|
Charles L. Bennett
Charles Leonard Bennett (born November 1956) is an American observational astrophysicist. He is a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor, the Alumni Centennial Professor of Physics and Astronomy and a Gilman Scholar at Johns Hopkins University. He is the Principal Investigator of NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP). Education Bennett received his B.S. from University of Maryland, College Park in physics and astronomy cum laude with High Honors in astronomy, which is part of the University of Maryland College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences. He earned a Ph.D. in Physics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1984. Career Bennett was at the Carnegie Institution of Washington's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism during the summers from 1976 to 1978. Prior to 2005, Bennett was a Senior Scientist for Experimental Cosmology, Goddard Senior Fellow, and Infrared Astrophysics Branch Head at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Before leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Brunswick, New Jersey
New Brunswick is a city (New Jersey), city in and the county seat of Middlesex County, New Jersey, Middlesex County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey.New Jersey County Map , New Jersey Department of State. Accessed July 10, 2017. A regional commercial hub for Central Jersey, Central New Jersey, the city is both a college town (the main campus of Rutgers University, the state's largest university) and a commuter town for residents commuting to New York City within the New York metropolitan area. New Brunswick is on the Northeast Corridor, Northeast Corridor rail line, southwest of New York City. The city is located on the southern banks of the Raritan River in the heart of the Raritan Valley Region. As of the 2020 United States census, the city's population was 55,266, an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. It publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. It is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021, it is led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the APS was to hold scientific m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
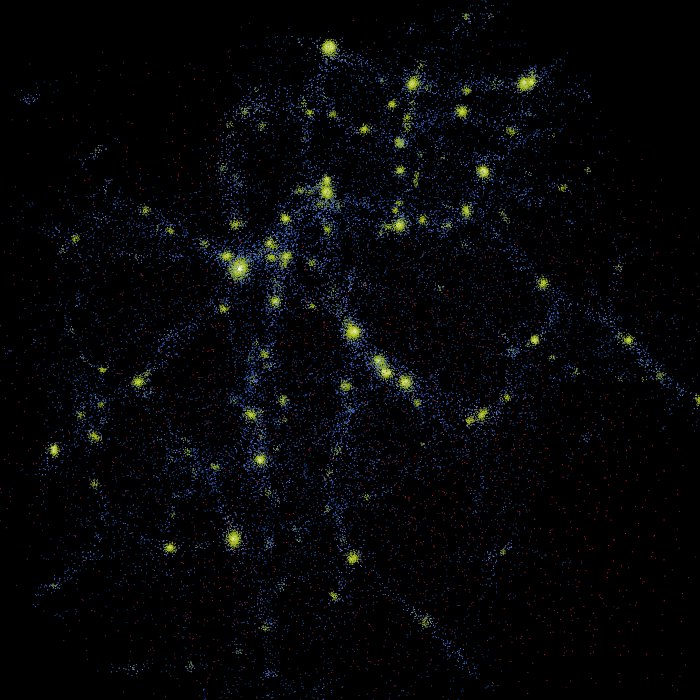
Structure Formation
In physical cosmology, structure formation describes the creation of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and larger structures starting from small fluctuations in mass density resulting from processes that created matter. The universe, as is now known from observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation, began in a hot, dense, nearly uniform state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. However, looking at the night sky today, structures on all scales can be seen, from stars and planets to galaxies. On even larger scales, galaxy clusters and sheet-like structures of galaxies are separated by enormous voids containing few galaxies. Structure formation models gravitational instability of small ripples in mass density to predict these shapes, confirming the consistency of the physical model. The modern Lambda-CDM model is successful at predicting the observed large-scale distribution of galaxies, clusters and voids; but on the scale of individual galaxies there are many complicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
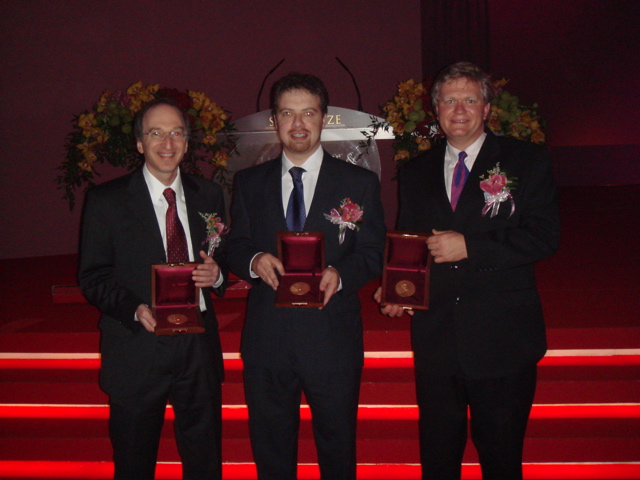
Gruber Cosmology Prize
The Gruber Prize in Cosmology, established in 2000, is one of three prestigious international awards worth US$500,000 awarded by the Gruber Foundation, a non-profit organization based at Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut. Since 2001, the Gruber Prize in Cosmology has been co-sponsored by the International Astronomical Union. Recipients are selected by a panel from nominations that are received from around the world. The Gruber Foundation Cosmology Prize honors a leading cosmologist, astronomer, astrophysicist or scientific philosopher for theoretical, analytical or conceptual discoveries leading to fundamental advances in the field. Recipients *2000 Allan Sandage and Philip James E. Peebles *2001 Lord Martin Rees *2002 Vera Rubin *2003 Rashid Sunyaev director at the Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik *2004 Alan Guth and Andrei Linde *2005 James E. Gunn principal designer of the Hubble Space Telescope *2006 John Mather (co-recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Spergel
David Nathaniel Spergel is an American theoretical astrophysicist and the Emeritus Charles A. Young Professor of Astronomy on the Class of 1897 Foundation at Princeton University. Since 2021, he has been the President of the Simons Foundation. He is known for his work on the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) project. In 2022, Spergel accepted the chair of NASA's UAP independent study team. Early life and education Spergel was born to a Jewish family in Rochester, New York. His father, Martin Spergel, was also a physicist and a professor at York College, City University of New York; he died in 2021. His mother was a high school home-economics teacher. The junior Spergel attended John Glenn High School in Huntington, New York. He has a brother and a sister. He considered his father, who had "a really satisfying career as a college teacher" a role model, especially the aspect of his father's work in mentoring students who were "first in their family" to attend co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman Page
Lyman Alexander Page, Jr. (born September 24, 1957) is the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor of Physics at Princeton University. He is an expert in observational cosmology and one of the original co-investigators for the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) project that made precise observations of the electromagnetic radiation from the Big Bang, known as cosmic microwave background radiation. Early life and education Page was born in San Francisco in 1957, and moved through Virginia and New Hampshire with his parents, eventually settling in Maine. His father was a pediatrician and his mother an artist. He has a younger brother and sister. He became interested in physics at Bowdoin College, Brunswick, Maine, where he did his undergraduate studies, after a course taught by Elroy O. LaCasce. He worked on the Mach’s principle for a course project and was drawn to cosmology. Page graduated with a BA in Physics in 1978. Page then became a research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaw Prize
The Shaw Prize is a set of three annual awards presented by the Shaw Prize Foundation in the fields of astronomy, medicine and life sciences, and mathematical sciences. Established in 2002 in Hong Kong, by Hong Kong entertainment mogul and philanthropist Run Run Shaw (邵逸夫), the awards honour "individuals who are currently active in their respective fields and who have recently achieved distinguished and significant advances, who have made outstanding contributions in academic and scientific research or applications, or who in other domains have achieved excellence." The prize has been described as the "Nobel of the East". Award The prize consists of three awards in the fields of astronomy, life science and medicine, and mathematical sciences; it is not awarded posthumously. Nominations are submitted by invited individuals beginning each year in September. Winners are announced in the summer and receive the award at a ceremony in early autumn. Each award consists of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvey Prize
The Harvey Prize is an annual Israeli award for breakthroughs in science and technology, as well as contributions to peace in the Middle East granted by the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, Technion in Haifa. The prize has become a "Nobel Prize, Nobel predictor" over the years, as around 30% of its recipients have become Nobel prize winners. It is the most prestigious award bestowed upon by the Technion. History The prize is named for industrialist and inventor Leo Harvey. Two prizes of $75,000 each are awarded each year. Candidates are submitted by past recipients, Technion Senate members and presidents of recognized institutions of higher learning and research in Israel and abroad. Generally, recipients of the Nobel Prize, Nobel or Wolf Prizes are not eligible for the Harvey Prize, unless the accomplishments cited in the nomination represent new or different work. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comstock Prize In Physics
The Comstock Prize in Physics is awarded by the U.S. National Academy of Sciences "for recent innovative discovery or investigation in electricity, magnetism, or radiant energy, broadly interpreted." Honorees must be residents of North America. Named after Cyrus B. Comstock, it has been awarded about every five years since 1913. List of Comstock Prize winners See also * List of physics awards * Prizes named after people This is a list of awards that are named after people. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P R S T U–V W Y Z See also * Lists of awards * List of eponyms * List of awards named after governo ... References {{National Academy of Sciences, state= collapsed Awards established in 1913 Physics awards Awards of the United States National Academy of Sciences 1913 establishments in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Medal
The Henry Draper Medal is awarded every 4 years by the United States National Academy of Sciences "for investigations in astronomical physics". Named after Henry Draper, the medal is awarded with a gift of USD $15,000. The medal was established under the Draper Fund by his widow, Anna Draper, in honor of her husband, and was first awarded in 1886 to Samuel Pierpont Langley "for numerous investigations of a high order of merit in solar physics, and especially in the domain of radiant energy". It has since been awarded 45 times. The medal has been awarded to multiple individuals in the same year: in 1977 it was awarded to Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson "for their discovery of the cosmic microwave radiation (a remnant of the very early universe), and their leading role in the discovery of interstellar molecules"; in 1989 to Riccardo Giovanelli and Martha P. Haynes "for the first three-dimensional view of some of the remarkable large-scale filamentary structures of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Membership in the academy is achieved through a nominating petition, review, and election process. The academy's quarterly journal, '' Dædalus'', is published by the MIT Press on behalf of the academy, and has been open-access since January 2021. The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research. Laurie L. Patton has served as President of the Academy since January 2025. History The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people." The sixty-tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highly Cited Researcher
Highly Cited Researchers is a list published annually by Clarivate of academic authors whose publications have received particularly high numbers of citations in academic journals indexed by ''Web of Science The Web of Science (WoS; previously known as Web of Knowledge) is a paid-access platform that provides (typically via the internet) access to multiple databases that provide reference and citation data from academic journals, conference proceedi ...''. These constitute approximately of all scientific researchers. History The list has been published yearly since 2001. In 2016, Clarivate sent a congratulatory email to many researchers who had not actually received the designation. It was not disclosed how many researchers the congratulations were erroneously sent to. Over 1,000 researchers were excluded from the 2023 list in total, largely for unethical citation practices and other examples of poor academic integrity. Specifically, researchers affiliated with Saudi A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |