|
Chaetodipterus
''Chaetodipterus'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ephippidae, the spadefishes. These fishes are found in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific Oceans. Taxonomy ''Chaetodipterus'' was first proposed as a monospecific genus in 1802 by the French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède with ''Chaetodon plumieri'', a species described by Marcus Elieser Bloch on 1787 from Jamaica, as its only species. ''Chaetodon plumieri'' is a synonym of ''Chaetodipterus faber''. This genus is classified within the family Ephippidae which is in the order Moroniformes. Etymology ''Chaetodipterus'' is a combination of ''di'', meaning "two", and ''pterus'', meaning "fin", prefixed with ''Chaetodon''. This is a reference to the original genus the type species was assigned to but with a split dorsal fin. Species ''Chaetodipterus'' contains three recognized species: *'' Chaetodipterus faber'' (Broussonet, 1782) (Atlantic spadefish) *'' Chaetodipterus lippei'' Steindachner, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Spadefish
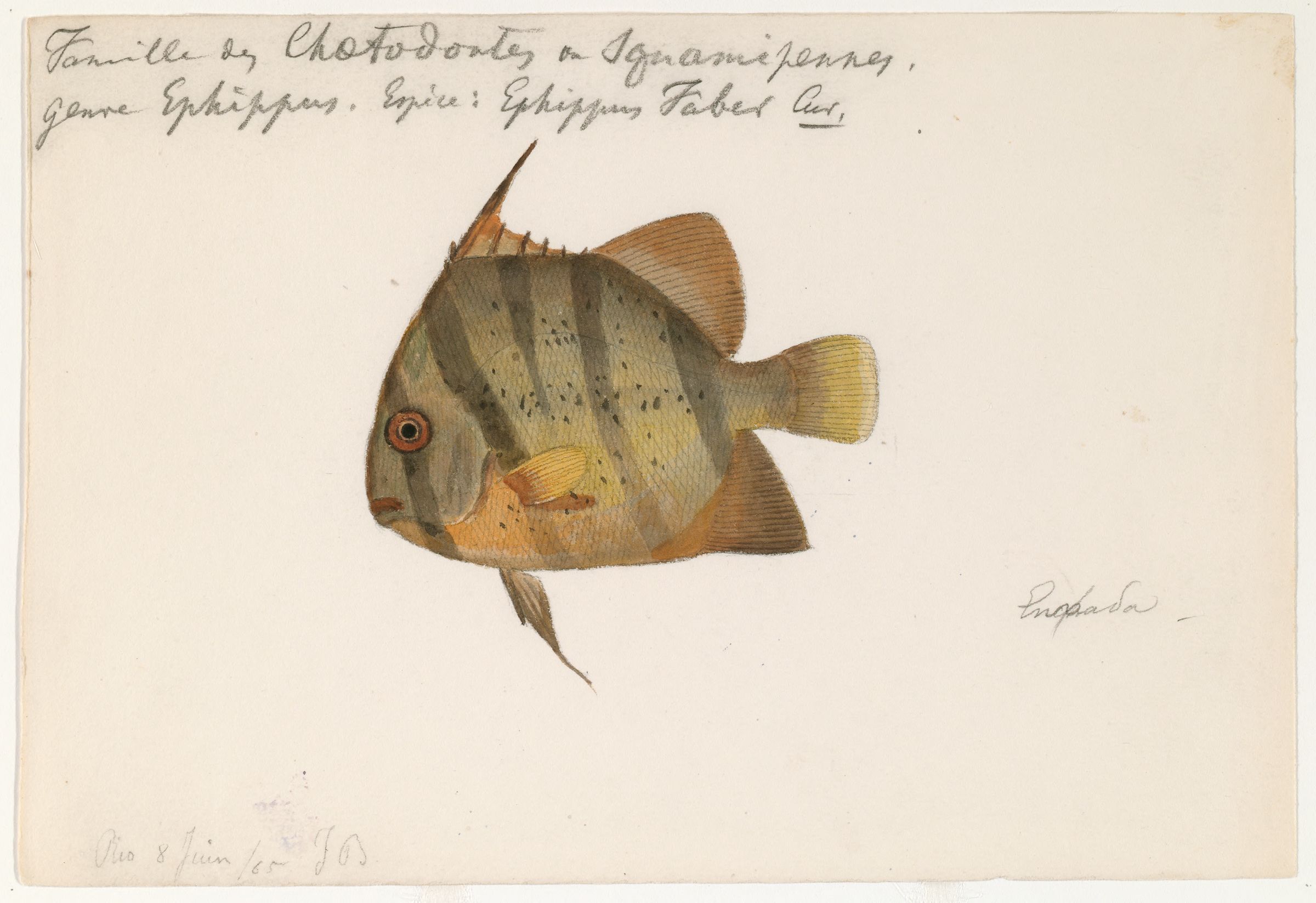
The Atlantic spadefish (''Chaetodipterus faber'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the Family (biology), family Ephippidae, the spadefishes. It is the symbol of the North Carolina Aquariums. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name is derived from the Greek word "chaíti" meaning "mane" and "dipteros" meaning "with two fins." The Atlantic spadefish belongs to the genus ''Chaetodipterus'', which includes two other species: the West African spadefish (''Chaetodipterus lippei'') and the Pacific spadefish (''Chaetodipterus zonatus''). The genus ''Chaetodipterus'' belongs to the family Ephippidae, which includes spadefish and batfish. ''Chaetodipterus faber'' is known by numerous other colloquial names, including angelfish, white angelfish, threetailed porgy, ocean cobbler, and moonfish. Description The disk-shaped body is very deep and compressed, and the snout is blunt. There are 9 dorsal spines and 21–24 soft dorsal rays, and there are 3 anal spines an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetodipterus Faber
The Atlantic spadefish (''Chaetodipterus faber'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ephippidae, the spadefishes. It is the symbol of the North Carolina Aquariums. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name is derived from the Greek word "chaíti" meaning "mane" and "dipteros" meaning "with two fins." The Atlantic spadefish belongs to the genus ''Chaetodipterus'', which includes two other species: the West African spadefish (''Chaetodipterus lippei'') and the Pacific spadefish (''Chaetodipterus zonatus''). The genus ''Chaetodipterus'' belongs to the family Ephippidae, which includes spadefish and batfish. ''Chaetodipterus faber'' is known by numerous other colloquial names, including angelfish, white angelfish, threetailed porgy, ocean cobbler, and moonfish. Description The disk-shaped body is very deep and compressed, and the snout is blunt. There are 9 dorsal spines and 21–24 soft dorsal rays, and there are 3 anal spines and 17–19 anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetodipterus
''Chaetodipterus'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ephippidae, the spadefishes. These fishes are found in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific Oceans. Taxonomy ''Chaetodipterus'' was first proposed as a monospecific genus in 1802 by the French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède with ''Chaetodon plumieri'', a species described by Marcus Elieser Bloch on 1787 from Jamaica, as its only species. ''Chaetodon plumieri'' is a synonym of ''Chaetodipterus faber''. This genus is classified within the family Ephippidae which is in the order Moroniformes. Etymology ''Chaetodipterus'' is a combination of ''di'', meaning "two", and ''pterus'', meaning "fin", prefixed with ''Chaetodon''. This is a reference to the original genus the type species was assigned to but with a split dorsal fin. Species ''Chaetodipterus'' contains three recognized species: *'' Chaetodipterus faber'' (Broussonet, 1782) (Atlantic spadefish) *'' Chaetodipterus lippei'' Steindachner, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetodipterus Zonatus
The Pacific spadefish (''Chaetodipterus zonatus'') is a species of fish of the family Ephippidae. It is native to the eastern Pacific, from San Diego, California to Peru, including the Galápagos Islands where it is known as Chambo. Appearance ''C. zonatus'' has a very deep, compressed body with a blunt snout and a sloping, slightly concave profile. It has a small mouth with the posterior end of the jaw not passing the front of the eye. The maximum recorded size was 65 cm but more commonly reach a length of 25 cm. They have six black bars on their head and the side of their body, although in large adults these can be difficult to see. Their dorsal fin is large and set well back on their body, the anal fin is opposite and of a similar shape; both have long spines. The pectoral and pelvic fins are small and the caudal fin is large and lunate. All the fins are black in colour. Habitat ''C. zonatus'' is found in subtropical inshore seas, in areas with coral reefs or sand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetodipterus Lippei
The West African spadefish (''Chaetodipterus lippei'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ephippidae, the spadefishes. This species is found over sandy and muddy bottoms at depths of in the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Senegal to Angola, including Cape Verde. The West African spadefish reaches a maximum total length of , although is more typical. This species was first formally described in 1895 by the Austrian ichthyologist Franz Steindachner with its type locality given as Freetown in Liberia. Its specific name honours a Dr Lippe who collected the type Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values used for computations. * File type * TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file. * ... while on a voyage on the '' SM Helgoland''. References {{taxonbar, from=Q5225983 West African spadefish Fish described in 1895 Taxa named by Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephippidae
Ephippidae is a family of percomorph fishes, the spadefishes, in the order Moroniformes. These fishes are found in the tropical and temperate oceans of the world, except for the central Pacific. Taxonomy Ephippidae was first proposed as a family in 1859 by the Dutch herpetologist and ichthyologist Pieter Bleeker. The 5th edition of the ''Fishes of the World'' classifies this family in the order Moroniformes with the Moronidae and Drepaneidae. Other authorities place this family alongside the Drepaneidae in the order Ephippiformes with the Moronidae classified as ''incertae sedis'' in the series Eupercaria. Other authorities classify all three families in the Moroniformes ''sensu'' ''Fishes of the World'' in the Acanthuriformes. Genera Ephippidae contains the following genera, 8 extant and 3 extinct ( means extinct): The extinct genus '' Exellia'' is classified within the Ephippidae by some authorities, other authorities place it in the family Exellidae. Characteristics Ephi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Elieser Bloch
Marcus Elieser Bloch (1723–1799) was a German physician and naturalist who is best known for his contribution to ichthyology through his multi-volume catalog of plates illustrating the fishes of the world. Brought up in a Hebrew-speaking Jewish family, he learned German and Latin and studied anatomy before settling in Berlin as a physician. He amassed a large natural history collection, particularly of fish specimens. He is generally considered one of the most important ichthyologists of the 18th century, and wrote many papers on natural history, comparative anatomy, and physiology. Life Bloch was born at Ansbach in 1723 where his father was a Torah writer and his mother owned a small shop. Educated at home in Hebrew literature he became a private tutor in Hamburg for a Jewish surgeon. Here he learned German, Latin and anatomy. He then studied medicine in Berlin and received a doctorate in 1762 from Frankfort on the Oder with a treatise on skin disorders. He then became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopatric
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from each other to an extent that prevents or interferes with gene flow. Various geographic changes can arise such as the movement of continents, and the formation of mountains, islands, bodies of water, or glaciers. Human activity such as agriculture or developments can also change the distribution of species populations. These factors can substantially alter a region's geography, resulting in the separation of a species population into isolated subpopulations. The vicariant populations then undergo genetic changes as they become subjected to different selective pressures, experience genetic drift, and accumulate different mutations in the separated populations' gene pools. The barriers prevent the exchange of genetic information between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
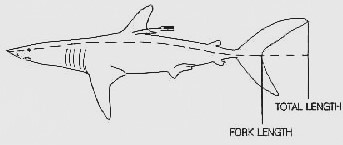
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines play an important role in schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. Early in the evolution of fish, some of the sensory organs of the lateral line were modified to function as the electroreceptors called ampullae of Lorenzini. The lateral line system is ancient and basal to the vertebrate clade, as it is found in fishes that diverged over 400 million years ago. Function The lateral line system allows the detection of movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the water surrounding an animal. It plays an essential role in orientation, predation, and fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are predominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods, which evolved from lobe-finned fish during the Middle Devonian. Structure and function Structure In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two endochondrally-derived bony girdles attached to bony radials. Dermal fin rays ( lepidotrichia) are positioned distally from the radials. There are three pairs of muscles each on the dorsal and ventral side of the pelvic fin girdle that abduct and adduct the fin from the body. Pelvic fin structures can be extremely specialized in actinopterygians. Gobiids and lumpsuckers modify their pelvic fins into a sucker disk that allow them to adhere to the substrate or climb structures, such as waterfalls. In priapiumfish, males have modified their pelvic structures into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |