|
Chiastic Structure
Chiastic structure, or chiastic pattern, is a literary technique in motif (narrative), narrative motifs and other textual passages. An example of chiastic structure would be two ideas, A and B, together with variants A' and B', being presented as A,B,B',A'. Chiastic structures that involve more components are sometimes called "ring structures" or "ring compositions". These may be regarded as chiasmus scaled up from words and clauses to larger segments of text. These often symmetrical patterns are commonly found in ancient literature such as the epic poetry of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey''. Classicist Bruno Gentili describes this technique as "the cyclical, circular, or 'ring' pattern (''ring composition''). Here the idea that introduced a compositional section is repeated at its conclusion, so that the whole passage is framed by material of identical content". Meanwhile, in classical prose, scholars often find chiastic narrative techniques in the ''Histories (Herodotus), Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Technique
A narrative technique (also, in fiction, a fictional device) is any of several storytelling methods the creator of a narrative, story uses, thus effectively relaying information to the audience or making the story more complete, complex, or engaging. Some scholars also call such a technique a narrative mode, though this term can also more narrowly refer to the particular technique of narration, using a commentary to deliver a story. Other possible synonyms within written narratives are literary technique or literary device, though these can also broadly refer to non-narrative writing strategies, as might be used in academic or essay writing, as well as poetic devices such as assonance, metre (poetry), metre, or rhyme scheme. Furthermore, narrative techniques are distinguished from Narrative#Basic elements, narrative elements, which exist inherently in all works of narrative, rather than being merely optional strategies. Setting Plots Perspective Style Theme C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Literature
Oral literature, orature, or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung in contrast to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used varying descriptions for oral literature or folk literature. A broad conceptualization refers to it as literature characterized by oral transmission and the absence of any fixed form. It includes the stories, legends, and history passed through generations in a spoken form. Background Pre-literate societies, by definition, have no written literature, but may possess rich and varied oral traditions—such as folk epics, folk narratives (including fairy tales and fables), folk drama, proverbs and folksongs—that effectively constitute an oral literature. Even when these are collected and published by scholars such as folklorists and paremiographers, the result is still often referred to as "oral literature". The different genr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Topical or locally injected anesthesia is generally used to reduce pain and physiologic stress. Circumcision is generally electively performed, most commonly done as a form of preventive healthcare, as a religious obligation, or as a cultural practice. It is also an option for cases of phimosis, other pathologies that do not resolve with other treatments, and chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs). The procedure is contraindicated in cases of certain genital structure abnormalities or poor general health. The procedure is associated with reduced rates of sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections. This includes reducing the incidence of cancer-causing forms of human papillomavirus (HPV) and reducing HIV transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenant (biblical)
The Hebrew Bible makes reference to a number of covenants () with God (YHWH). These include the Noahic Covenant set out in Genesis 9, which is decreed between God and all living creatures, as well as a number of more specific covenants with Abraham, the whole Israelite people, the Israelite priesthood, and the Davidic lineage of kings. In form and terminology, these covenants echo the kinds of treaty agreements existing in the surrounding ancient world. The Book of Jeremiah, verses says that YHWH will establish a new covenant with the house of Israel and the house of Judah. Most Christians believe this New Covenant is the "replacement" or "final fulfilment" of the Old Covenant described in the Old Testament and as applying to the People of God, while some believe both covenants are still applicable in a dual covenant theology. Ancient Near Eastern The Hebrew term בְּרִית ''bĕriyth'' for "covenant" is from a root with the sense of "cutting", because pacts or cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
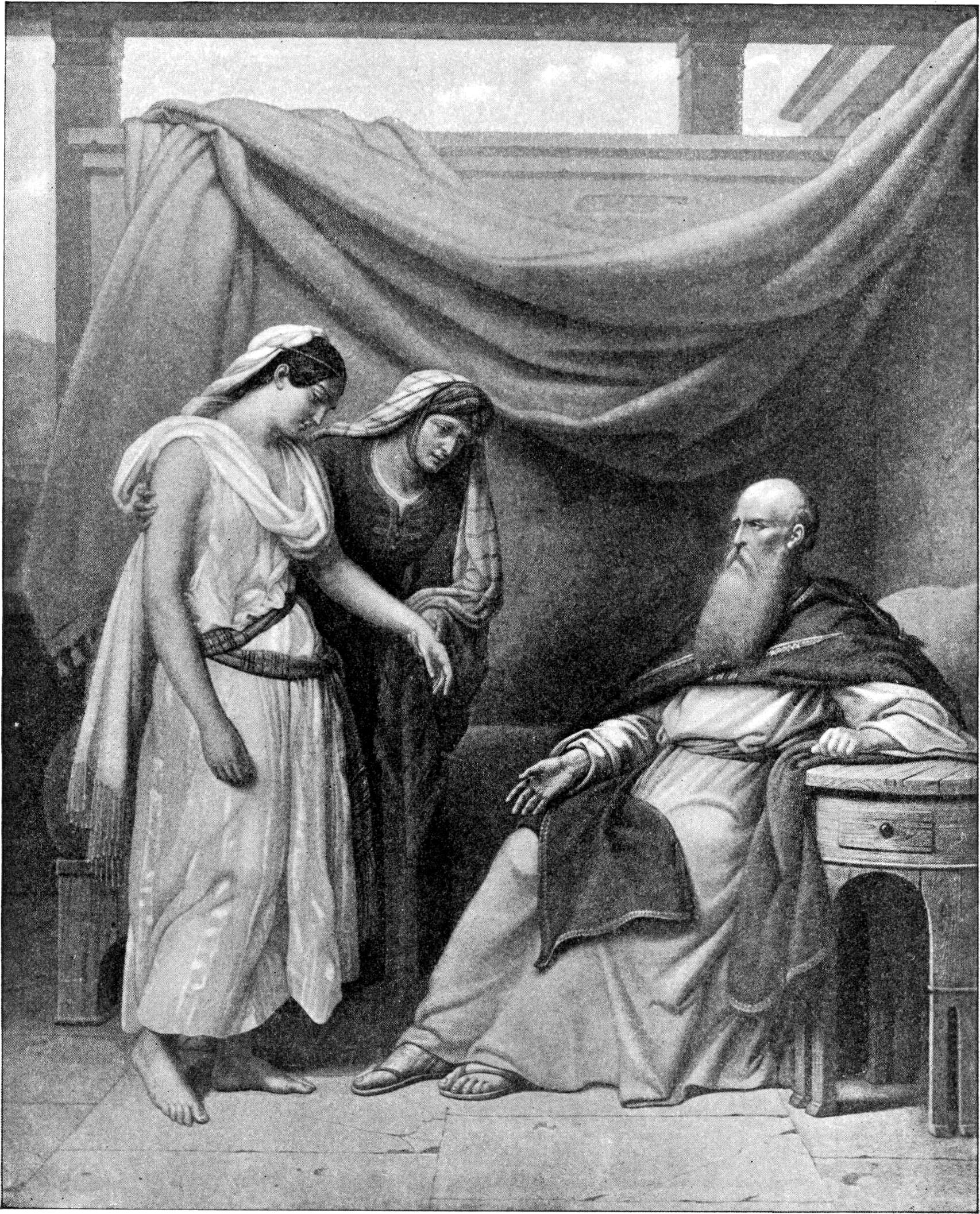
Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenantal relationship between the Jewish people and God in Judaism, God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, whether Jewish or gentile, non-Jewish; and Abraham in Islam, in Islam, he is a link in the Prophets and messengers in Islam, chain of Islamic prophets that begins with Adam in Islam, Adam and culminates in Muhammad. Abraham is also revered in other Abrahamic religions such as the Baháʼí Faith and the Druze, Druze faith. The story of the life of Abraham, as told in the narrative of the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible, revolves around the themes of posterity and land. He is said to have been called by God to leave the house of his father Terah and settle in the land of Canaan, which God now promises to Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God In Judaism
In Judaism, God has been conceived in a variety of ways. Traditionally, Judaism holds that Yahweh—that is, the God in Abrahamic religions#Judaism, god of Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, and the national god of the Israelites—delivered them from The Exodus, slavery in Egypt, and gave them the Law of Moses at Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai as described in the Torah. Jews traditionally believe in a Monotheism, monotheistic conception of God ("Shema Yisrael, God is one"), characterized by both Transcendence (religion), transcendence (independence from, and separation from, the material universe) and immanence (active involvement in the material universe). God is seen as unique and perfect, free from all faults, and is believed to be omnipotent, omnipresent, omniscient, and Absolute infinite, infinite in all attributes, with no partner or equal, serving as the sole Creator deity, creator of everything in existence. In Judaism, Aniconism in Judaism, God is never portrayed in any ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abram
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenantal relationship between the Jewish people and God in Judaism, God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, whether Jewish or gentile, non-Jewish; and Abraham in Islam, in Islam, he is a link in the Prophets and messengers in Islam, chain of Islamic prophets that begins with Adam in Islam, Adam and culminates in Muhammad. Abraham is also revered in other Abrahamic religions such as the Baháʼí Faith and the Druze, Druze faith. The story of the life of Abraham, as told in the narrative of the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible, revolves around the themes of posterity and land. He is said to have been called by God to leave the house of his father Terah and settle in the land of Canaan, which God now promises to Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis 17
Lech-Lecha, Lekh-Lekha, or Lech-L'cha ( ''leḵ-ləḵā''—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "go!" or "leave!", literally "go for you"—the incipit, fifth and sixth words in the parashah) is the third weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes Book of Genesis, Genesis 12:1–17:27. The parashah tells the stories of God in Judaism, God's calling of Abram (who would become Abraham), Abram's Wife–sister narratives in the Book of Genesis, passing off his wife Sarah, Sarai as his sister, Abram's dividing Land of Israel, the land with his nephew Lot (Bible), Lot, the Battle of Siddim, war between the four kings and the five, the Covenant of the pieces, covenant between the pieces, Sarai's tensions with her maid Hagar (Bible), Hagar and Hagar's son Ishmael, and the covenant of circumcision (''brit milah''). The parashah is made up of 6,336 Hebrew letters, 1,686 Hebrew words, 126 Chapters and verses of the Bible, verses, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Ostrowski
Donald "Don" Gary Ostrowski (born 1945) is an American historian, and a lecturer in history at Harvard Extension School. He specialises in the political and social history Kievan Rus' and Muscovy (early modern Russia). Biography Ostrowski received his PhD in history from Pennsylvania State University The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ... in 1977. He is known for his work on textual criticism of the ''Primary Chronicle''. ''The Povest’ vremennykh let: An Interlinear Collation and Paradosis'' ( Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute, 2003) under his co-editorship received the Early Slavic Studies Association Award for Distinguished Scholarship. Together with scholars such as Oleksiy Tolochko and (1917–2009), Ostrowski is credited with having reignited interest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
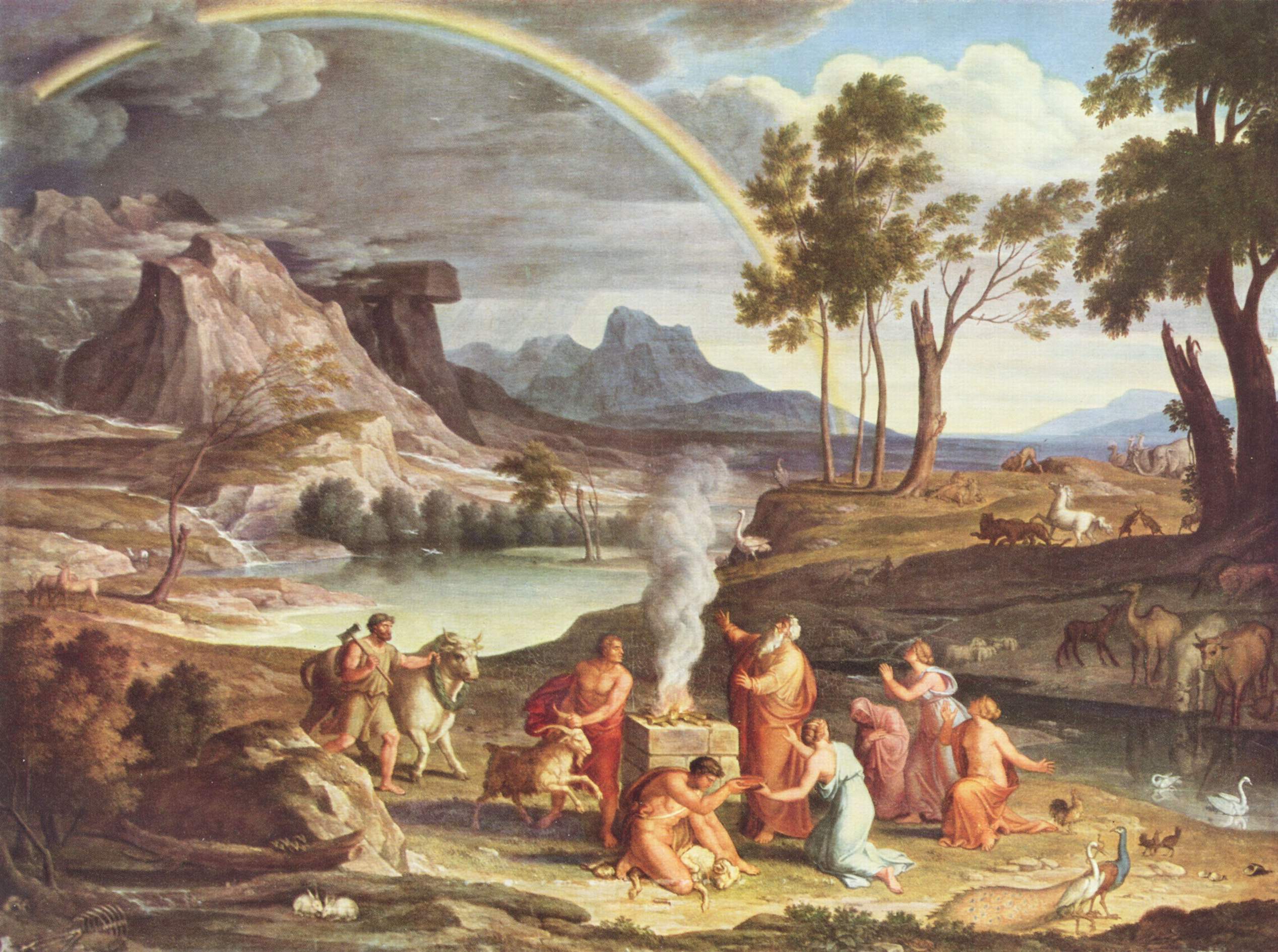
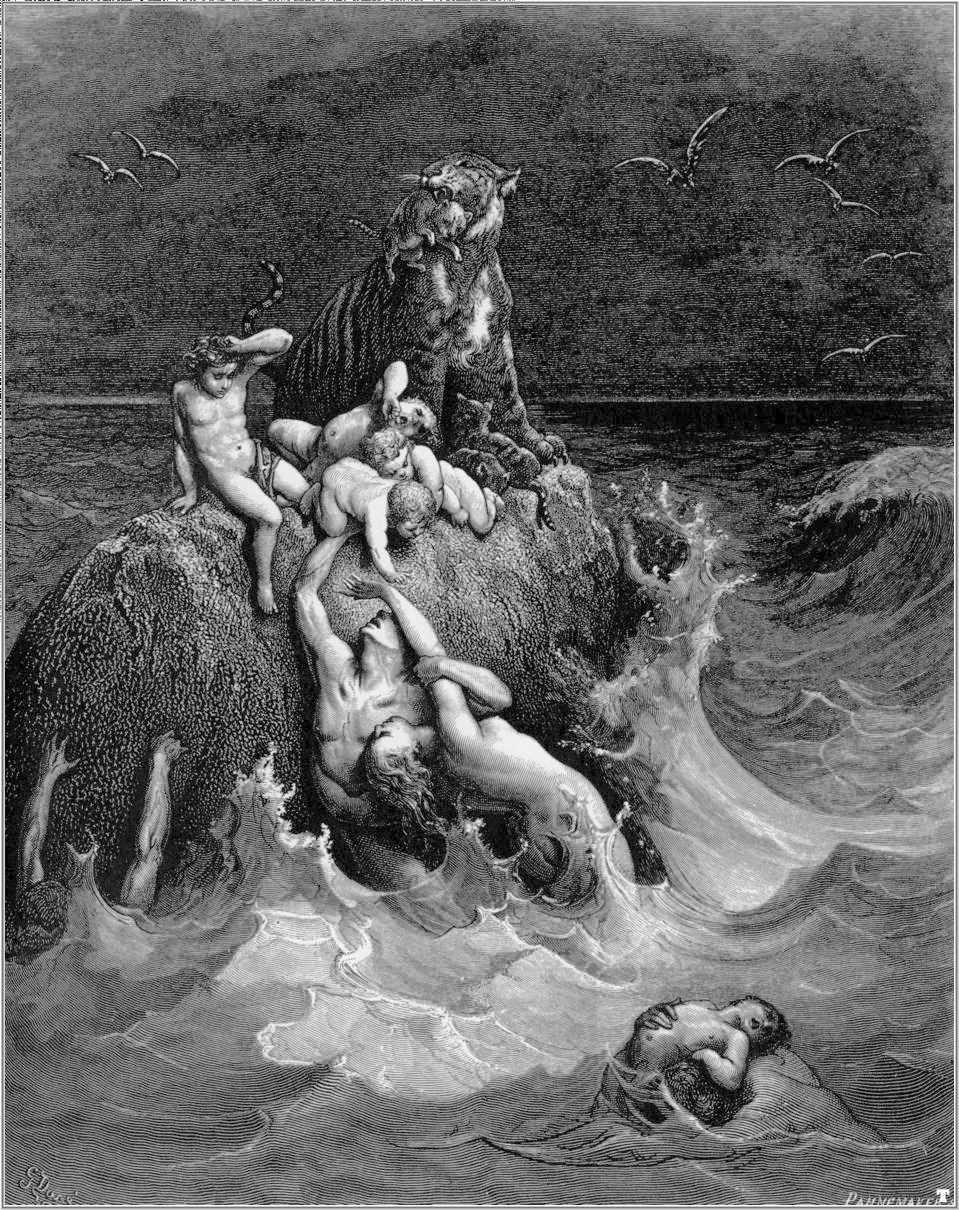
Genesis Flood Narrative
The Genesis flood narrative (chapters 6–9 of the Book of Genesis) is a Hebrew flood myth. It tells of God's decision to return the universe to its pre- creation state of watery chaos and remake it through the microcosm of Noah's ark. The Book of Genesis was probably composed around the 5th century BCE; although some scholars believe that primeval history (chapters 1–11), including the flood narrative, may have been composed and added as late as the 3rd century BCE. It draws on two sources, called the Priestly source and the non-Priestly or Yahwist, and although many of its details are contradictory, the story forms a unified whole. A global flood as described in this myth is inconsistent with the physical findings of geology, archeology, paleontology, and the global distribution of species. A branch of creationism known as flood geology is a pseudoscientific attempt to argue that such a global flood actually occurred. Some Christians have preferred to interpret th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Wenham
Gordon J. Wenham (; 21 May 1943 – 13 May 2025) was a Reformed British Old Testament scholar and writer. He authored several books about the Bible. Tremper Longman called him "one of the finest evangelical commentators today." Early life and education Wenham read theology at Cambridge University, graduating in 1965 with distinction, and completed his PhD on Deuteronomy in 1970. He was awarded several scholarships in connection with Old Testament studies and studied in Germany, the US, and Israel. He was the son of John Wenham and the brother of David Wenham. While at Cambridge, he was active in the Cambridge Inter-Collegiate Christian Union. He first met his wife Lynne when she was a student at Cambridge, 1966–1969. Career Gordon studied theology at Cambridge University, and went on to do Old Testament research at King's College London. He spent time at Harvard University and in Jerusalem at the École Biblique and the Hebrew University. He taught Old Testament in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavic Languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West Slavic languages, West and East Slavic languages, East) by a belt of German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian and Romanian language, Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic language, Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a Dialect continuum#South Slavic continuum, dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |