|
Circeii
Circeii was an ancient Roman city on the site of modern San Felice Circeo and near Mount Circeo, the mountain promontory on the southwest coast of Italy. The area around Circeii and Mount Circeo was thickly populated with Roman villas and other buildings, of which the remains of many can still be seen. The origin of the name is uncertain: it has naturally been connected with Homer's Circe, legend of Circe. The difficulty has been raised that the promontory ceased to be an island well before Homer's time; but Procopius remarked that the promontory has all the appearance of an island until one is actually upon it. History The town on the eastern side of Monte Circeo was probably founded by Greeks at the end of the Bronze Age, when they established ports and emporiums along the Italian coast. At the east end of the promontory ridge are the remains of Bronze Age cyclopean walls that roughly form a rectangle of 200 by 100 metres. It seems to have been an acropolis and contains o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Felice Circeo
San Felice Circeo is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Latina, in the Lazio region of central Italy. It was an ancient city called Circeii. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy"). It is included in the Circeo National Park. Sites include the Grotta Guattari, one of the oldest Neanderthal sites in Italy, in which remains of nine Neanderthals were discovered. Capo Circeo Lighthouse is from the old town. History In the Treaties between Rome and Carthage#First treaty 509 BC, treaty signed between Carthage and Rome in 509 BC, the Carthaginians agreed not to harm Circeii. In 209 BC, during the Second Punic War, Circeii was one of twelve Latin colonies to refuse any more military contributions towards Rome and in 204 it was severely punished as a result, by furnishing double the greatest number of foot soldiers they had ever provided and 120 horsemen, all chosen from the wealthiest of the inhabitants, and to be sent out of Italy. Als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
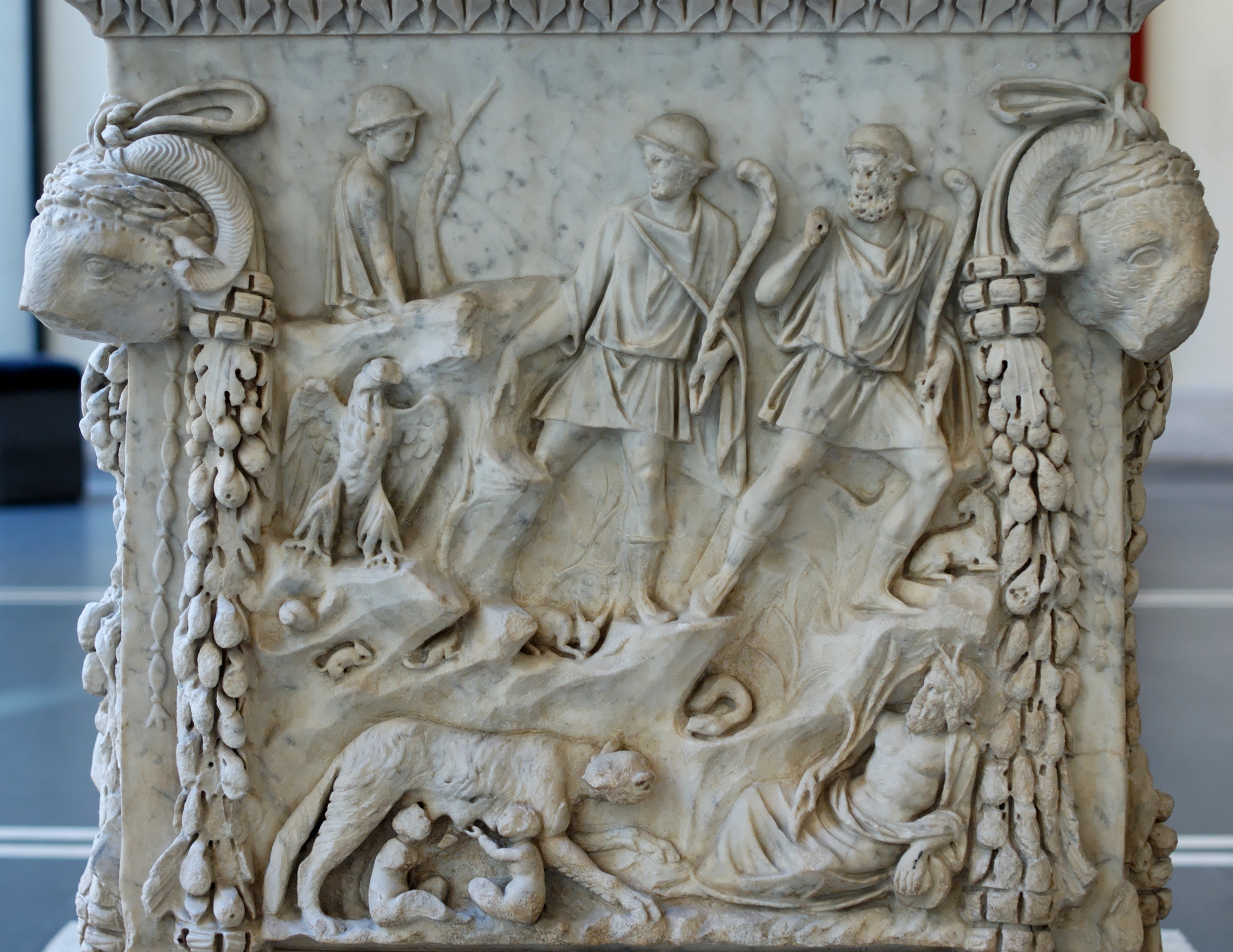
Lepidus (triumvir)
Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (; 89 BC – late 13 or early 12 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who formed the Second Triumvirate alongside Octavian and Mark Antony during the final years of the Roman Republic. Lepidus had previously been a close ally of Julius Caesar. He was also the last '' pontifex maximus'' before the Roman Empire, and (presumably) the last ''interrex'' and ''magister equitum'' to hold military command. Though he was an able military commander and proved a useful partisan of Caesar, Lepidus has always been portrayed as the least influential member of the Triumvirate. He typically appears as a marginalised figure in depictions of the events of the era, most notably in Shakespeare's plays. While some scholars have endorsed this view, others argue that the evidence is insufficient to discount the distorting effects of propaganda by his opponents, principally Cicero and, later, Augustus. Family Lepidus was the son of Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (consul in 78 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Latin War
The (Second) Latin War of 340–338 BCThe Romans customarily dated events by noting the consuls who held office that year. The Latin War broke out in the year that Titus Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus and Publius Decius Mus were consuls and ended in the year that Lucius Furius Camillus and Gaius Maenius were consuls. When converted to the western calendar using the traditional Varronian chronology, those years become 340 and 338 BC. However, modern historians have shown that the Varronian chronology dates the Latin War four years too early because of inclusion of unhistorical "dictator years". Despite that known inaccuracy, the Varronian chronology remains in use by convention also in academic literature and so is also the chronology used in this article. Forsythe(2005), pp. 369-370 was a conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors, the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopean
Cyclopean masonry is a type of masonry, stonework found in Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean architecture, built with massive limestone boulders, roughly fitted together with minimal Engineering tolerance, clearance between adjacent stones and with clay mortar or no use of Mortar (masonry), mortar. The boulders typically seem unworked, but some may have been worked roughly with a hammer and the gaps between boulders filled in with smaller chunks of limestone. The most famous examples of Cyclopean masonry are found in the walls of Mycenae and Tiryns, and the style is characteristic of Mycenaean fortifications. Similar styles of stonework are found in other cultures and the term has come to be used to describe typical stonework of this sort. The term comes from the belief of classical Greeks that only the mythical Cyclopes had the strength to move the enormous boulders that made up the walls of Mycenae and Tiryns. Natural History (Pliny), Pliny's ''Natural History'' reported the tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', wikisource:From_the_Founding_of_the_City/Book_1, I He is commonly known as Tarquin the Proud, from his cognomen ''Superbus'' (Latin for "proud, arrogant, lofty"). Ancient accounts of the Roman Kingdom, regal period mingle history and legend. Tarquin was said to have been either the son or grandson of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome, and to have gained the throne through the murders of both his wife and his elder brother, followed by the assassination of his predecessor, Servius Tullius. His reign has been described as a tyranny that justified the abolition of Roman Kingdom, the monarchy. Background The most ancient sources, such as that of Quintus Fabius Pictor, assert Tarquin was the son of Tarquinius Priscus, but modern historians believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Circeo
Monte Circeo or Cape Circeo ( , ) is a mountain promontory that marks the southwestern limit of the former Pontine Marshes, located on the southwest coast of Italy near San Felice Circeo. At the northern end of the Gulf of Gaeta, it is about long by wide at the base, running from east to west and surrounded by the sea on all sides except the north. The land to the northeast is the former ancient Pontine Marshes. Most of the ancient swamp has been land reclamation, reclaimed for agriculture and urban areas. The mountain, the coastal zone as far north as Latina, Lazio, Latina, including the only remaining remnant of the swamp, and two of the Pontine Islands offshore, Zannone and Ponza, have been included in the Parco Nazionale del Circeo, Circeo National Park. Geology Although a headland, it was not formed by coastal erosion – as headlands are usually formed – but is a remnant of the Orogeny, orogenic processes that created the Apennines. The entire coast of La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created at the end of the Roman Republic, Roman republic for Mark Antony, Lepidus, and Augustus, Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November 43 BC with a term of five years; it was renewed in 37 BC for another five years before expiring in 32 BC. Constituted by the ''lex Titia'', the triumvirs were given broad powers to make or repeal legislation, issue judicial punishments without due process or right of appeal, and appoint all other magistrates. The triumvirs also split the Roman world into three sets of Roman province, provinces. The triumvirate, formed in the aftermath of a War of Mutina, conflict between Antony and the senate, emerged as a force to reassert Caesarian control over the western provinces and wage war on the ''liberatores'' led by the men who Assassination of Julius Caesar, assassinated Julius Caesar. After proscriptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaside Resort
A seaside resort is a city, resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of an official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements such as in the German ''Seebad''. Where a beach is the primary focus for tourists, it may be called a beach resort. History Seaside resorts have existed since antiquity. In Ancient Rome, Roman times, the town of Baiae by the Tyrrhenian Sea in Italy was a resort for those who were sufficiently prosperous. Barcola by the Adriatic Sea in northern Italy with its Roman luxury villas is considered a special example of ancient leisure culture by the sea. Mersea Island in Essex, England was a seaside holiday destination for wealthy ancient Romans living in Colchester. The development of the beach as a popular leisure resort from the mid-19th century was the first manifestation of what is now the global tourist industry. The first seasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social War (91–88 BC)
Social War may refer to: * Social War (357–355 BC), or the War of the Allies, fought between the Second Athenian Empire and the allies of Chios, Rhodes, and Cos as well as Byzantium * Social War (220–217 BC), fought among the southern Greek states * Social War (91–87 BC) The Social War (from Latin , "war of the allies"), also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought largely from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies () in Roman Italy, Italy. Some of the ..., or the Italian or Marsic War, fought between the Roman Republic and several Italian cities * '' The Social War'', an 1872 novel by Simon Mohler Landis {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Urbe Condita (book)
The ''History of Rome'', perhaps originally titled , and frequently referred to as (), is a monumental history of ancient Rome, written in Latin between 27 and 9 BC by the Roman historian Titus Livius, better known in English as "Livy". The work covers the period from the legends concerning the arrival of Aeneas and the refugees from the fall of Troy, to the city's founding in 753 BC, the expulsion of the Kings in 509 BC, and down to Livy's own time, during the reign of the emperor Augustus. The last event covered by Livy is the death of Drusus in 9 BC. 35 of 142 books, about a quarter of the work, are still extant. The surviving books deal with the events down to 293 BC (books 1–10), and from 219 to 166 BC (books 21–45). Contents Corpus The ''History of Rome'' originally comprised 142 "books", 35 of which—Books 1–10 with the Preface and Books 21–45—still exist in reasonably complete form. Damage to a manuscript of the 5th century resulted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult and an era of imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirate to defeat the assassins of Caesar. Following their victory at the Battle of Philippi (42 BC), the Triumvir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Roman Italy, Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, Kingdom of Syracuse, Syracuse and several Numidians, Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Celtiberians, Iberian and Gauls, Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main Theater (military), military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal (Barcid), Hasdru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |