichenicolous), lichens in the family Rhizocarpaceae. The genus is common in arctic-alpine environments, but also occurs throughout temperate, subtropical, and even tropical regio ...
'' (e.g. the species ''Rhizocarpon geographicum
''Rhizocarpon geographicum'' (the map lichen) is a species of lichen, which grows on rocks in mountainous areas of low air pollution. Each lichen is a flat patch bordered by a black line of fungal hyphae. These patches grow adjacent to each other ...
'', map lichen) and ''Xanthoria
''Xanthoria'' is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Teloschistaceae. Common names include orange lichen,[polyester resin Polyester resins are synthetic resins formed by the reaction of dibasic organic acids and polyhydric alcohols. Maleic anhydride is a commonly used raw material with diacid functionality in unsaturated polyester resins. Unsaturated polyester res ...]
s, as can be seen in archaeological sites in the Roman city of Baelo Claudia
Baelo Claudia was an ancient Roman town of Hispania, located outside of Tarifa, near the village of Bolonia, in southern Spain. Lying on the shores of the Strait of Gibraltar, the town was originally a fishing village and trade link when it was ...
in Spain. Lichens can accumulate several environmental pollutants such as lead, copper, and radionuclides.Parmelia sulcata
''Parmelia sulcata'' is a foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is very tolerant of pollution and has a cosmopolitan distribution, making it one of the most common lichens. It harbours a unicellular '' Trebouxia'' green algal symbiont.
...
'' (called a hammered shield lichen, among other names) and '' Lobaria pulmonaria'' (lung lichen), and many in the ''Cladonia'' genus, have been shown to produce serine protease
Serine proteases (or serine endopeptidases) are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site.
They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Seri ...
s capable of the degradation of pathogenic forms of prion protein
Major prion protein (PrP), is encoded in the human by the ''PRNP'' gene also known as CD230 (cluster of differentiation 230). Expression of the protein is most predominant in the nervous system but occurs in many other tissues throughout the bod ...
(PrP), which may be useful in treating contaminated environmental reservoirs.
Dyes
Many lichens produce secondary compounds, including pigments
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compoun ...
that reduce harmful amounts of sunlight and powerful toxins that deter herbivores or kill bacteria. These compounds are very useful for lichen identification, and have had economic importance as dyes such as cudbear or primitive antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
.
A pH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties. Hence, ...
(which can indicate acidic or basic substances) called litmus
Litmus is a water-soluble mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator, used to test materials for acidity. It is a purple dye that is extracted fro ...
is a dye extracted from the lichen ''Roccella tinctoria
''Roccella tinctoria'' is a lichenised species of fungus in the genus ''Roccella'', homotypic synonym of ''Lecanora tinctoria'' (DC.) Czerwiak., 1849. It was first described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805. It has the following varietie ...
'' ("dyer's weed") by boiling. It gives its name to the well-known litmus test.
Traditional dyes of the Scottish Highlands for Harris tweed[ and other traditional cloths were made from lichens, including the orange '']Xanthoria parietina
''Xanthoria parietina'' is a foliose lichen in the family Teloschistaceae. It has wide distribution, and many common names such as common orange lichen, yellow scale, maritime sunburst lichen and shore lichen. It can be found near the shore on ...
'' ("common orange lichen") and the grey foliaceous '' Parmelia saxatilis'' common on rocks and known colloquially as "crottle".
There are reports dating almost 2,000 years old of lichens being used to make purple and red dyes.[ Of great historical and commercial significance are lichens belonging to the family '']Roccellaceae
The Roccellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Arthoniomycetes. Most taxa are lichenized with green algae, although some are lichenicolous, growing on other lichens.
Genera
, Species Fungorum (in the Catalogue of Life) accepts 47 genera ...
'', commonly called orchella weed or orchil. Orcein
Orcein, also archil, orchil, lacmus and C.I. Natural Red 28, are names for dyes extracted from several species of lichen, commonly known as "orchella weeds", found in various parts of the world. A major source is the archil lichen, '' Roccella tinc ...
and other lichen dyes have largely been replaced by synthetic versions.
Traditional medicine and research
Historically, in traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
of Europe, '' Lobaria pulmonaria'' was collected in large quantities as "lungwort", due to its lung-like appearance (the "doctrine of signatures
The doctrine of signatures, dating from the time of Dioscorides and Galen, states that herbs resembling various parts of the body can be used by herbalists to treat ailments of those body parts. A theological justification, as stated by botanist ...
" suggesting that herbs can treat body parts that they physically resemble). Similarly, '' Peltigera leucophlebia'' ("ruffled freckled pelt") was used as a supposed cure for thrush, due to the resemblance of its cephalodia to the appearance of the disease.[
Lichens produce metabolites being researched for their potential therapeutic or diagnostic value. Some metabolites produced by lichens are structurally and functionally similar to ]broad-spectrum antibiotics
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial i ...
while few are associated respectively to antiseptic similarities.[Morton, E.; Winters, J. and Smith, L. (2010)]
"An Analysis of Antiseptic and Antibiotic Properties of Variously Treated Mosses and Lichens"
. University of Michigan Biological Station Usnic acid is the most commonly studied metabolite produced by lichens.[ It is also under research as a bactericidal agent against '']Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' and '' Staphylococcus aureus''.
Aesthetic appeal
 Colonies of lichens may be spectacular in appearance, dominating the surface of the visual landscape as part of the aesthetic appeal to visitors of
Colonies of lichens may be spectacular in appearance, dominating the surface of the visual landscape as part of the aesthetic appeal to visitors of Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park ( ) is an American national park in California, surrounded on the southeast by Sierra National Forest and on the northwest by Stanislaus National Forest. The park is managed by the National Park Service and covers an ...
, Sequoia National Park
Sequoia National Park is an American national park in the southern Sierra Nevada east of Visalia, California. The park was established on September 25, 1890, and today protects of forested mountainous terrain. Encompassing a vertical relief ...
, and the Bay of Fires.[ ]Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
and yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the ...
lichens add to the ambience of desert trees, tundras, and rocky seashores. Intricate webs of lichens hanging from tree branches add a mysterious aspect to forests. Fruticose lichens are used in model railroading
Railway modelling (UK, Australia, New Zealand, and Ireland) or model railroading (US and Canada) is a hobby in which rail transport systems are modelled at a reduced scale.
The scale models include locomotives, rolling stock, streetcars, t ...
and other modeling hobbies as a material for making miniature trees and shrubs.
In literature
In early Midrashic
''Midrash'' (;["midrash"]
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
literature, the Hebrew word "''vayilafeth''" in Ruth
Ruth (or its variants) may refer to:
Places
France
* Château de Ruthie, castle in the commune of Aussurucq in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques département of France
Switzerland
* Ruth, a hamlet in Cologny
United States
* Ruth, Alabama
* Ruth, Ar ...
3:8 is explained as referring to Ruth
Ruth (or its variants) may refer to:
Places
France
* Château de Ruthie, castle in the commune of Aussurucq in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques département of France
Switzerland
* Ruth, a hamlet in Cologny
United States
* Ruth, Alabama
* Ruth, Ar ...
entwining herself around Boaz
Boaz (; Hebrew: בֹּעַז ''Bōʿaz''; ) is a biblical figure appearing in the Book of Ruth in the Hebrew Bible and in the genealogies of Jesus in the New Testament and also the name of a pillar in the portico of the historic Temple in J ...
like lichen. The 10th century Arab physician, Al-Tamimi, mentions lichens dissolved in vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting simple sugars to eth ...
and rose water
Rose water ( fa, گلاب) is a flavoured water made by steeping rose petals in water. It is the hydrosol portion of the distillate of rose petals, a by-product of the production of rose oil for use in perfume. Rose water is also used to fla ...
being used in his day for the treatment of skin diseases and rashes.
The plot of John Wyndham
John Wyndham Parkes Lucas Beynon Harris (; 10 July 1903 – 11 March 1969) was an English science fiction writer best known for his works published under the pen name John Wyndham, although he also used other combinations of his names ...
's science fiction novel '' Trouble with Lichen'' revolves around an anti-aging chemical extracted from a lichen.
History
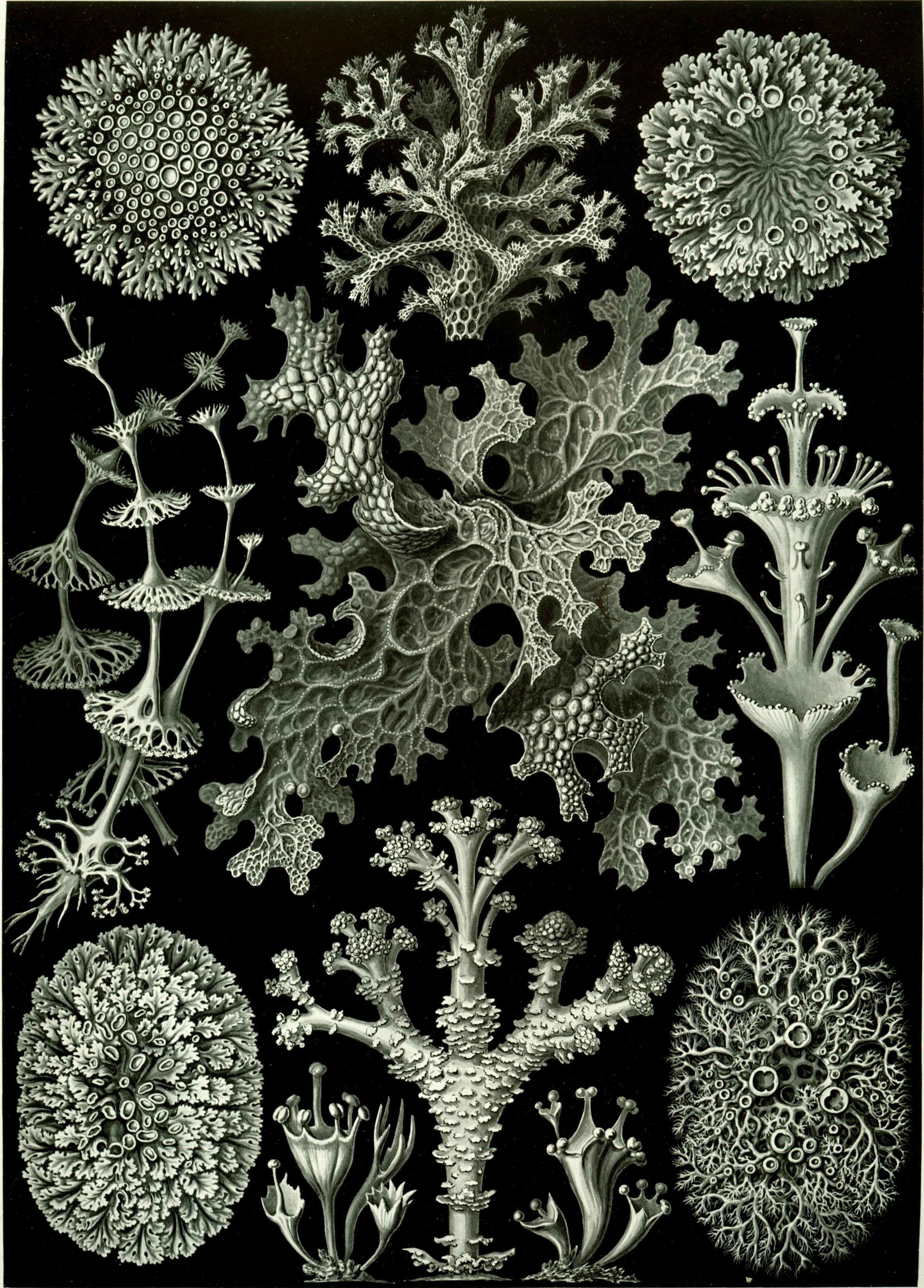 Although lichens had been recognized as organisms for quite some time, it was not until 1867, when Swiss botanist Simon Schwendener proposed his dual theory of lichens, that lichens are a combination of fungi with algae or cyanobacteria, whereby the true nature of the lichen association began to emerge.
Although lichens had been recognized as organisms for quite some time, it was not until 1867, when Swiss botanist Simon Schwendener proposed his dual theory of lichens, that lichens are a combination of fungi with algae or cyanobacteria, whereby the true nature of the lichen association began to emerge.[ Schwendener's hypothesis, which at the time lacked experimental evidence, arose from his extensive analysis of the anatomy and development in lichens, algae, and fungi using a light microscope. Many of the leading lichenologists at the time, such as James Crombie and Nylander, rejected Schwendener's hypothesis because the common consensus was that all living organisms were autonomous.][
Other prominent biologists, such as ]Heinrich Anton de Bary
Heinrich Anton de Bary (26 January 183119 January 1888) was a German surgeon, botanist, microbiologist, and mycologist (fungal systematics and physiology).
He is considered a founding father of plant pathology (phytopathology) as well as the fou ...
, Albert Bernhard Frank
Albert Bernhard Frank (January 17, 1839 – September 27, 1900) was a German botanist, plant pathologist, and mycologist, born in Dresden. He is credited with coining the term ''mycorrhiza'' in his 1885 paper "Über die auf Wurzelsymbiose beruhen ...
, Beatrix Potter
Helen Beatrix Potter (, 28 July 186622 December 1943) was an English writer, illustrator, natural scientist, and conservationist. She is best known for her children's books featuring animals, such as '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'', which was ...
, Melchior Treub
Melchior Treub (26 December 1851 – 3 October 1910) was a Dutch botanist. He worked at the Bogor Botanical Gardens in Buitenzorg on the island of Java, south of Batavia, Dutch East Indies, gaining renown for his work on tropical flora. He also f ...
and Hermann Hellriegel were not so quick to reject Schwendener's ideas and the concept soon spread into other areas of study, such as microbial, plant, animal and human pathogens.[
In the 2010s, a new facet of the fungi-algae partnership was discovered. Toby Spribille and colleagues found that many types of lichen that were long thought to be ascomycete-algae pairs were actually ascomycete- basidiomycete-algae trios.]
Gallery
Lobaria pulmonaria 01.JPG, '' Lobaria pulmonaria'', tree lungwort, lung lichen, lung moss; Upper Bavaria, Germany
Cladonia macilenta 9497.JPG, '' Cladonia macilenta'' var. ''bacillaris'' 'Lipstick Cladonia'
Usnea australis.jpg, '' Usnea australis'', a fruticose form, growing on a tree branch
Kananakislichen.jpg, ''Hypogymnia'' cf. ''tubulosa'' with ''Bryoria'' sp. and ''Tuckermannopsis'' sp. in the Canadian Rockies
Fruticose lichen branches blackpine lake.jpg, ''Letharia'' sp. with ''Bryoria'' sp. on pine branches near Blackpine Lake, Washington State
Lettucelichen.jpg, '' Lobaria oregana'', commonly called 'Lettuce lichen', in the Hoh Rainforest, Washington State
Epiphytic lichen.jpg, A lichen growing on a rock in a Brazilian cloud forest
Lichen squamulose.jpg, '' Xanthoparmelia'' cf. ''lavicola,'' a foliose lichen, on basalt.
Rhizocarpon geographicum01.jpg, Map lichen (''Rhizocarpon geographicum
''Rhizocarpon geographicum'' (the map lichen) is a species of lichen, which grows on rocks in mountainous areas of low air pollution. Each lichen is a flat patch bordered by a black line of fungal hyphae. These patches grow adjacent to each other ...
'') on rock
LogLichen.jpg, ''Physcia millegrana'' (a foliose lichen), with an unlichenized polypore fungus (bottom right), on a fallen log.
caribou moss.jpg, Reindeer moss
''Cladonia rangiferina'', also known as reindeer cup lichen, reindeer lichen (cf. Sw. ''renlav'') or grey reindeer lichen, is a light-colored fruticose, cup lichen species in the family Cladoniaceae. It grows in both hot and cold climates in w ...
(''Cladonia rangiferina'')
Lichenlimestone.JPG, Crustose lichens on limestone in Alta Murgia-Southern Italy
Plants flowers ice rocks lichens 209.jpg, ''Cladonia'' cf. ''cristatella,'' a lichen commonly referred to as 'British Soldiers'. Notice the red tips.
N2 Lichen.jpg, A crusty crustose lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cor ...
on a wall
Lichen on Lilac bush.JPG, Lichen on a lilac bush
Plants flowers ice rocks lichens 230.jpg, Foliose lichens on rock growing outward and dying in the center. These lichens are at least several decades old.
Reddish-colored lichen on volcanic rock.jpg, ''Xanthoria'' sp. lichen on volcanic rock in Craters of the Moon National Monument (Idaho, USA)
Lichen on the riverside.jpg, ''Lecanora'' cf. ''muralis'' lichen on the banks of the Bega canal in Timișoara
), City of Roses ( ro, Orașul florilor), City of Parks ( ro, Orașul parcurilor)
, image_map = Timisoara jud Timis.svg
, map_caption = Location in Timiș County
, pushpin_map = Romania#Europe
, pushpin_ ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
Lichen growing on concrete dust (2010 04 08).jpg, Microscopic view of lichen growing on a piece of concrete dust.
See also
* Lichenology
Lichenology is the branch of mycology that studies the lichens, symbiotic organisms made up of an intimate symbiotic association of a microscopic alga (or a cyanobacterium) with a filamentous fungus.
Study of lichens draws knowledge from several ...
* Lichens and nitrogen cycling Some types of lichen are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere. This process relies on the presence of cyanobacteria as a partner species within the lichen. The ability to fix nitrogen enables lichen to live in nutrient-poor environments. Lichen ...
* Outline of lichens
* Symbiosis in lichens
Notes
References
Further reading
* Jorgensen, Per M., and Lücking, Robert (April 2018)
"The 'Rustici Pauperrimi': A Linnaean Myth about Lichens Rectified"
''The Linnean'' 34(1), pp. 9–12.
{{Authority control
Cryptogams
Polyextremophiles
Oligotrophs
Bioindicators
Mycology
Symbiosis
 A lichen ( , ) is a composite
A lichen ( , ) is a composite  A lichen consists of a simple photosynthesizing organism, usually a green alga or
A lichen consists of a simple photosynthesizing organism, usually a green alga or  Many lichens reproduce asexually, either by a piece breaking off and growing on its own (
Many lichens reproduce asexually, either by a piece breaking off and growing on its own ( Structures involved in reproduction often appear as discs, bumps, or squiggly lines on the surface of the thallus. Though it has been argued that sexual reproduction in photobionts is selected against, there is strong evidence that suggests meiotic activities (sexual reproduction) in ''Trebouxia''. Many lichen fungi reproduce sexually like other fungi, producing spores formed by
Structures involved in reproduction often appear as discs, bumps, or squiggly lines on the surface of the thallus. Though it has been argued that sexual reproduction in photobionts is selected against, there is strong evidence that suggests meiotic activities (sexual reproduction) in ''Trebouxia''. Many lichen fungi reproduce sexually like other fungi, producing spores formed by  A "
A " Lichens cover about 7% of the planet's surface and grow on and in a wide range of substrates and habitats, including some of the most extreme conditions on earth. They are abundant growing on bark, leaves, and hanging from epiphyte branches in
Lichens cover about 7% of the planet's surface and grow on and in a wide range of substrates and habitats, including some of the most extreme conditions on earth. They are abundant growing on bark, leaves, and hanging from epiphyte branches in  Lichens do not have roots and do not need to tap continuous reservoirs of water like most higher plants, thus they can grow in locations impossible for most plants, such as bare rock, sterile soil or sand, and various artificial structures such as walls, roofs, and monuments. Many lichens also grow as epiphytes (''epi''- on the surface, ''phyte''- plant) on plants, particularly on the trunks and branches of trees. When growing on plants, lichens are not
Lichens do not have roots and do not need to tap continuous reservoirs of water like most higher plants, thus they can grow in locations impossible for most plants, such as bare rock, sterile soil or sand, and various artificial structures such as walls, roofs, and monuments. Many lichens also grow as epiphytes (''epi''- on the surface, ''phyte''- plant) on plants, particularly on the trunks and branches of trees. When growing on plants, lichens are not  If lichens are exposed to air pollutants at all times, without any
If lichens are exposed to air pollutants at all times, without any 

 Lichenometry is a technique used to determine the age of exposed rock surfaces based on the size of lichen thalli. Introduced by Beschel in the 1950s, the technique has found many applications. it is used in
Lichenometry is a technique used to determine the age of exposed rock surfaces based on the size of lichen thalli. Introduced by Beschel in the 1950s, the technique has found many applications. it is used in  Colonies of lichens may be spectacular in appearance, dominating the surface of the visual landscape as part of the aesthetic appeal to visitors of
Colonies of lichens may be spectacular in appearance, dominating the surface of the visual landscape as part of the aesthetic appeal to visitors of  Although lichens had been recognized as organisms for quite some time, it was not until 1867, when Swiss botanist Simon Schwendener proposed his dual theory of lichens, that lichens are a combination of fungi with algae or cyanobacteria, whereby the true nature of the lichen association began to emerge. Schwendener's hypothesis, which at the time lacked experimental evidence, arose from his extensive analysis of the anatomy and development in lichens, algae, and fungi using a light microscope. Many of the leading lichenologists at the time, such as James Crombie and Nylander, rejected Schwendener's hypothesis because the common consensus was that all living organisms were autonomous.
Other prominent biologists, such as
Although lichens had been recognized as organisms for quite some time, it was not until 1867, when Swiss botanist Simon Schwendener proposed his dual theory of lichens, that lichens are a combination of fungi with algae or cyanobacteria, whereby the true nature of the lichen association began to emerge. Schwendener's hypothesis, which at the time lacked experimental evidence, arose from his extensive analysis of the anatomy and development in lichens, algae, and fungi using a light microscope. Many of the leading lichenologists at the time, such as James Crombie and Nylander, rejected Schwendener's hypothesis because the common consensus was that all living organisms were autonomous.
Other prominent biologists, such as