|
Charles Claude Guthrie
} Charles Claude Guthrie (September 26, 1880 – June 16, 1963) was an American physiologist. Early life and education He was born at Gilmore, Missouri. He graduated (M.D.) from the University of Missouri in 1901 and ( Ph.D.) from the University of Chicago in 1908. Career Guthrie taught physiology while engaged in advanced studies, and was professor of physiology and pharmacology at Washington University in 1906–1909 and at the University of Pittsburgh after 1909. He was author of ''Blood-Vessel Surgery and its Applications'' (1912) and of contributions on blood reactions and alterations, resuscitation, cerebral and other anæmias, isolated and ungrafted tissues, and sutures and anastomosis of blood vessels. Guthrie collaborated in his work on vascular surgery with French physician Alexis Carrel, who won the 1912 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Arguments were made that the primary credit for this work should have gone to Guthrie rather than Carrel. However, Guthrie's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilmore, Missouri
Gilmore is an unincorporated community in St. Charles County, in the U.S. state of Missouri. History A post office called Gilmore was established in 1884, and remained in operation until 1959. Gilmore was named for Thomas Gilmore, an early settler who was one of a company to march against the British at Rock Island and who was killed by Indians. Notable people * Charles Claude Guthrie } Charles Claude Guthrie (September 26, 1880 – June 16, 1963) was an American physiologist. Early life and education He was born at Gilmore, Missouri. He graduated (M.D.) from the University of Missouri in 1901 and ( Ph.D.) from the Universit ... (1880–1963), physiologist and surgeon References Unincorporated communities in Missouri Unincorporated communities in St. Charles County, Missouri {{StCharlesCountyMO-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
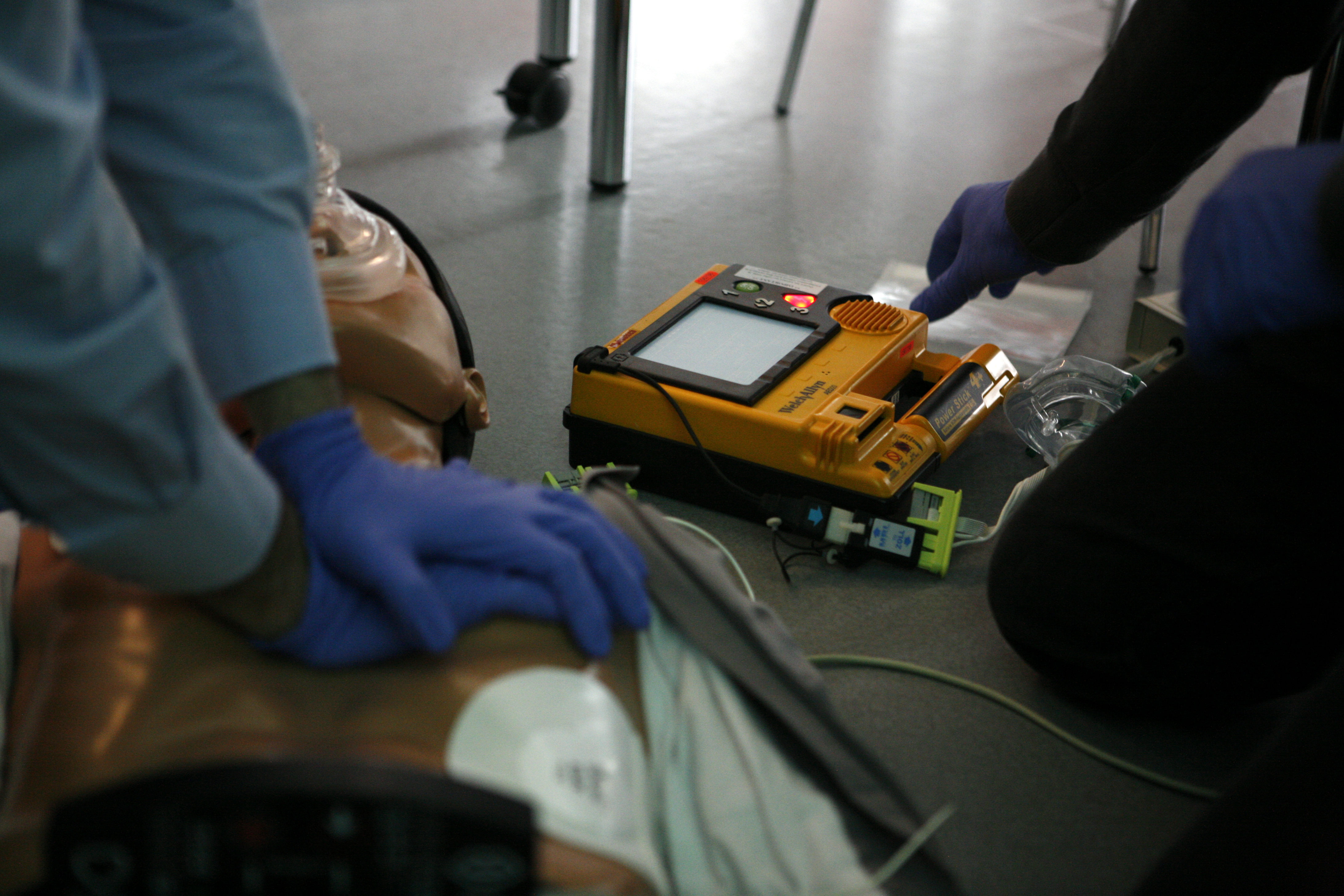
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure used during Cardiac arrest, cardiac or Respiratory arrest, respiratory arrest that involves chest compressions, often combined with artificial ventilation, to preserve brain function and maintain circulation until spontaneous breathing and heartbeat can be restored. It is indication (medicine), recommended for those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations. CPR involves chest compressions for adults between and deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations emphasize early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1880 Births
Events January *January 27 – Thomas Edison is granted a patent for the incandescent light bulb. Edison filed for a US patent for an electric lamp using "a carbon filament or strip coiled and connected ... to platina contact wires." granted 27 January 1880 Although the patent described several ways of creating the carbon filament ,including using "cotton and linen thread, wood splints, papers coiled in various ways," Edison and his team later discovered that a carbonized bamboo filament could last more than 1200 hours. * January **The international White slave trade affair scandal in Brussels is exposed and attracts international infamy. **The Gokstad ship is found in Norway, the first Viking ship burial to be excavated. February * February 2 ** The first electric streetlight is installed in Wabash, Indiana. ** The first successful shipment of frozen mutton from Australia arrives in London, aboard the SS ''Strathleven''. * February 4 – The Black Donnelly Massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From St
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Missouri Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physiologists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Transplant
A head transplant or full body transplant is an experimental surgical operation involving the grafting of one organism's head onto the body of another. In many experiments, the recipient's head has not been removed, but in others it has been. Experimentation in animals began in the early 1900s. , no lasting successes have been achieved. Medical challenges There are three main technical challenges. As with any organ transplant, managing the immune response to avoid transplant rejection is necessary. Also, the brain is highly dependent on continuous flow of blood to provide oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products, with damage setting in quickly at normal temperatures when blood flow is cut off. Finally, managing the nervous systems in both the body and the head is essential, in several ways. The autonomic nervous system controls essential functions like breathing and the heart beating and is governed largely by the brain stem; if the recipient body's head is removed this c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Medicine or Physiology, Chemistry, Literature, and Peace. The Nobel Prize is presented annually on the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death, 10 December. As of 2024, 115 Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to 229 laureates, 216 men and 13 women. The first one was awarded in 1901 to the German physiologist, Emil von Behring, for his work on serum therapy and the development of a vaccine against diphtheria. The first woman to receive the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Gerty Cori, received it in 1947 for her role in elucida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Surgery
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general surgery, general and cardiac surgery, cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular (minimally invasive) techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomosis
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale in a fetus' heart) or abnormal (such as the patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Greek ἀναστόμωσις, anastomosis, "outlet, opening", Greek ana- "up, on, upon", stoma "mouth" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |