|
Climate Change And Civilizational Collapse
Climate change and civilizational collapse refers to a hypothetical risk that the negative impacts of climate change might reduce global socioeconomic complexity to the point that complex human civilization effectively ends around the world, with humanity reduced to a less developed state. This hypothetical risk is typically associated with the idea of a massive reduction of human population caused by the direct and indirect impacts of climate change, and also with a permanent reduction of Earth's carrying capacity. Finally, it is sometimes suggested that a civilizational collapse caused by climate change would soon be followed by human extinction. Some researchers connect historical examples of societal collapse with adverse changes in local and/or global weather patterns. In particular, the 4.2-kiloyear event, a millennial-scale megadrought which took place in Africa and Asia between 5,000 and 4,000 years ago, has been linked with the collapse of the Old Kingdom in Egypt, the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Of Climate Change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an Instrumental temperature record, overall warming trend, Effects of climate change on the water cycle, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather. As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification. These changes impact ecosystems and societies, and can become irreversible once Tipping points in the climate system, tipping points are crossed. Climate activists are engaged in a range of activities around the world that seek to ameliorate these issues or prevent them from happening. The effects of climate change vary in timing and location. Up until now the polar amplification, Arctic has warmed faster than most other regions due to climate change feedbacks. Surface air temperatures over land have also increased at ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liangzhu Culture
The Liangzhu () culture or civilization (3300–2300 BC) was the last Chinese Neolithic jade culture in the Yangtze River Delta. The culture was highly stratified, as jade, silk, ivory and lacquer artifacts were found exclusively in elite burials, while pottery was more commonly found in the burial plots of poorer individuals. This division of class indicates that the Liangzhu period was an early state, symbolized by the clear distinction drawn between social classes in funeral structures. A pan-regional urban center had emerged at the Liangzhu site in northwestern Hangzhou, Zhejiang, and elite groups from this site presided over the local centers. The Liangzhu culture was extremely influential and its sphere of influence reached as far north as Shanxi and as far south as Guangdong. The primary Liangzhu site was perhaps among the oldest Neolithic sites in East Asia that would be considered a state society. The type site at Liangzhu was discovered in Yuhang County, Zhejiang and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Uninhabitable Earth
"The Uninhabitable Earth" is an article by American journalist David Wallace-Wells published in the July 10, 2017, issue of ''New York (magazine), New York'' magazine. The Long-form journalism, long-form article depicts a worst-case scenario of what might happen in the near-future due to global warming. The story was the most-read article in the history of the magazine. The article became the inspiration for ''The Uninhabitable Earth (book), The Uninhabitable Earth: Life After Warming'', a book-length treatment of the ideas explored in the original essay. Paperback version. Content The article opens with a warning:[Global warming] is, I promise, worse than you think. If your anxiety about global warming is dominated by fears of sea level rise, you are barely scratching the surface of what terrors are possible, even within the lifetime of a teenager today. And yet the swelling seas — and the cities they will drown — have so dominated the picture of global warming, and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Scientist
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "slope"; and , ''-logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospheric condition during an extended to indefinite period of time; weather is the condition of the atmosphere during a relative brief period of time. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. This topic of study is regarded as part of the atmospheric sciences and a subdivision of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology includes some aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry. The main methods employed by climatologists are the analysis of observations and modelling of the physical processes that determine climate. Short term weather forecasting can be interpreted in terms of knowledge of longer-term phenomena of climate, for instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Output (economics), output of an economy in a given year or over a period of time. The rate of growth is typically calculated as List of countries by real GDP growth rate, real gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate, List of countries by real GDP per capita growth, real GDP per capita growth rate or List of countries by GNI per capita growth, GNI per capita growth. The "rate" of economic growth refers to the Exponential growth, geometric annual rate of growth in GDP or GDP per capita between the first and the last year over a period of time. This growth rate represents the trend in the average level of GDP over the period, and ignores any fluctuations in the GDP around this trend. Growth is usually calculated in "real" value, which is real v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, and III) covered the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report was finished in March 2023. It includes a summary for policymakers and was the basis for the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai. The first of the three working groups published its report on 9 August 2021, ''Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis''.IPCC, 2021Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
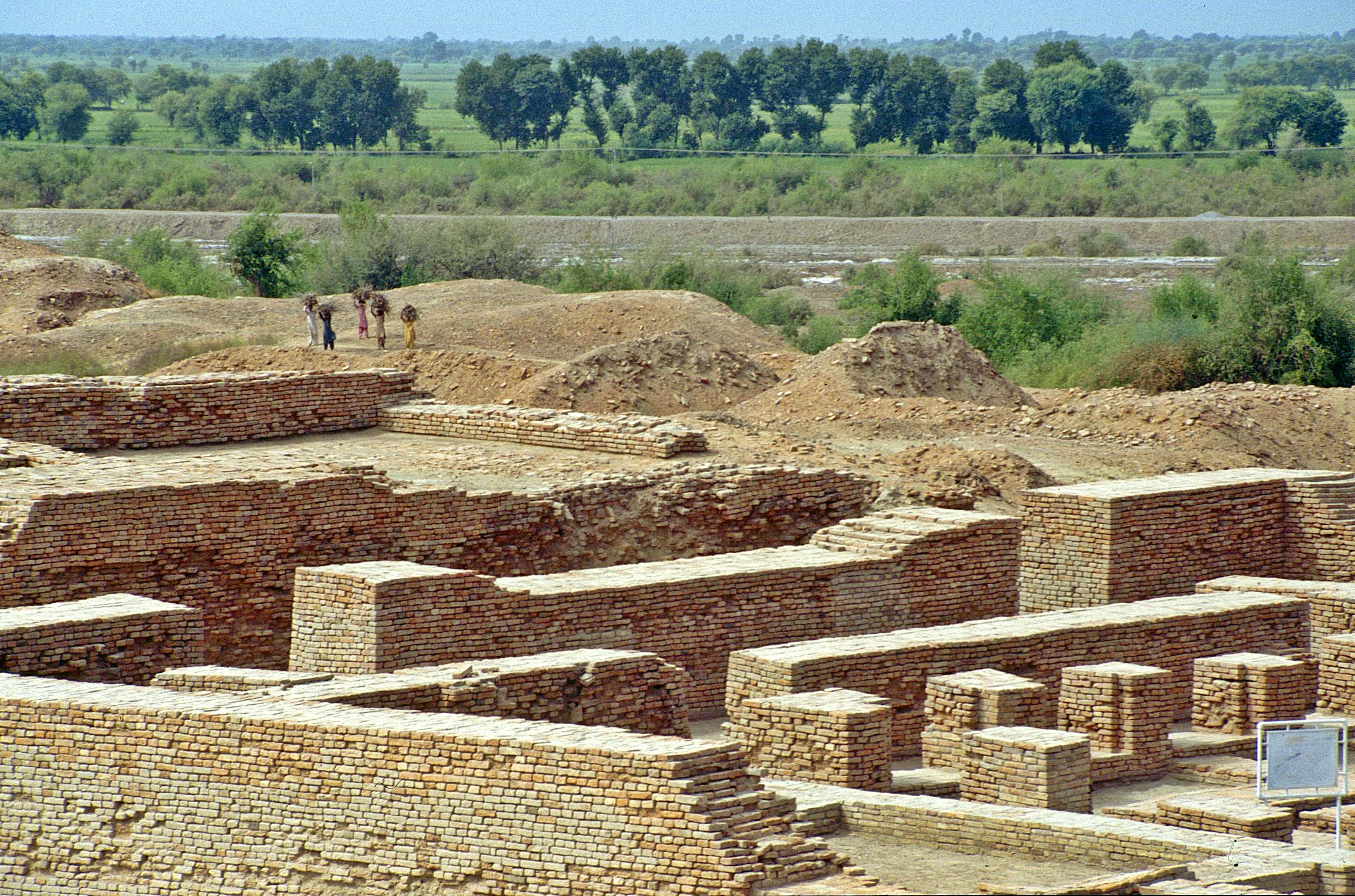
Classic Maya Collapse
In archaeology, the classic Maya collapse was the destabilization of Classic Maya civilization and the violent collapse and abandonment of many southern lowlands city-states between the 7th and 9th centuries CE. Not all Mayan city-states collapsed, but there was a period of instability for the cities that survived. At Ceibal, the Preclassic Maya experienced a similar collapse in the 2nd century. The Classic Period of Mesoamerican chronology is generally defined as the period from 250 to 900 CE, the last century of which is referred to as the Terminal Classic. The Classic Maya collapse is one of the greatest unsolved mysteries in archaeology. Urban centers of the southern lowlands, among them Palenque, Copán, Tikal, and Calakmul, went into decline during the 8th and 9th centuries and were abandoned shortly thereafter. Archaeologically, this decline is indicated by the cessation of monumental inscriptions and the reduction of large-scale architectural construction at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Matthes described glaciers in the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada of California that he believed could not have survived the hypsithermal; his usage of "Little Ice Age" has been superseded by "Neoglaciation". The period has been conventionally defined as extending from the 16th to the 19th centuries, (noted in Grove 2004: 4). but some experts prefer an alternative time-span from about 1300 to about 1850. The NASA Earth Observatory notes three particularly cold intervals. One began about 1650, another about 1770, and the last in 1850, all of which were separated by intervals of slight warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC Third Assessment Report, Third Assessment Report considered that the timing and the areas affecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Failure
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulses for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor-intensive activity of the growing season. On large mechanized farms, harvesting uses farm machinery, such as the combine harvester. Automation has increased the efficiency of both the seeding and harvesting processes. Specialized harvesting equipment, using conveyor belts for gentle gripping and mass transport, replaces the manual task of removing each seedling by hand. The term "harvesting" in general usage may include immediate postharvest handling, including cleaning, sorting, packing, and cooling. The completion of harvesting marks the end of the growing season, or the growing cycle for a particular cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The General Crisis
The General Crisis is a term used by some historians to describe an alleged period of widespread regional conflict and instability that occurred from the early 17th century to the early 18th century in Europe, and in more recent historiography in the world at large. The concept of a general 17th-century crisis was by 1990 thought by historian Niels Steensgaard to be part of a superseded historiographic debate lasting from 1954 to 1978. Definitions and debates Since the mid-20th century, some scholars have proposed widely different definitions, causes, events, periodisations and geographical applications of a 'General Crisis', disagreeing with each other in debates. Other scholars have rejected the various concepts of a General Crisis altogether, claiming there was no such generalised phenomenon connecting various events due to a lack of linkeages between the events and widely shared commonalities in their character, and that generalised historical concepts such as the 'Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |