Drought on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021
Water Cycle Changes
In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often exerts substantial impacts on the
 The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to National Integrated Drought Information System, a multi-agency partnership, drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage”. The National Weather Service office of the NOAA defines drought as "a deficiency of moisture that results in adverse impacts on people, animals, or vegetation over a sizeable area".
Drought is a complex phenomenon − relating to the absence of water − which is difficult to monitor and define. By the early 1980's, over 150 definitions of "drought" had already been published. The range of definitions reflects differences in regions, needs, and disciplinary approaches.
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to National Integrated Drought Information System, a multi-agency partnership, drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage”. The National Weather Service office of the NOAA defines drought as "a deficiency of moisture that results in adverse impacts on people, animals, or vegetation over a sizeable area".
Drought is a complex phenomenon − relating to the absence of water − which is difficult to monitor and define. By the early 1980's, over 150 definitions of "drought" had already been published. The range of definitions reflects differences in regions, needs, and disciplinary approaches.
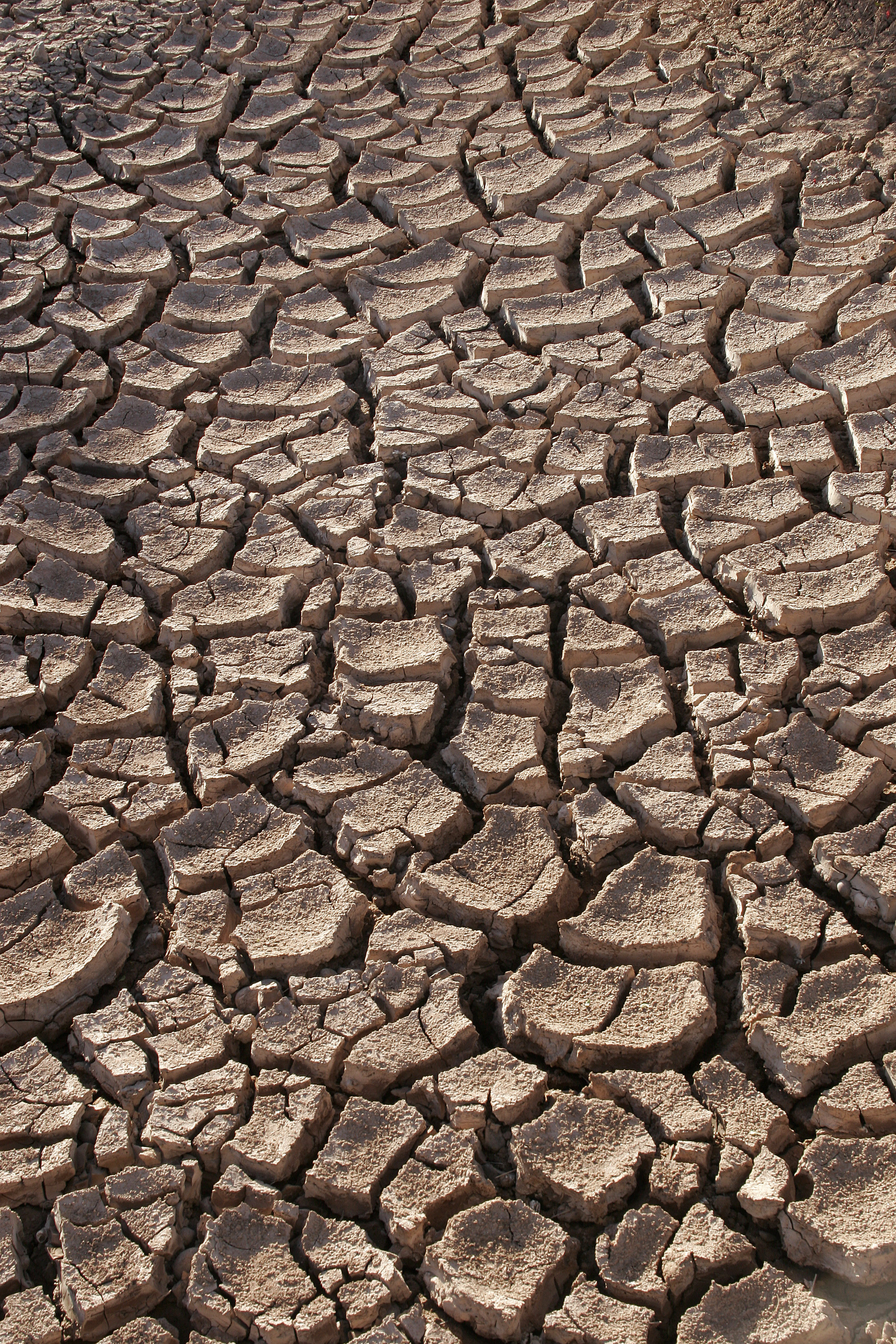

 The
The 
2 August 2007 New Scientist, Catherine Brahic There is a rise of compound warm-season droughts in Europe that are concurrent with an increase in potential evapotranspiration.


 One can divide the effects of droughts and water shortages into three groups: environmental, economic and social (including health).
* In the case of environmental effects: lower surface and subterranean water-levels, lower flow-levels (with a decrease below the minimum leading to direct danger for amphibian life), increased pollution of surface water, the drying out of wetlands, more and larger
One can divide the effects of droughts and water shortages into three groups: environmental, economic and social (including health).
* In the case of environmental effects: lower surface and subterranean water-levels, lower flow-levels (with a decrease below the minimum leading to direct danger for amphibian life), increased pollution of surface water, the drying out of wetlands, more and larger

 Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the
Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the
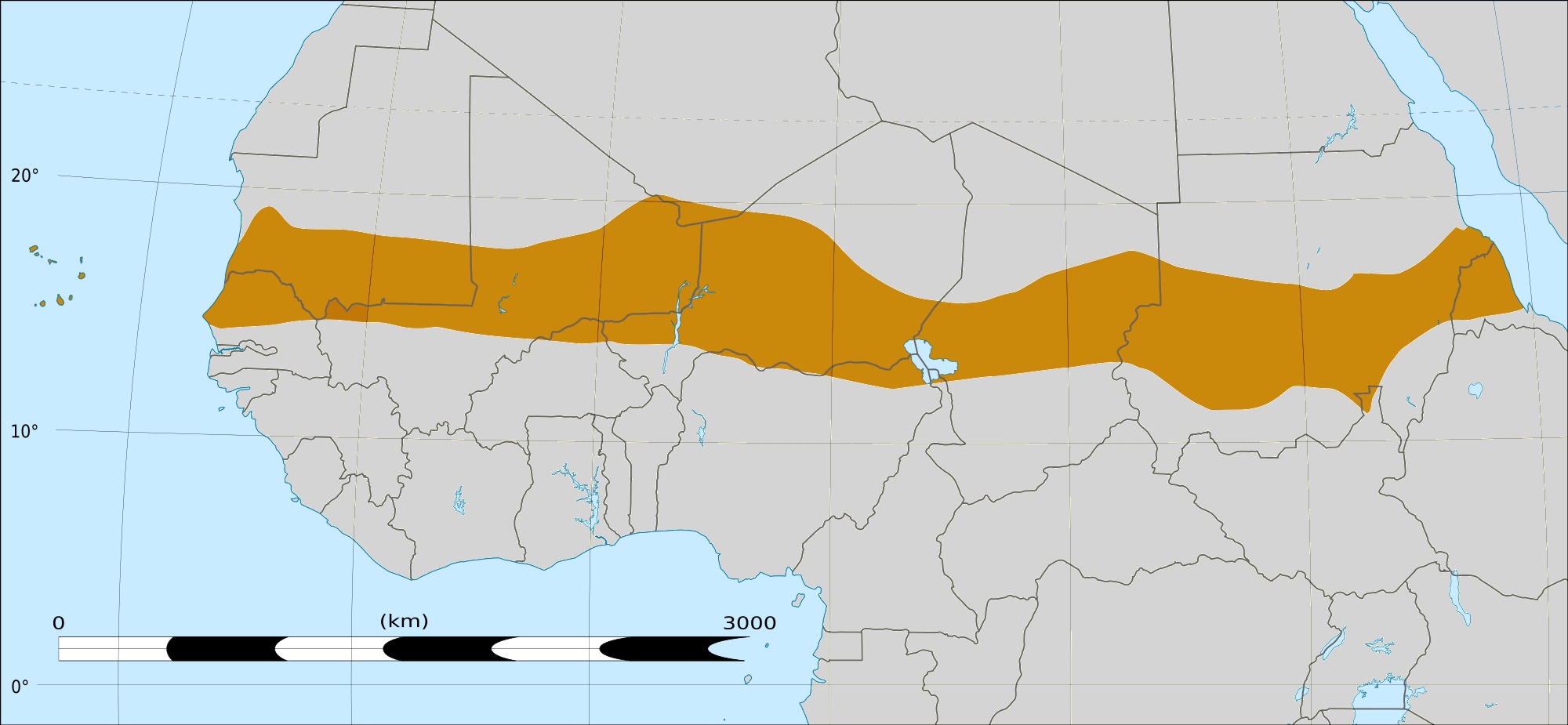 The Darfur conflict in Sudan, also affecting Chad, was fueled by decades of drought; combination of drought, desertification and overpopulation are among the causes of the Darfur conflict, because the Arab
The Darfur conflict in Sudan, also affecting Chad, was fueled by decades of drought; combination of drought, desertification and overpopulation are among the causes of the Darfur conflict, because the Arab  Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the
Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the 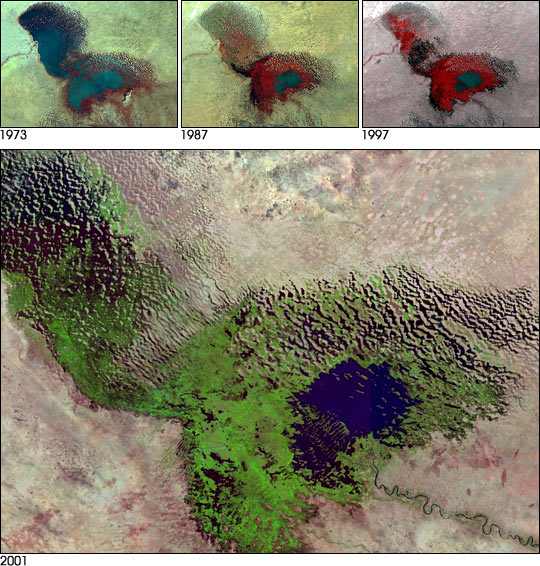 By far the largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid lands commonly known as the outback. A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to
By far the largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid lands commonly known as the outback. A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to
Taking drought into account Addressing chronic vulnerability among pastoralists in the Horn of Africa
 Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural forces. It is among the earliest documented climatic events, present in the Epic of Gilgamesh and tied to the Biblical story of Joseph's arrival in and the later Exodus from ancient Egypt. Hunter-gatherer migrations in 9,500 BC Chile have been linked to the phenomenon, as has the exodus of early humans
Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural forces. It is among the earliest documented climatic events, present in the Epic of Gilgamesh and tied to the Biblical story of Joseph's arrival in and the later Exodus from ancient Egypt. Hunter-gatherer migrations in 9,500 BC Chile have been linked to the phenomenon, as has the exodus of early humans
GIDMaPS
Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System, University of California, Irvine
from FAO Water (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
Global Real-Time Drought Media Monitoring
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Civil defense Climate variability and change Hydrology Water and the environment Weather hazards Articles containing video clips Natural disasters
Water Cycle Changes
In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often exerts substantial impacts on the
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing and subsequent wildfires. Periods of heat can significantly worsen drought conditions by hastening evaporation of water vapour
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
.
Drought is a recurring feature of the climate in most parts of the world, becoming more extreme and less predictable due to climate change, which dendrochronological studies date back to 1900. There are three kinds of drought effects, environmental, economic and social. Environmental effects include the drying of wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
s, more and larger wildfires, loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
. Economic consequences include disruption of water supplies for municipal economies; lower agricultural, forest, game, and fishing outputs; higher food-production costs; and problems with water supply for the energy sector. Social and health costs include the negative effect on the health of people directly exposed to this phenomenon (excessive heat waves
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
), high food costs, stress caused by failed harvests, water scarcity, etc. Prolonged droughts have caused mass migrations and humanitarian crisis
A humanitarian crisis (or sometimes humanitarian disaster) is defined as a singular event or a series of events that are threatening in terms of health, safety or well-being of a community or large group of people. It may be an internal or extern ...
.
Many plant species, such as those in the family Cactaceae (or cacti), have drought tolerance
Drought tolerance is the ability to which a plant maintains its biomass production during arid or drought conditions. Some plants are naturally adapted to dry conditions'','' surviving with protection mechanisms such as desiccation tolerance, detox ...
adaptations like reduced leaf area and waxy cuticles to enhance their ability to tolerate drought. Some others survive dry periods as buried seeds. Semi-permanent drought produces arid biomes such as deserts and grasslands. Most arid ecosystems have inherently low productivity.
The most prolonged drought ever in the world in recorded history continues in the Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert ( es, Desierto de Atacama) is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in th ...
in Chile (400 years). Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural forces.
Definition
 The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to National Integrated Drought Information System, a multi-agency partnership, drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage”. The National Weather Service office of the NOAA defines drought as "a deficiency of moisture that results in adverse impacts on people, animals, or vegetation over a sizeable area".
Drought is a complex phenomenon − relating to the absence of water − which is difficult to monitor and define. By the early 1980's, over 150 definitions of "drought" had already been published. The range of definitions reflects differences in regions, needs, and disciplinary approaches.
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines a drought simply as "drier than normal conditions". This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season".
According to National Integrated Drought Information System, a multi-agency partnership, drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage”. The National Weather Service office of the NOAA defines drought as "a deficiency of moisture that results in adverse impacts on people, animals, or vegetation over a sizeable area".
Drought is a complex phenomenon − relating to the absence of water − which is difficult to monitor and define. By the early 1980's, over 150 definitions of "drought" had already been published. The range of definitions reflects differences in regions, needs, and disciplinary approaches.
Categories
There are three major categories of drought based on where in the water cycle the moisture deficit occurs: meteorological drought, hydrological drought, and agricultural or ecological drought. A meteorological drought occurs due to lack of precipitation. A hydrological drought is related to low runoff, streamflow, and reservoir storage. An agricultural or ecological drought is causing plant stress from a combination of evaporation and low soil moisture. Some organizations add another category: socioeconomic drought occurs when the demand for an economic good exceeds supply as a result of a weather-related shortfall in water supply. The socioeconomic drought is a similar concept to water scarcity. The different categories of droughts have different causes but similar effects: # Meteorological drought occurs when there is a prolonged time with less than average precipitation. Meteorological drought usually precedes the other kinds of drought. As a drought persists, the conditions surrounding it gradually worsen and its impact on the local population gradually increases. #Hydrological
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
drought is brought about when the water reserves available in sources such as aquifers, lakes and reservoirs fall below a locally significant threshold. Hydrological drought tends to show up more slowly because it involves stored water that is used but not replenished. Like an agricultural drought, this can be triggered by more than just a loss of rainfall. For instance, around 2007 Kazakhstan was awarded a large amount of money by the World Bank to restore water that had been diverted to other nations from the Aral Sea under Soviet rule. Similar circumstances also place their largest lake, Balkhash, at risk of completely drying out.
# Agricultural or ecological droughts affect crop production or ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
in general. This condition can also arise independently from any change in precipitation levels when either increased irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
or soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
conditions and erosion triggered by poorly planned agricultural endeavors cause a shortfall in water available to the crops.
Causes

General precipitation deficiency
Mechanisms of producing precipitation include convective, stratiform, and orographic rainfall. Convective processes involve strong vertical motions that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation, while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions and less intense precipitation over a longer duration. Precipitation can be divided into three categories, based on whether it falls as liquid water, liquid water that freezes on contact with the surface, or ice. Droughts occur mainly in areas where normal levels of rainfall are, in themselves, low. If these factors do not support precipitation volumes sufficiently to reach the surface over a sufficient time, the result is a drought. Drought can be triggered by a high level of reflected sunlight and above average prevalence of highpressure system
A pressure system is a peak or lull in the sea level pressure distribution. The surface pressure at sea level varies minimally, with the lowest value measured and the highest recorded . High- and low-pressure systems evolve due to interactio ...
s, winds carrying continental, rather than oceanic air masses, and ridges of high pressure area
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interpl ...
s aloft can prevent or restrict the developing of thunderstorm activity or rainfall over one certain region. Once a region is within drought, feedback mechanisms such as local arid air, hot conditions which can promote warm core ridging, and minimal evapotranspiration can worsen drought conditions.
Dry season
Within the tropics, distinct, wet and dry seasons emerge due to the movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone orMonsoon trough
The monsoon trough is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, ...
. The dry season greatly increases drought occurrence, and is characterized by its low humidity, with watering holes and rivers drying up. Because of the lack of these watering holes, many grazing animals are forced to migrate due to the lack of water in search of more fertile lands. Examples of such animals are zebras
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebr ...
, elephants, and wildebeest. Because of the lack of water in the plants, bushfires are common. Since water vapor becomes more energetic with increasing temperature, more water vapor is required to increase relative humidity values to 100% at higher temperatures (or to get the temperature to fall to the dew point). Periods of warmth quicken the pace of fruit and vegetable production, increase evaporation and transpiration from plants, and worsen drought conditions.
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
 The
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an irregular periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea te ...
(ENSO) phenomenon can sometimes play a significant role in drought. ENSO comprises two patterns of temperature anomalies in the central Pacific Ocean, known as La Niña and El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date ...
. La Niña events are generally associated with drier and hotter conditions and further exacerbation of drought in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and the Southwestern United States, and to some extent the U.S. Southeast. Meteorological scientists have observed that La Niñas have become more frequent over time.
Conversely, during El Niño events, drier and hotter weather occurs in parts of the Amazon River Basin, Colombia, and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. Winters during the El Niño are warmer and drier than average conditions in the Northwest, northern Midwest, and northern Mideast United States, so those regions experience reduced snowfalls. Conditions are also drier than normal from December to February in south-central Africa, mainly in Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, and Botswana. Direct effects of El Niño resulting in drier conditions occur in parts of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and Northern Australia
The unofficial geographic term Northern Australia includes those parts of Queensland and Western Australia north of latitude 26° and all of the Northern Territory. Those local government areas of Western Australia and Queensland that lie p ...
, increasing bush fires, worsening haze, and decreasing air quality dramatically. Drier-than-normal conditions are also in general observed in Queensland, inland Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
, inland New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, and eastern Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
from June to August. As warm water spreads from the west Pacific and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
to the east Pacific, it causes extensive drought in the western Pacific. Singapore experienced the driest February in 2014 since records began in 1869, with only 6.3 mm of rain falling in the month and temperatures hitting as high as 35 °C on 26 February. The years 1968 and 2005 had the next driest Februaries, when 8.4 mm of rain fell.Precipitation deficiency due to climate change
Global climate change is expected to trigger droughts with a substantial impact on agriculture throughout the world, and especially indeveloping nation
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
s. Along with drought in some areas, flooding and erosion could increase in others. Some proposed climate change mitigation actions that focus on more active techniques, solar radiation management through the use of a space sunshade for one, may also carry with them increased chances of drought.''Sunshade' for global warming could cause drought''2 August 2007 New Scientist, Catherine Brahic There is a rise of compound warm-season droughts in Europe that are concurrent with an increase in potential evapotranspiration.
Erosion and human activities
Human activity can directly trigger exacerbating factors such as over farming, excessiveirrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
, deforestation, and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
adversely impact the ability of the land to capture and hold water. In arid climates, the main source of erosion is wind. Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. The wind can cause small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region (deflation). Suspended particles within the wind may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation.
Loess is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable
Friability ( ), the condition of being friable, describes the tendency of a solid substance to break into smaller pieces under duress or contact, especially by rubbing. The opposite of friable is indurate.
Substances that are designated hazardous, ...
, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown ( Aeolian) sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess. Wind erosion is much more severe in arid areas and during times of drought. For example, in the Great Plains, it is estimated that soil loss due to wind erosion can be as much as 6100 times greater in drought years than in wet years.Consequences


wildfires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
, higher deflation intensity, loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
, worse health of trees and the appearance of pests and dendroid diseases.
* Economic losses include lower agricultural, forests, game and fishing output, higher food-production costs, lower energy-production levels in hydro plants, losses caused by depleted water tourism and transport revenue, problems with water supply for the energy sector and for technological processes in metallurgy, mining, the chemical, paper, wood, foodstuff industries etc., disruption of water supplies for municipal economies.
* Social and health costs include the negative effect on the health of people directly exposed to this phenomenon (excessive heat waves
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
), possible limitation of water supplies, increased pollution levels, high food-costs, stress caused by failed harvests, water scarcity, etc. This explains why droughts and water scarcity operate as a factor which increases the gap between developed and developing countries.
Effects vary according to vulnerability. For example, subsistence farmers are more likely to migrate during drought because they do not have alternative food-sources. Areas with populations that depend on water sources as a major food-source are more vulnerable to famine.
Environmental and economic consequences
Common environmental and economic consequences of drought include: * Diminished crop growth or yield productions and carrying capacity for livestock *Wildfires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
, such as Australian bushfires
Bushfires in Australia are a widespread and regular occurrence that have contributed significantly to shaping the nature of the continent over millions of years. Eastern Australia is one of the most fire-prone regions of the world, and its p ...
and wildfires in the United States, become more common during times of drought and may cause human deaths.
* Dust bowl
The Dust Bowl was a period of severe dust storms that greatly damaged the ecology and agriculture of the American and Canadian prairies during the 1930s. The phenomenon was caused by a combination of both natural factors (severe drought) a ...
s, themselves a sign of erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
, which further erode the landscape
* Dust storms
A dust storm, also called a sandstorm, is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions. Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface. Fine particles are trans ...
, when drought hits an area suffering from desertification and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
* Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
damage, affecting both terrestrial
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth.
Terrestrial may also refer to:
* Terrestrial animal, an animal that lives on land opposed to living in water, or sometimes an animal that lives on or near the ground, as opposed to ...
and aquatic wildlife
* Reduced electricity production
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery (transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its storag ...
due to reduced water-flow through hydroelectric dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s
* Shortages of water for industrial users
* Snake migration, which results in snake-bites
* Exposure and oxidation of acid sulfate soils due to falling surface- and ground-water levels.Mosley LM, Zammit B, Jolley A, and Barnett L (2014). Acidification of lake water due to drought. Journal of Hydrology. 511: 484–493.Mosley LM, Palmer D, Leyden E, Fitzpatrick R, and Shand P (2014). Acidification of floodplains due to river level decline during drought. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 161: 10–23.Mosley LM, Palmer D, Leyden E, Fitzpatrick R, and Shand P (2014). Changes in acidity and metal geochemistry in soils, groundwater, drain and river water in the Lower Murray River after a severe drought. Science of the Total Environment 485–486: 281–291.
* Reduced water quality, because lower water-flows reduce dilution of pollutants and increase contamination of remaining water-sources.
* Land degradation and loss of soil moisture, resulting in the destruction of cropland productivity.
Social and health consequences
* Water scarcity,crop failure
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor- ...
, famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
and hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic Human nutrition, nutritional needs for a sustaine ...
– drought provides too little water to support food crops; malnutrition, dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
and related diseases
* Mass migration, resulting in internal displacement and international refugees
*Social unrest
* War
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
over natural resources, including water and food
* Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exp ...
accumulation within food chains and water supply (some of which are among the most potent toxins known to science) can cause cancer with low exposure over the long term. High levels of microcystin
Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. C ...
appeared in San Francisco Bay Area salt-water shellfish and fresh-water supplies throughout the state of California in 2016.
Impacts on crops
Water stress affects plant development and quality in a variety of ways: firstly drought can cause poor germination and impaired seedling development. At the same time plant growth relies on cellular division, cell enlargement, and differentiation. Drought stress impairs mitosis and cell elongation via loss of turgor pressure which results in poor growth. Development of leaves is also dependent upon turgor pressure, concentration of nutrients, and carbon assimilates all of which are reduced by drought conditions, thus drought stress lead to a decrease in leaf size and number. Plant height, biomass, leaf size and stem girth has been shown to decrease in maize under water limiting conditions. Crop yield is also negatively effected by drought stress, the reduction in crop yield results from a decrease in photosynthetic rate, changes in leaf development, and altered allocation of resources all due to drought stress. Crop plants exposed to drought stress suffer from reductions in leaf water potential and transpiration rate. Water-use efficiency increases in crops such as wheat while decreasing in others, such as potatoes. Plants need water for the uptake of nutrients from the soil, and for the transport of nutrients throughout the plant: drought conditions limit these functions leading to stunted growth. Drought stress also causes a decrease in photosynthetic activity in plants due to the reduction of photosynthetic tissues, stomatal closure, and reduced performance of photosynthetic machinery. This reduction in photosynthetic activity contributes to the reduction in plant growth and yields. Another factor influencing reduced plant growth and yields include the allocation of resources; following drought stress plants will allocate more resources to roots to aid in water uptake increasing root growth and reducing the growth of other plant parts while decreasing yields.Protection, mitigation and relief

 Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the
Agriculturally, people can effectively mitigate much of the impact of drought through irrigation and crop rotation. Failure to develop adequate drought mitigation strategies carries a grave human cost in the modern era, exacerbated by ever-increasing population densities. President Roosevelt on April 27, 1935, signed documents creating the Soil Conservation
Soil conservation is the prevention of loss of the topmost layer of the soil from erosion or prevention of reduced fertility caused by over usage, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination.
Slash-and-burn and other uns ...
Service (SCS)—now the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). Models of the law were sent to each state where they were enacted. These were the first enduring practical programs to curtail future susceptibility to drought, creating agencies that first began to stress soil conservation measures to protect farm lands today. It was not until the 1950s that there was an importance placed on water conservation was put into the existing laws (NRCS 2014).
Strategies for drought protection, mitigation or relief include:
* Dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s – many dams and their associated reservoirs supply additional water in times of drought.
* Cloud seeding – a form of intentional weather modification to induce rainfall. This remains a hotly debated topic, as the United States National Research Council released a report in 2004 stating that to date, there is still no convincing scientific proof of the efficacy of intentional weather modification.
* Desalination – use of sea water for irrigation or consumption.
* Drought monitoring – Continuous observation of rainfall levels and comparisons with current usage levels can help prevent man-made drought. For instance, analysis of water usage in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
has revealed that their water table (underground water level) is put at grave risk by over-use to fertilize their Khat crop. Careful monitoring of moisture levels can also help predict increased risk for wildfires, using such metrics as the Keetch-Byram Drought Index or Palmer Drought Index.
* Land use – Carefully planned crop rotation can help to minimize erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
and allow farmers to plant less water-dependent crops in drier years.
* Outdoor water-use restriction – Regulating the use of sprinklers, hoses or buckets on outdoor plants, filling pools, and other water-intensive home maintenance tasks. Xeriscaping yards can significantly reduce unnecessary water use by residents of towns and cities.
* Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir ...
– Collection and storage of rainwater from roofs or other suitable catchments.
* Recycled water – Former wastewater (sewage) that has been treated and purified for reuse.
* Transvasement – Building canals or redirecting rivers as massive attempts at irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
in drought-prone areas.
Scale and examples
Some large scale droughts in the 21st century included: * The 1997–2009Millennium Drought
The 2000s drought in Australia, also known as the Millennium drought is said by some to be the worst drought recorded since European settlement.
This drought affected most of southern Australia, including its largest cities and largest agricul ...
in Australia led to a water supply crisis across much of the country. As a result, many desalination plants were built for the first time ( see list).
* In 2006, Sichuan Province China experienced its worst drought in modern times with nearly 8 million people and over 7 million cattle facing water shortages.
* 12-year drought that was devastating southwest Western Australia, southeast South Australia, Victoria and northern Tasmania was "very severe and without historical precedent".
* 2015–2018 Cape Town water crisis. This likelihood was tripled by climate change.
 The Darfur conflict in Sudan, also affecting Chad, was fueled by decades of drought; combination of drought, desertification and overpopulation are among the causes of the Darfur conflict, because the Arab
The Darfur conflict in Sudan, also affecting Chad, was fueled by decades of drought; combination of drought, desertification and overpopulation are among the causes of the Darfur conflict, because the Arab Baggara
The Baggāra ( ar, البَقَّارَة "heifer herder") or Chadian Arabs are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile ri ...
nomads searching for water have to take their livestock further south, to land mainly occupied by non-Arab farming people.
 Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the
Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Himalayan rivers. India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
and Myanmar could experience floods followed by droughts in coming decades. Drought in India
Drought in India has resulted in tens of millions of deaths over the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the country's climate: a favorable monsoon is critical to securing water for irrigating India's crops ...
affecting the Ganges is of particular concern, as it provides drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
and agricultural irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
for more than 500 million people. The west coast of North America, which gets much of its water from glaciers in mountain ranges such as the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
and Sierra Nevada, also would be affected.
In 2005, parts of the Amazon basin experienced the worst drought in 100 years. A 23 July 2006 article reported Woods Hole Research Center results showing that the forest in its present form could survive only three years of drought. Scientists at the Brazilian National Institute of Amazonian Research
The National Institute of Amazonian Research (Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia or INPA) is a public educational and research institution headquartered in Manaus, Brazil. It was founded in 1952, with the purpose of furthering scientific ...
argue in the article that this drought response, coupled with the effects of deforestation on regional climate, are pushing the rainforest towards a " tipping point" where it would irreversibly start to die. It concludes that the rainforest is on the brink of being turned into savanna or desert, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate. According to the WWF, the combination of climate change and deforestation increases the drying effect of dead trees that fuels forest fires.
 By far the largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid lands commonly known as the outback. A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to
By far the largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid lands commonly known as the outback. A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
settlers who arrived about 50,000 years ago. Regular burning by these settlers could have prevented monsoons from reaching interior Australia. In June 2008 it became known that an expert panel had warned of long term, maybe irreversible, severe ecological damage for the whole Murray-Darling basin if it did not receive sufficient water by October 2008. Australia could experience more severe droughts and they could become more frequent in the future, a government-commissioned report said on July 6, 2008. Australian environmentalist Tim Flannery, predicted that unless it made drastic changes, Perth in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
could become the world's first ghost metropolis, an abandoned city with no more water to sustain its population. The long Australian Millennial drought broke in 2010.
Recurring droughts leading to desertification in East Africa have created grave ecological catastrophes, prompting food shortages in 1984–85, 2006 and 2011.Sara Pantuliano and Sara Pavanello (2004Taking drought into account Addressing chronic vulnerability among pastoralists in the Horn of Africa
Overseas Development Institute
ODI (formerly the 'Overseas Development Institute') is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the ...
During the 2011 drought, an estimated 50,000 to 150,000 people were reported to have died, though these figures and the extent of the crisis are disputed. In February 2012, the UN announced that the crisis was over due to a scaling up of relief efforts and a bumper harvest. Aid agencies subsequently shifted their emphasis to recovery efforts, including digging irrigation canals and distributing plant seeds. The 2020-2022 Horn of Africa drought has surpassed the horrific drought in 2010-2011 in both duration and severity.
In 2012, a severe drought struck the western Sahel. The Methodist Relief & Development Fund (MRDF) reported that more than 10 million people in the region were at risk of famine due to a month-long heat wave that was hovering over Niger, Mali, Mauritania and Burkina Faso. A fund of about £20,000 was distributed to the drought-hit countries.
History
 Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural forces. It is among the earliest documented climatic events, present in the Epic of Gilgamesh and tied to the Biblical story of Joseph's arrival in and the later Exodus from ancient Egypt. Hunter-gatherer migrations in 9,500 BC Chile have been linked to the phenomenon, as has the exodus of early humans
Throughout history, humans have usually viewed droughts as "disasters" due to the impact on food availability and the rest of society. Humans have often tried to explain droughts as either a natural disaster, caused by humans, or the result of supernatural forces. It is among the earliest documented climatic events, present in the Epic of Gilgamesh and tied to the Biblical story of Joseph's arrival in and the later Exodus from ancient Egypt. Hunter-gatherer migrations in 9,500 BC Chile have been linked to the phenomenon, as has the exodus of early humans out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on ...
and into the rest of the world around 135,000 years ago. Rituals exist to prevent or avert drought, rainmaking could go from dances to scapegoating
Scapegoating is the practice of singling out a person or group for unmerited blame and consequent negative treatment. Scapegoating may be conducted by individuals against individuals (e.g. "he did it, not me!"), individuals against groups (e.g., ...
to human sacrifices. Nowadays, those ancient practices are for the most part relegated to folklore and replaced by more rational water management.
Historical droughts include:
* 1540 Central Europe, said to be the “worst drought of the millennium” with eleven months without rain and temperatures of 5–7 °C above the average of the 20th century
* 1900 India killing between 250,000 and 3.25 million.
* 1921–22 Soviet Union in which over 5 million perished from starvation due to drought.
* 1928–30 Northwest China resulting in over 3 million deaths by famine.
* 1936 and 1941 Sichuan Province China resulting in 5 million and 2.5 million deaths respectively.
See also
References
External links
GIDMaPS
Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System, University of California, Irvine
from FAO Water (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
Global Real-Time Drought Media Monitoring
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Civil defense Climate variability and change Hydrology Water and the environment Weather hazards Articles containing video clips Natural disasters