|
Civic Statistics
Civic statistics is a sub-discipline of statistics focused on the analysis of evidence relevant to understanding and addressing issues of public concern such as human migration, poverty and inequality. It lies at the intersection of politics, social science, statistics, and education. History There is a long history of advocacy for the role of evidence to promote social. Marquis de Condorcet’s notion of – knowledge that empowers people to liberate themselves from social oppression - provides an example; William Playfair‘s Political and Commercial Atlas (1786) is an early publication designed to make complex evidence accessible to a wide audience; John Snow John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the so ... and Florence Nightingale both used powerful graphical displays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (external migration), but internal migration (within a single country) is also possible; indeed, this is the dominant form of human migration globally. Migration is often associated with better human capital at both individual and household level, and with better access to migration networks, facilitating a possible second move. It has a high potential to improve human development, and some studies confirm that migration is the most direct route out of poverty.Age is also important for both work and non-work migration. People may migrate as individuals, in family units or in large groups. There are four major forms of migration: invasion, conquest, colonization and emigration/ immigration. Persons moving from their home due to forced di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse , , and causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in statistics or economics there are two main measures: '' absolute poverty'' compares income against the amount needed to meet basic personal needs [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of wealth people own). Besides economic inequality between countries or states, there are important types of economic inequality between different groups of people. Important types of economic measurements focus on wealth, income, and consumption. There are many methods for measuring economic inequality, the Gini coefficient being a widely used one. Another type of measure is the Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index, which is a statistic composite index that takes inequality into account. Important concepts of equality include equity, equality of outcome, and equality of opportunity. Whereas globalization has reduced global inequality (between nations), it has increased inequality within nations. Income inequality between nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, communication science and political science. Positivist social scientists use methods resembling those of the natural sciences as tools for understanding society, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Interpretivist social scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its broader sense. In modern academic practice, researchers are often eclectic, using multiple methodologies (for instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis De Condorcet
Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet (; 17 September 1743 – 29 March 1794), known as Nicolas de Condorcet, was a French philosopher and mathematician. His ideas, including support for a liberal economy, free and equal public instruction, constitutional government, and equal rights for women and people of all races, have been said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment, of which he has been called the "last witness," and Enlightenment rationalism. He died in prison after a period of hiding from the French Revolutionary authorities. Early years Condorcet was born in Ribemont (in present-day Aisne), descended from the ancient family of Caritat, who took their title from the town of Condorcet in Dauphiné, of which they were long-time residents. Fatherless at a young age, he was taken care of by his devoutly religious mother who dressed him as a girl till age eight. He was educated at the Jesuit College in Reims and at the ''Collège de Navarr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
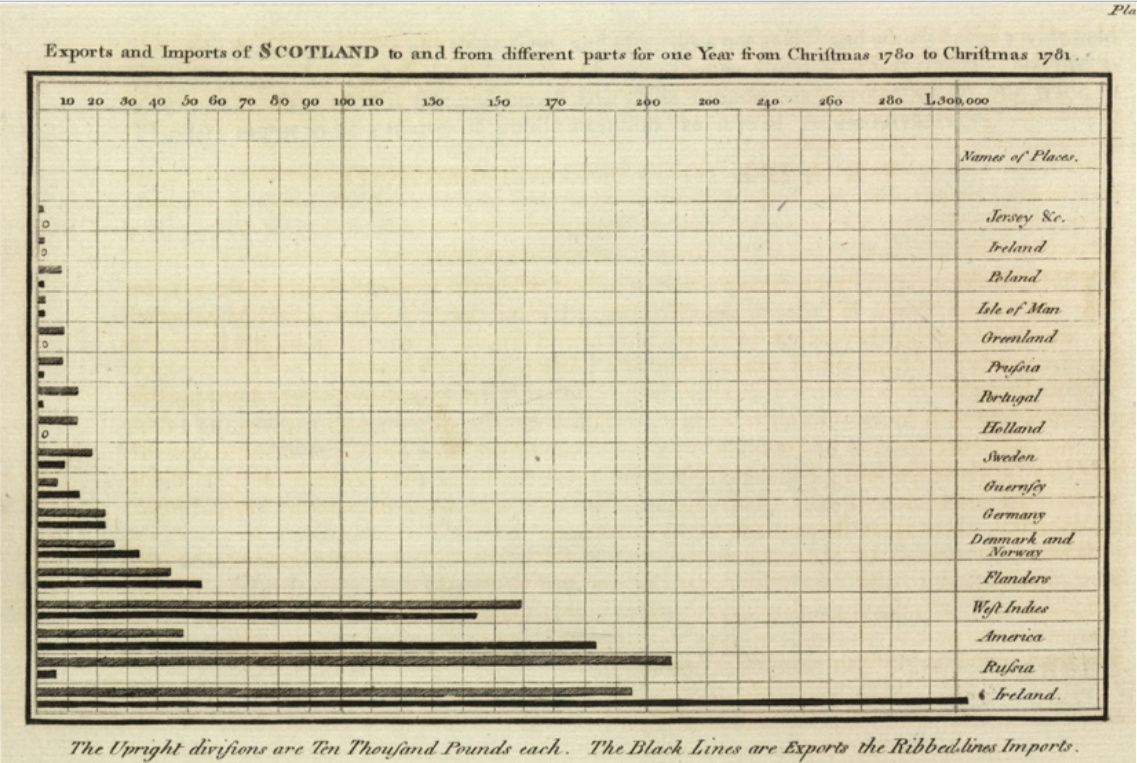
William Playfair
William Playfair (22 September 1759 – 11 February 1823), a Scottish engineer and political economist, served as a secret agent on behalf of Great Britain during its war with France. The founder of graphical methods of statistics, Playfair invented several types of diagrams: in 1786 the line, area and bar chart of economic data, and in 1801 the pie chart and circle graph, used to show part-whole relations. As a secret agent, Playfair reported on the French Revolution and organized a clandestine counterfeiting operation in 1793 to collapse the French currency. Biography Playfair was born in 1759 in Scotland. He was the fourth son (named after his grandfather) of the Reverend James Playfair of the parish of Liff & Benvie near the city of Dundee in Scotland; his notable brothers were architect James Playfair and mathematician John Playfair. His father died in 1772 when William was 13, leaving the eldest brother John to care for the family and his education. After his appren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the source of a cholera outbreak in Soho, London, in 1854, which he curtailed by removing the handle of a water pump. Snow's findings inspired the adoption of anaesthesia as well as fundamental changes in the water and waste systems of London, which led to similar changes in other cities, and a significant improvement in general public health around the world. Early life and education Snow was born on 15 March 1813 in York, England, the first of nine children born to William and Frances Snow in their North Street home, and was baptised at All Saints' Church, North Street, York. His father was a labourer who worked at a local coal yard, by the Ouse, constantly replenished from the Yorkshire coalfield by barges, but later was a farmer in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople. She significantly reduced death rates by improving hygiene and living standards. Nightingale gave nursing a favourable reputation and became an icon of Victorian culture, especially in the persona of "The Lady with the Lamp" making rounds of wounded soldiers at night. Recent commentators have asserted that Nightingale's Crimean War achievements were exaggerated by the media at the time, but critics agree on the importance of her later work in professionalising nursing roles for women. In 1860, she laid the foundation of professional nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas' Hospital in London. It was the first secular nursing school in the world an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Neurath
Otto Karl Wilhelm Neurath (; 10 December 1882 – 22 December 1945) was an Austrian-born philosopher of science, sociologist, and political economist. He was also the inventor of the ISOTYPE method of pictorial statistics and an innovator in museum practice. Before he fled his native country in 1934, Neurath was one of the leading figures of the Vienna Circle. Early life Neurath was born in Vienna, the son of Wilhelm Neurath (1840–1901), a well-known political economist at the time. Otto's mother was a Protestant, and he would also become one. Helene Migerka was his cousin. He studied mathematics and physics at the University of Vienna (he formally enrolled for classes only for two semesters in 1902–3). In 1906, he gained his PhD in the department of Political Science and Statistics at the University of Berlin with a thesis entitled ''Zur Anschauung der Antike über Handel, Gewerbe und Landwirtschaft'' (''On the Conceptions in Antiquity of Trade, Commerce and Agriculture'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)

